
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Fill in the missing products for when the following molecules are reacted with various reagents.
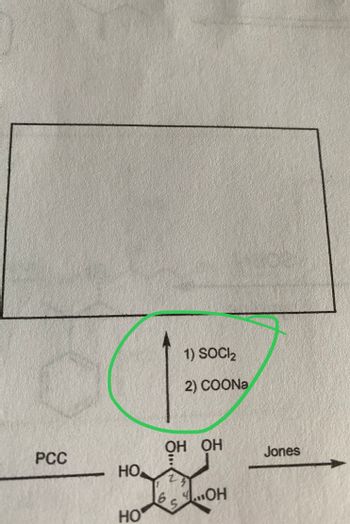
Transcribed Image Text:The image shows a chemical transformation diagram involving a hexose molecule. The structure of the hexose is labeled with carbon numbers (1 through 6) and displays hydroxyl groups (OH) attached to each carbon.
- **Reagents and Reaction Conditions:**
- An arrow pointing upwards is labeled with two reagents:
1. SOCl₂ (thionyl chloride)
2. COONa (sodium carboxylate)
- **Additional Information:**
- To the left of the hexose structure, "PCC" (pyridinium chlorochromate) is noted, often used for oxidation in organic chemistry.
- To the right of the structure, "Jones" is mentioned, referring to Jones oxidation, a method using chromium trioxide (CrO₃) in sulfuric acid, which oxidizes alcohols to carboxylic acids.
This setup likely represents a proposed synthetic pathway involving oxidation and substitution reactions to modify the hydroxyl groups on the hexose ring.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Complete these syntheses.arrow_forwardDraw the principal organic product for the reaction when 2-bromopropane is treated with lithium in diethyl ether, followed by copper(I) iodide and then 1-bromoethane. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardDraw the structure(s) of the major organic product(s) of the following reaction. or. Phyrion Ph₂ +arrow_forward
- Give the main organic product that would form after the following reaction. OMe OMe H₂O H*arrow_forwardSelect all of the compounds in the enol form of keto-enol tautomerism. он HC он H.C. H.C. H.C CH, CH, HC CH, HC a b darrow_forward6. Complete the following reactions by providing the intermediate(s) and product(s). CH3OH, Harrow_forward
- complete these reactions with reagents and intermediates.arrow_forwardDraw the structure for the major organic product of the following Wittig reaction. + Ph, P Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 0 X 0:1arrow_forward6. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? Brzarrow_forward
- Provide the reagents necessary to carry out the following transformations. Some of these may be multiple steps syntheses and may involve the use of other organic molecules. a. b. CH₂ OH Ph OHarrow_forwardComplete the following synthesis writing each step for the synthesis of the product showing all reactants and conditionsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY