
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
fischer esterification:
5.4mL of isopentyl alcohol, molar mass 88.15g/mol:
8.5mL of acetic acid, molar mass 60.05 g/mol:
Experimental final product(Isopentyl acetate) I got: 3.10g.
1.Calculate for theretical yield.
2.Percentage yield
3. % recovery.
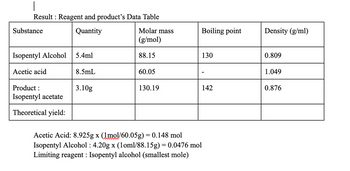
Transcribed Image Text:|
Result : Reagent and product's Data Table
Quantity
Substance
Isopentyl Alcohol 5.4ml
Acetic acid
Product:
Isopentyl acetate
Theoretical yield:
8.5mL
3.10g
Molar mass
(g/mol)
88.15
60.05
130.19
Boiling point
Acetic Acid: 8.925g x (1mol/60.05g) = 0.148 mol
Isopentyl Alcohol: 4.20g x (1oml/88.15g) = 0.0476 mol
Limiting reagent: Isopentyl alcohol (smallest mole)
130
142
Density (g/ml)
0.809
1.049
0.876
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please don't provide handwritten solution....arrow_forwardThis series demonstrates a drop-by-drop addition of 0.5 M barium chloride solution (???? ) to 0.5 M sodium carbonate solution (?? ?? 1. 1. What observations indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred? 2. Break up the reactants into ions. Switch the cations. Use the “criss-cross” method to get the balanced formulas for the products. Write the balanced molecular equation for this reaction, including phase labels. 3. Write the complete ionic equation for this reaction. 4. Write the net ionic equation for this reaction. 5. What is the precipitate?arrow_forward3arrow_forward
- Percent Yield of product 71,2% Melting point of product 7/.5°C IV. Predict the products of the following reactions NO2 N. HNO H,SO осн, HNO, H,SO, CN HNO, H,SO4 NOR C(CH3)3 HNO, C(CHs)3 H,SO4 Č(CH3)s cièits)s 27arrow_forwardWhat would the % yield of ester be if the reaction were simply allowed to equilibrate (i.e. no products are removed)? C3H7OH+C2H5COOH=C6H12O2+H2O Percent yield of ester was 71.6% weight of product= 20.7868g 19.0mL (0.25mol) of n- propanol 18.5 mL (0.25 mol) of propionic acid At room temperature, the equilibrium constant, Keq is approximately 3.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? -NHCH, H,0, H heat но NHCH, NHCH, A. В. CH,NH,"cr CH, CH,NH,"cr D. CH,NH, "cr O A OB O D MacBook Pro G Search or type URL $ & * 4 6. 7 8. E T. Y U H Karrow_forward
- If the Kc for the following reaction A is 5.0 at what is the Kc for reaction B?Show work.A. Cl2 (g) + CO (g) ↔ COCl2 (g)B. 3 COCl2 (g) ↔ 3 Cl2 (g) + 3 CO (garrow_forward6. Complete the following reactions by filling what is left out; either the reactants, starting material, or the major product. a. b. C. CI 1. Excess NaNH, 2. H₂O 3.HgSO4 4. NaBH₁, NaOH 1.NAOMe 2.03 3. Zn, H* Coquearrow_forwardKk.284.arrow_forward
- Using the appropriate bond energies, calculate the heat of reaction AĦ for the following reaction: Omar bin V CI CI do Data CI-C- CI + H-H- CI-C-CI + H-CI [+] Molal freezing point depression and boiling point elevation constants For example, the Kf and K for water. CI H. [-] Bond energies You can find a table of bond energies by using the Data button on the ALEKS toolbar. energy energy (k)/mol) bond (k)/mol) energy (kJ/mol) Round your answer to the nearest k/mol. bond bond Note: For clarity, all lone pairs have been omitted from the molecular structures. H-H 436 O-H 497 F-F 159 H-F 570 O-F 215 F-a 261 H-CI 431 O-CI 234 F-Br 280 kJ H-Br 366 O-Br 210 F-I 272 mol H-I 298 0-1 213 C-a 243 H-C 413 O-C 385 Cl-Br 219 H-O 497 O=C 532 C-I 211 H-N 391 1077 Br-Br 194 H-P 351 0-0 210 Br-I 179 H-S 381 O=0 498 I-1 152 O-N 206 O=N 631 O=S 551 energy (k/mol) energy (k)/mol) bond energy (kJ/mol) bond bond S-H 381 N-H 391 C-H 413 392 N-C 356 S-F C-F 460 272 S-d N=C 615 C-CI 350 S-Br 230 NEC 749 C-Br 293…arrow_forwardCalculate the weight of salicylic acid (FW: 138.12) needed to generate 6.00 g of aspirin (FW: 180.16), given that the recrystallization has 78% yield. how many moles of aspirin was produced? a. 0.0427 moles b. 0.0347 moles c. 0.0278 moles d. 0.0333 molesarrow_forward1. For the reaction: ____C2H5COOH + ____O2 --------> _____CO2 + _____H2O A. Calculate the number of moles of H2O produced from 0.750 mole C2H5COOH reacting with sufficient O2. SET-UP: Answer:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY