
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
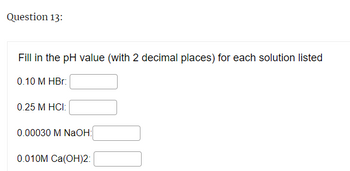
Transcribed Image Text:Question 13:
Fill in the pH value (with 2 decimal places) for each solution listed
0.10 M HBr:
0.25 M HCI:
0.00030 M NaOH:
0.010M Ca(OH)2:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which solution below has the highest concentration of hydroxide ions? pH = 8.2 pH = 5.6 pH = 3.7 pH = 11.0 pH = 11arrow_forwardCalculate the hydroxide ion concentration of an aqueous solution of 0.480 M hydrofluoric acid. (Assume that K₂ (HF) = 7.2 × 10−4.) [OH] =| Marrow_forwardEach row of the table below describes an aqueous solution at about 25 °C. Complete the table. That is, fill in any missing entries in the second and third columns. Be sure each entry you write includes the correct number of significant digits. [1,0] H,O solution pH x10 A 1.2 X 10 mol/L mol/L 10.46 0.16 mol/Larrow_forward
- ch1arrow_forwardDetermine the [OH−], pH, and pOH of a solution with an [H+] of 2.4×10−13 M at 25 °C. [OH−]= pH= pOH= Determine the [H+], pH, and pOH of a solution with an [OH−] of 2.1×10−9 M at 25 °C. [H+]= pH= pOH= Determine the [H+], [OH−], and pOH of a solution with a pH of 2.20 at 25 °C. [H+]= [OH−]= pOH= Determine the [H+], [OH−], and pH of a solution with a pOH of 4.50 at 25 °C. [H+]= [OH−]= pH=arrow_forwardEach row of the table below describes an aqueous solution at about 25 °C. Complete the table. That is, fill in any missing entries in the second and third columns. Round your entries for [H₂O*] to 2 significant digits, and your entries for pH to 2 decimal places. solution A B с [H₂O*] -6 6.5 × 10 mol/L mol/L 8 6.6 X 10 mol/L pH 0 9.24 0 x10 X Śarrow_forward
- What is the [H3O-] and [OH-] ion concentration respectively in a solution that contains 0.155 M HNO3? 0.200 M, 5x10^-14 M 6.45x10^-14 M, 0.155 M 0.155 M, 6.45x10^-14 M 5x10^-14 M, 0.200 Marrow_forwardUsing the graph, calculate the concentration (Molarity) of the weak acid HA.arrow_forwardEach value represents a different aqueous solution at 25 °C. Classify each solution as acidic, basic, or neutral. Incorrect Acidic pH = 4.57 pOH = 4.97 pOH = 9.52 [H+] = = 9.8 x 10-5 Basic pH = 9.45 [H+] = 5.5 x 10-¹¹ [OH-] = 4.9 × 10-¹1 [OH-] = 5.4 x 10-² Answer Bank Neutral [H+] = 1.0 x 10-7 pOH = 7.00arrow_forward
- Determine the [OH−] , pH, and pOH of a solution with a [H+] of 5.7 ×10−11 M at 25 °C. [OH−]= M pH= pOH= Determine the [H+] , pH, and pOH of a solution with an [OH−] of 0.0087 M at 25 °C. [H+]= M pH= pOH= Determine the [H+] , [OH−] , and pOH of a solution with a pH of 7.71 at 25 °C. [H+]= M [OH−]= M pOH= Determine the [H+] , [OH−] , and pH of a solution with a pOH of 10.78 at 25 °C. [H+]= M [OH−]= M pH=arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of a solution that is 0.20 M HOCI and 0.88 M KOCI. Kg = 3.5x10-8 pH =arrow_forwardA) Find [OH−][OH−] for a 0.046 MM solution of LiOHLiOH. Express the concentration to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. B) Find the pHpH of a 0.046 MM LiOHLiOH solution. Express your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY