Question
thumb_up100%
Find all image charges for the following configurations of single point charge and infinite conducting planes. The point charge always bisects the angle:
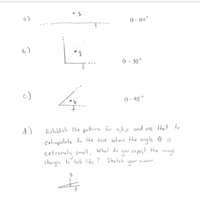
Transcribed Image Text:a)
O = 180°
(9
O = 90°
4.
c)
O = 45°
d)
Establish the patern for ab,c and use that to
extrapolate to the cose where the angle e is
expect the image
extremely small.
What do
you
chorges to look like ? Sketch
answen.
your
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider an infinite line of charge with a constant charge density of À lying on the z-axis. Using Coulomb's law to write the equation of dĎ at any point (xo, 0, 0). Write all vectors in vector notation clearly also draw the figure showing all the important vectors as you saw in the video lectures as well as in our class lectures.arrow_forwardQuestion 6 := Homework. Unanswered Multiple Plates -- Two infinite, uniformly charged plates have the same magnitude of surface charge density O. They are orientated in the illustration looking down the planes. Please note that is a positive value. Place your target in a region (inside a blue circle) of net electric field that points to the RIGHT. To do this, you will have to add two constant electric field vectors produced by the Then select the region where the net field points to the RIGHT. Figure [6.24]. planes for each region. 00 -0 Undo Delete selected Remove All o O Targets placed: 0/1 You can place up to 1 targetsarrow_forwardPlease write all details and properties. I would much appreciate it a lot. Any property or remark, regardless of how insignificant, please include in the answer. Thank you very much.arrow_forward
- In the space between two parallel planes separated by a distance 2d some charge is uniformly distributed with density po. Calculate the electric field in all space as a function of x 2darrow_forwardShown in the figure below is a hollow disk of charge. The disk carries a charge density ? and has an inner radius R1 and an outer radius R2. You are to calculate the magnitude of the field at the point P which is a distance z above the plane of the disk. Determine the area element, dA = Determine the charge element, dQ = Determine the distance, s = Determine the so-called, cos(?) = Determine the integrand, ∬ Determine the lower bound of the ? integral: Determine the upper bound of the ? integral: Determine the lower bound of the r integral: Determine the upper bound of the r integral: Determine the final result of the integration: NOTE: Please use k in your answers. Please do not use ?0.arrow_forwardTwo spherical cavities, of radii a and b, are hollowed out from the interior of a (neutral) conducting sphere of radius R (see attatched image). At the center of each cavity a point charge is placed. Call these charges qa and qb. What is the field outside the conductor and what is the field within each cavity?arrow_forward
- Consider the following image, point P is located on the x axis with coordinates (X, 0). Two positive charged particles are on the y-axis, ad and b apart respectively from the point of origin (0, 0). Draw each component of the electric field at point P?arrow_forwardThe uniformly charged straight wire in the figure has the length I, Find the field at point P, a perpendicular distance x from 0, if lambda (λ) is the charge per unit length. Express your answer in terms of , I, x, and appropriate constants. y 0 \r² = (x^² + y²) ² X P dEy dE dEarrow_forwardA negative point charge q with a uniform electric field is subject to a force that is exerted on it in the -y direction as shown. What would be the direction of the electric field?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios