
Concept explainers
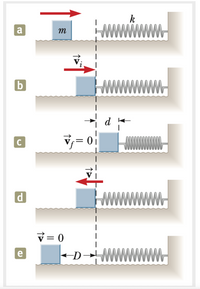
figure A) A 2.0 kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.25
figure B) the object has a initial speed vi = 3m/s when it makes contact with a light spring that has a spring constant of 50 N/m.
figure c) The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed by distance d.
For this problem set, use g = 10m/s^2.
1)Find the distance of the compression d in figure C. Answer (in [m]) to 2 decimal places.
2)Find the speed v (in m/s) at the unstretched position when the object moves to the left in figure D. Answer to 2 decimal places in m/s
3) Finally, in figure E, the object comes to rest at distance D to the left of the unstretched spring. Find D. Answer to two decimal places, in [m].
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

- Ablock of mass of 1.0 kg is moving across a frictionless floor and comes in contact with an idoal spring If the block compresses the spring by 5.0 cm before stopping, what is the force constant of the spring? 10.0 m/s ww k = ? O 2, 000 Nim O 40, 000 Nm O 4 Nm O 4, 000 Nim Activatearrow_forwardA 1.10-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of v₁ = 2.60 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e). m √ƒ=( V=0 ww DWW karrow_forwardA 235 kg roller coaster is at the top of a hill with a velocity of 5.60 m/s from a height of 100.0 m above the ground. A) Determine the velocity of the roller coaster at a height of 40.0 m furtherdown the track, neglecting friction. B) What reference point did you choose as zero height? Show how you could come up with the same answer to A if you chose another reference point for height.arrow_forward
- A 1.30-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of vi = 2.60 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e). k a m b C V = 0 e -D (a) Find the distance of compression d. You will find that you need to use the quadratic equation to find this distance. m (b) Find the speed v at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d). m/s (c) Find the distance D where the object comes to rest.arrow_forwardA 1.10-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of vi = 2.60 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e). a b d e m V=0 DMM m k (a) Find the distance of compression d (in m). (b) Find the speed v (in m/s) at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d). m/sarrow_forwardA spring is used to launch a coffee mug. The 20cm long spring can be compressed by a maximum of 8cm. The mug has a mass of 700 g. What kind of spring do you need to launch the mug at least 2 stories high (5 m) - as measured from the relaxed spring position - using the maximum compression? N/marrow_forward
- You push a 2.0 kg block against a horizontal spring, compressing the spring by 15 cm. Then you release the block, and the spring sends it sliding across a tabletop. It stops 75 cm from where you released it. The spring constant is 200 N/m. What is the block–table coefficient of kinetic friction? Draw free-body diagram.arrow_forwardee 2M Two blocks, of masses M = 4.0 kg and 2M, are connected to a spring of spring constant k = 150 N/m that has one end fixed, as shown in the Figure. The horizontal surface and the pulley are frictionless, and the pulley has negligible mass. The blocks are released from rest with the spring relaxed. What maximum distance does the hanging block fall before momentarily stopping? 1.57 m 2.29 m 1.05 m 1.96 marrow_forwardIn the figure below, a block of m= mass 19 kg is released from rest on a frictionless incline angled of angle theta= 30 degrees. Below the block is a spring that can be compressed 2.0cm by a force of 240 N. The block momentairly stops when it compresses the spring by 5.6cm. A) How far has the block moved down the incline to this stopping point? B) What is the speed of the block just as it touches the spring?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





