
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
find the
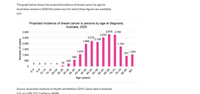
Transcribed Image Text:The graph illustrates the projected incidence of breast cancer by age for Australian women in 2020. It is based on the latest available data.
**Graph: Projected Incidence of Breast Cancer by Age at Diagnosis, Australia, 2020**
- **Age Groups and Number of Cases:**
- Age 0–4: 0 cases
- Age 5–9: 0 cases
- Age 10–14: 0 cases
- Age 15–19: 4 cases
- Age 20–24: 9 cases
- Age 25–29: 79 cases
- Age 30–34: 255 cases
- Age 35–39: 580 cases
- Age 40–44: 1,070 cases
- Age 45–49: 1,969 cases
- Age 50–54: 2,215 cases
- Age 55–59: 2,139 cases
- Age 60–64: 2,532 cases
- Age 65–69: 2,816 cases
- Age 70–74: 2,782 cases
- Age 75–79: 1,742 cases
- Age 80–84: 931 cases
- Age 85+: 1,053 cases
The graph reveals that breast cancer incidence increases significantly with age, peaking in the 65–69 age group, before declining in older age groups.
**Source:**
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2019. *Cancer data in Australia.* Cat. no. CAN 122. Canberra: AIHW.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
- If the distribution is divided into two parts and the two sides are a mirror image of each other, then it is known as symmetric distribution.
- There is only one peak (a highest point) in the histogram and is roughly in the middle therefore, it is roughly symmetric.
- Mean refers to the average value of the data set under consideration.
- It is obtained by the formula , where denotes the sum of all data points and (n) denotes the total number of observations.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Help me ASAParrow_forwardCreate a histogram for each of your variables using the same classes that you used for your frequency table. Discuss the distribution of each histogram. Based on the shape of each histogram, would the mean or median be a better measure of center for each variable? Explain.The graphs go up by 2.5. male stats: mean-18.1667 standard deviation-2.7796 N-183 female stats: mean-20.8973 standard deviation-3.3859 N-183arrow_forwardThe prices vary depending on the condition of the radio. $210, $210, $320, $200, $300, $10, $340, $300, $245, $325, $700, $250, $240, $200 a. Find the mean of the radio prices. Round to the nearest cent.arrow_forward
- The scores of 10 golfers were 73; 71; 78; 72; 67; 76; 67; 75; 73; 75. Calculate the range of the dataset.arrow_forwardThe ages in years of a random sample of shoppers at a gamming store are shown. 12, 17, 23, 13, 20, 16, 20, 18, 13, 18. Find the range, mean, variance and standard deviation.arrow_forwardState whether one would expect the data set described below to be normally distributed. Explain why or why not. The genders of 1,000 randomly selected adultsarrow_forward
- Given the set of 3 data points 82, ____, _____ Find the 2 missing terms if the median is 84. Once you find one answer, explain how you found your answer and if it is possible to have more than one answer. Please give details about the other possible data pointsarrow_forwardA simple data set has been provided to practice the basics of finding measures of variation. 2, 4, 8, 8 For the data set, determine the range and the sample standard deviation.arrow_forwardEarnings of Nonliving Celebrities Forbes magazine prints an annual Top-Earning Nonliving Celebrities list (based on royalties and estate earnings). Find the mean, median, mode, and midrange for the data. Comment on the skewness. Figures represent millions of dollars. Rodgers & Hammerstein 235 John Lennon 15 Michael Jackson 90 Dr. Seuss 15 Elvis Presley 55 Albert Einstein 10 JRR Tolkien 50 Michael Crichton 9. Charles Schulz 35 Jimi Hendrix 8 Send data to Excel Part: 0 / 5 Part 1 of 5 Find the mean. Rounding rule for the mean: round to one more decimal place than the data as needed. Mean:arrow_forward
- Find the median?arrow_forwardWhat is the mean of data setarrow_forwardRun the descriptive statistics for hrs/week of exercise. Include the mean, median, quartiles, min, max, standard deviation and IQR. First do this for hrs/week of exercise overall. Copy and paste the values below. Then redo this splitting up the data by sex. Copy and paste that below too. What similarities and/or differences do you see? Age Gender Height Arm Length Number Siblings Birth Order Handedness Number Classes Number Credits Hrs. Exercise Athlete at Broome Hrs. TV Award Pulse Number Piercings Facebook Friends Followers on Instagram Tattoo Division Local section 18 f 63 27.5 2 3 r 4 14 1.5 n 3 NP 74 2 82 72 n HS y 4 19 m 74 31.5 4 5 r 4 11 5 n 1.5 O 0 600 700 n STEM y 4 17 f 66 29.2 2 2 l 6 15 5 y 21 NP 64 2 1801 1370 n HS y 4 18 f 66 30 5 5 r 4 12 30 n 15 NP 91 1…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman