
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
So what needs to be found is the charge q in coulombs, and the number of particles that make up this charge.
The data values are:
Length (L) of string and ball = 0.23 m
Distance (r) between the balls when repelled = 0.08 m
Mass (m) of each ball = 6 x 10^-6 kg
Calculate the charge q (in coulombs ) on each of the pith balls from the results
Calculate the number of particles (electrons or holes) that make up this charge. In your conclusions, discuss the magnitude of this number.
I am so lost on this, any help would be much appreciated. Thank you
Transcribed Image Text:5 / 6
2
100%
e
Ag
FwZ
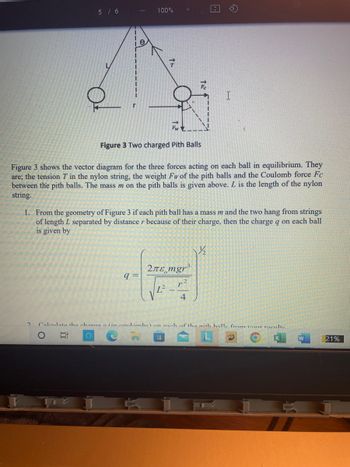
Figure 3 Two charged Pith Balls
Figure 3 shows the vector diagram for the three forces acting on each ball in equilibrium. They
are; the tension T in the nylon string, the weight Fw of the pith balls and the Coulomb force Fc
between the pith balls. The mass m on the pith balls is given above. L is the length of the nylon
string.
1. From the geometry of Figure 3 if each pith ball has a mass m and the two hang from strings
of length L separated by distance r because of their charge, then the charge q on each ball
is given by
q=
*
2лε mgr³
L²-
4
½½/₂2
Calculate the charge a (in coulomhel on anch of the nith halle from our roculte
O Et O
W
21%

Transcribed Image Text:u/d21/le/dropbox/8671100/8125167/DownloadAttachment?fid=288334436
с
F5
Nas
Balls charged by induction
PVC and will repel each other.
If using the PVC does not produce enough charge on the pith balls then place the pith balls on the
fur material and gently rub the balls with the fur material. The pith balls will then fly apart. The
separation between the two charged balls should be between 2 and 6 cm. Do not touch the pith
balls or they may be partially discharged. Measure the distance r between the centers of the balls
by holding a ruler just below them. The measured value of r is needed to calculate the charge q on
the pith balls.
(a)
F6
4 / 6
100
Mass of Ball, m=0.006g
Length of string, L =
Distance between centers of balls, r=
F7
Balls charged by conduction
(b)
Figure 2 Charging the Pith Balls
F8
100% +
8
F9
09
F10
L
-*-
F11
Balls repelled
(c)
F12
PrtSc
20%
Insert
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Particles A and B collide to produce particles C, D, and E: A+B ---> C +D+E. A has a charge of le, B has no charge, C has a charge of -2e, and D has a charge of 1e. What charge does E have? -2e -e +2e none of thesearrow_forwardA +5 nC point charge and a -10 nC point charge are 0.02 m apart. (a) What is the strength of the Coulomb force on the +5 nC charge? (b) What is the strength of the Coulomb force on the -10 nC charge? (c) Is the -10 nC charge attracted to or repelled by the +5 nC charge (d) If the distance between the charges is doubled to 0.04 m, what is the force on the +5 nC charge now?arrow_forwardIP A particle with a mass of 4.0 g and a charge of +5.0x10-2 μC is released from rest at point A in the figure (Figure 1). Figure Ag 3.0 cm во 5.0 cm 4.0 cm OC E 1 of 1 L X > In which direction will this charge move? Positive Y- direction Negative y- direction Negative x-direction Positive x-direction Submit Part B V= Request Answer What speed will it have after moving through a distance of 5.5 cm ? The electric field has a magnitude of 1600 N/C Express your answer using two significant figures. 15. ΑΣΦ SFR P Pearson ? m/sarrow_forward
- Two electrostatic point charges of +30 uC and +20 uC exert a repulsive force on each other of 225 N. What is the distance between the two charges.arrow_forwardA metallic plate holds a charge of Q = -18 nC. Does the plate have excess or lack of electrons? Excess What total number of elementary charges does Q represent? Units no units required The number of elementary charges, N = 1.125E11 After 43.1 × 10¹0 electrons were added to the plate, what is the new net charge on the pla The new charge of the plate, Qnew = Units nCarrow_forwardBead A has a mass of 15 g and a charge of -5.2 nC . Bead B has a mass of 22 g and a charge of -11.7 nC . The beads are held 15 cm apart (measured between their centers) and released.arrow_forward
- A sphere has an excess of 3 electrons. What is the charge of the sphere? A. – 5.3 × 10^-20 C B. – 4.8 × 10^-19 C C. 5.3 × 10^-20 C D. 4.8 × 10^-20 Carrow_forwardIf you touch 62 nC and -11 nC charges, what will be the net charge after touching them together?arrow_forwardTwo charges +2 µC and +8 µC are placed along the z axis, with the first charge at the origin (z =0) and the second charge at z = +1 m. Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on a -2 nC charge when placed at the following locations below. Overall Hint Review Section 5.3 Coulomb's Law. Use Coulomb's Law to calculate force due to each of two charges and add them together for the net force, minding the directions. For part (c), you will need to do the vector sum (more below). a. halfway between the two charges: magnitude of force is direction is Select an answer b. on the axis at x = -0.5 m: magnitude of force is is Select an answer c. at the coordinate (x, y) = (1 m, 0.5 m) (half a meter above the +8 µC charge in a direction perpendicular to the line joining the two fixed charges): Hint for (c) This problem is fully 2-dimensional. The charge at x = 1 m exerts force along y direction; the charge at the origin exerts force along the line connecting (x, y) = (0,0) and (z,y) = (1…arrow_forward
- The figure below shows four small beads, each with a positive charge, at the corners of a square. The length of each side of the square is a. The bead at top-right has a charge of q; the one at lower-left has a charge of 8.0q; the other two each have a charge of 6.0g. (Assume that the +x-axis is to the right and the +y-axis is up along the page.) a 6.09 а 8.0g 6.0g a (a) What is the magnitude of the force on the bead with charge q? Express your answer in terms of k, q, and a in symbolic form. ka [12.485] F = a? What is the magnitude of the force due to each charge? (Be careful with distances.) What is the direction of each force? Using trigonometry, can you find the x- and y-components of each force? After finding the x- and y-components of the net force, how can you use them to find the magnitude of the net force? (b) What is the direction of the force on the bead with charge q? (Enter your answer in degrees counterclockwise from the +x-axis.) 45 ° counterclockwise from the +x-axisarrow_forwardA +30 nC charge is placed at a distance r = 5 mm from a +10 nC charge in free space. Calculate the magnitude of the force between the charges. Note: ε0=8.85x10-12 Fm-1arrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON