Question
Mass m is on a rough surface of mass M (µ coefficient of friction). M is on a smooth surface and initially at rest. At position A, m is given an initial velocity of V0 and then slowed down and finally when m is at position B, m and M move at the same speed. With the parameters M, m, V0, and g known
[A] Calculate the time it takes m to travel AB
[B] Calculate the kinetic energy of the system when the velocity m is V0
[C] Calculate the kinetic energy of the system when m and M have the same velocity
- Compare result [B] and result [C]
Description on the picture -> Licin= Slippery
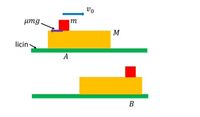
Transcribed Image Text:vo
umg
m
M
licin
А
В
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- After the power is turned off, an object on a nearly frictionless surface slows down such that it travels 99.9% as far during 1 second as during the previous second. If it travels 100 cm during the first second after the power is tuned off, how far does it travel while stopping?arrow_forwardPart A Compute the kinetic energy, in joules, of an automobile of mass 1650 kg traveling at a speed of 56.0 km/h. Submit Correct Part B Previous Answers By what factor does the kinetic energy change if the speed is doubled? Submit | ΑΣΦ Request Answer BMW ?arrow_forwardA ball of mass m= 0.38 kg is tied to a massless string of length L=1.2m. The ball is released at rest from point A as shown in the figure. a) What is the speed of the ball as it passes through point B? b) What is the tension in the string at point B? 35 1.2 m Aarrow_forward
- The coefficient of kinetic friction between the m (kg) crate and the plane is u = 0.25. Initially the spring is compressed at x (m) and the crate is at rest. The initial state is at h =0 m. Find the equation that will define the distance d the crate will travel upward and be again at rest. k = 2 kN/m and e (degrees) is the angle between the plane and the horizontal. g = 9.81 m/s². O mx? /(9.81 * m * cos0 + 0.25 * 9.81 * m * sind) m O mx? /(9.81 * m * sind) m O mx? /(9.81 * m * sino + 0.25 * 9.81 * m * cos0) m O Imx? /(9.81 * m * cos0 0.25 *9.81 * m* sino) m Clear my choicearrow_forwardA 4.0-kg battery operated toy car has a speed of 7.5 m/s at point C and kinetic energy of 205 J at point D. What is the total work done on the particle as it moves from C to D?arrow_forwardA spring with k = 15 N/m with equilibrium length 30 cm is attached vertically to a surface and then allowed to come to equilibrium, after which a weight with mass 0.2 kg is attached to the top side of the spring. → What is the speed of the weight when it first reaches the new equilibrium height?arrow_forward
- Two blocks with masses 0.342 kg (A) and 0.719 kg (B) sit on a frictionless surface. Between them is a spring with spring constant 27.7 N/m, which is not attached to either block The two blocks are pushed together, compressing the spring by 0.270 meter, after which the system is released from rest. What is the final speed of the block A? (Hint: you will need to use both conservation of energy and conservation of momentum to solve this problem).arrow_forwardAn object is attached to a light string and is forced to move in uniform circular motion on a frictionless table. The radius of the circular path is 0.5m and the maximum amount of tension the rope can withstand without breaking is 16N. What is the maximum amount of kinetic energy this object can have?arrow_forwardThis problem uses the ideal spring force in one dimension. F = -kx, where x is the deviation from equilibrium, and k is the spring constant. Calculate the particle's maximum speed (vmax), with these numbers: k = 2000 N/m = 2000 kg/s2 m = 5 kg (the mass of the particle) x0 = 0.2 m (the initial position) v0 = 5 m/s (the initial velocity)arrow_forward
- The spring in the image has a spring constant of 8000 N/m. it is pressed 24.0cm from its normal length. When released, the spring launches a 5 kg block on a frictionless horizontal surface. The block then climbs a 2 m high ramp inclined at an angle of 35.0 degrees above the horizontal And has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.480. calculate the following: a. The initial speed of the block at the base of the ramp (vi) b. The final speed of the block at the very top of the ramp (v) c. The horizontal distance the block travels after it takes off from the top of the ramp (d) 35° Ramp 2marrow_forwardLet Á = 2.0 m/s i – 9.0 m/s j+5.0 m/s k and let B = 2.0 kg kg j+ 2.0 kg k ,what is A· B?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios