
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Figure P8.29 shows a uniform
beam of mass m pivoted at
its lower end, with a horizontal
spring attached between its top
end and a vertical wall. The
beam makes an angle θ with the
horizontal. Find expressions for
(a) the distance d the spring is
stretched from equilibrium and
(b) the components of the force
exerted by the pivot on the
beam.
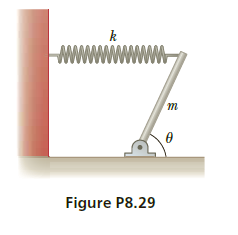
Transcribed Image Text:Figure P8.29
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two children with masses of 24 kg and 34 kg are sitting on a balanced seesaw. If the heavier child is sitting O.8 m from the center, at what distance from the center is the lighter child sitting? Your answerarrow_forwardA uniform drawbridge must be held at a 37° angle abovethe horizontal to allow ships to pass underneath. The drawbridge weighs45,000 N and is 14.0 m long. A cable is connected 3.5 m from thehinge where the bridge pivots (measured along the bridge) and pullshorizontally on the bridge to hold it in place. What is the angular speed of the drawbridge as it becomes horizontal?arrow_forwardA 500.-N uniform rectangular sign 4.00 mwide and 3.00 m high is suspended from ahorizontal, 6.00-m-long, uniform, 100.-N rodas indicated in Figure P8.25. The left end ofthe rod is supported by a hinge, and the rightend is supported by a thin cable making a30.0° angle with the vertical. (a) Find the tensionT in the cable. (b) Find the horizontaland vertical components of force exerted onthe left end of the rod by the hinge.arrow_forward
- The drawing shows an A-shaped ladder. Both sides of the ladder are equal in length. This ladder is standing on a frictionless horizontal surface, and only the crossbar (which has a negligible mass) of the " A " keeps the ladder from collapsing. The ladder is uniform and has a mass of 15.2Kg. Det k mine the tension in the crossbar of the ladder.arrow_forwardA hungry bear weighing 700. Nwalks out on a beam in an attemptto retrieve a basket of goodieshanging at the end of the beam(Fig. P8.28). The beam is uniform,weighs 200. N, and is 6.00 m long,and it is supported by a wire atan angle of θ = 60.0°. The basketweighs 80.0 N. (a) Draw a forcediagram for the beam. (b) Whenthe bear is at x = 1.00 m, find thetension in the wire supporting thebeam and the components ofthe force exerted by the wall on the left end of the beam. (c) Ifthe wire can withstand a maximum tension of 900. N, what is themaximum distance the bear can walk before the wire breaks?arrow_forwardTwo blocks, each of mass 2 kg are suspendedfrom the ends of a rigid massless rod of lengthL. The rod is held horizontally on the fulcrumand then released. The length L1 is 15 cm andthe length L2 is 85 cm. Draw the force diagram for the rod. Clearly label all forces. Write Newton’s 2nd Law equation: (for F of y) Write Newton’s 2nd Law equation: (for net torque) What is the magnitude of the linear acceleration of the block closest to the fulcrum? What is the magnitude of the linear acceleration of the block furthest from the fulcrum?arrow_forward
- A uniform beam has a length of 17.7 m and a mass of 39.6 kg. The beam is horizontal and resting (in equilibrium) on two supports. One of the supports is located 3.32 m to the right of the beam's center of mass. This support applies an upward force of 245 N to the beam. Ehat distance separates the two supports?arrow_forwardA schoolyard teeter-totter with a totallength of 6.4 m and a mass of 41 kg is pivoted at its center. A 21-kgchild sits on one end of the teeter-totter. (a) Where should a parentpush vertically downward with a force of 210 N in order to hold theteeter-totter level? (b) Where should the parent push with a force of310 N? (c) How would your answers to parts (a) and (b) change if themass of the teeter-totter were doubled? Explainarrow_forwardThe forearm of length Larm = 35.2 cm shown in the figure is positioned at an angle with respect to the upper arm, and a 5.05-kg ball is held in the hand. The total mass motal of the forearm and hand is 2.75 kg, and their center of mass is located at Le 15.0 cm from the elbow. The biceps muscle attaches to the forearm at a distance Lbiceps = 4.5 cm from the elbow. What is the magnitude of the force Fbiceps that the biceps muscle exerts on the forearm for 0 = 27"? Foiceps 451.9 Fjoint Incorrect What is the magnitude of the force Fjoint that the forearm exerts on the elbow joint for 0= 27"? 375.4 N N AIarrow_forward
- You have been hired to design a family-friendly see-saw. Your design will feature a uniform board (mass M, length L) that can be moved so that the pivot is a distance d from the center of the board. This will allow riders to achieve static equilibrium even if they are of different mass, as most people are. You have decided that each rider will be positioned so that his/her center of mass will be a distance xoffset from the end of the board when seated as shown. You have selected a child of mass m (shown on the right), and an adult of mass n times the mass of the child (shown on the left) to test out your prototype. (a) Derive an expression for the torque applied by the adult rider (on the left) in terms of given quantities and variables available in the palette. Assume counterclockwise is positive. (b) Derive an expression for the torque applied by the child rider (on the right) in terms of given quantities and variables available in the palette. Assume counterclockwise is positive.…arrow_forward. The forces exerted by the bicep muscle and acting on the elbow when a 12 kg barbell is being curledcan be modeled based on the diagram above. The bicep muscle can be treated as a vertical cable. Themass and length of the forearm are 2 kg and 32 cm, respectively. The center of mass of the forearm is adistance of 14 cm from the point P, while the bicep connects to the forearm at a point 4.5 cm from P.a) Determine the tension in bicep muscle and the force of the humerus acting downward on the elbowat point P. b) Assuming the tension in the bicep muscle continues to be oriented vertically, determinethe tension in the bicep muscle and the force acting at P after the barbell has been raised by an angleof 30 relative to the horizontal.arrow_forwardA bean of wood with negligible mass and the lenght 5.0 m is placed on a tirangular support. A mass of 9.5 kg is hanging on the left end of the beam, and a box with mass 23kg is placed on the beam. In order to prevent the beam form moving and to keep it in equilibrium, a person has to support the beam at the right end. IF the distance from the pivot to the hanging mass is 1.2 m, and the distance from the pivot to the point where the force from the box is applied on te beam is 2.3 m, with that magnitude of force F in the unit N , does the person have to hold the beam tokeep the equilibrium? Use g=9.8 m/s^2 as acceleration due to gravityarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON