
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
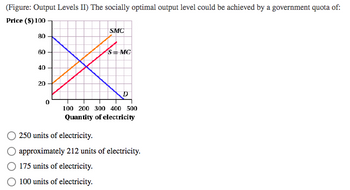
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website:**
**Figure: Output Levels II**
The socially optimal output level could be achieved by a government quota of:
- ○ 250 units of electricity.
- ○ approximately 212 units of electricity.
- ○ 175 units of electricity.
- ○ 100 units of electricity.
**Graph Explanation:**
The graph presents the relationship between price and quantity of electricity, with two key curves and a demand line:
- **Price Axis (vertical):** Ranges from $0 to $100.
- **Quantity of Electricity Axis (horizontal):** Ranges from 0 to 500 units.
**Curves:**
- **SMC (Social Marginal Cost):** An upward-sloping orange line, indicating the additional cost incurred by society for each additional unit of electricity.
- **S = MC (Supply equals Marginal Cost):** A red upward-sloping line, usually representing the supply curve in traditional economic models.
- **D (Demand):** A downward-sloping blue line, reflecting the relationship between price and the quantity demanded by consumers.
The socially optimal output level is where the **SMC** intersects with the **D** curve, suggesting the production level where social costs and consumer demand are balanced. The graph suggests this point is approximately 212 units of electricity.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 21 24 P 500 300 250 50 50 M DE J F CH 91 ABG K S MSB D 50 80 90 100 Q Which of the following would lead to the allocatively efficient outcome? A subsidy A price floor of $250 A quota of 90 units A taxarrow_forwardConsider the supply of soybeans in South America and the demand for soybeans in China. Draw a graph in which you show the current market equilibrium price of soybeans and quantity of soybeans traded. Include the curve that shows the true social costs of soybean production. Show the socially optimal amount of soybeans traded. Show the price that should really be charged for soybeans to ensure that production moves to the socially optimal level. Ensure that you label your graph correctly (all curves, axes, prices and quantities labeled). Show the deadweight loss of soybean production. What intervention could be used to change the market price for soybeans to the level that would move the quantity of soybeans traded to the optimal level? Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardSocial cost associated with a community owned resource can be internalized if a) the state imposes a tax on the user of the resource b) people are considerate of others account for the social cost in their consumption of the resource c) the community owned resources is converted to a privately-owned resource d) all of the abovearrow_forward
- Some economists claim that early child care generates an external benefit to society. a. What is the market equilibrium? What is the socially optimal outcome? How do they differ? b. The government is planning to provide a per-unit subsidy for child care to achieve the socially optimal outcome. How large should this subsidy be? c. How much is the total government subsidy each month to reach a socially optimal outcome?arrow_forwardBN12.2 (d) (e) Case: The market for dry cleaning is reflected by the demand and supply curves (Q is in thousands): Pa = 5-Q Ps= 2 + 2Q Producing dry cleaning creates ground water pollution with a constant marginal external cost of 1.2. Question: (d) What is the equilibrium price and quantity if the government decides to impose a per-unit tax of $1.20 is added to dry cleaning? (e) Does the tax cause a Pareto improvement? (Use the definition of a Pareto improvement to justify the answer.)arrow_forwardanswer to this q?arrow_forward
- Please no written by hand solutionarrow_forwardA market that is efficient in allocating scarce resources to their best use. Which of the following markets is likely to be the most efficient without any government intervention? a) electricity in virginia (hint: Dominion Energy is a monopoly) b) retail market for gasoline c) university education d) internet servicearrow_forwardTo model the effects of a carbon tax on CO2 emissions, policymakers study the marginal cost of abatement B(x), defined as the cost of increas- ing CO2 reduction from x to x +1 tons (in units of ten thousand tons- Figure 4). Which quantity is represented by the area under the curve over [0, 3] in Figure 4? B(x) ($/ton) 100 75 50+ 25- 1 3 Tons reduced (ten thousands) FIGURE 4 Marginal cost of abatement B(x).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education