
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
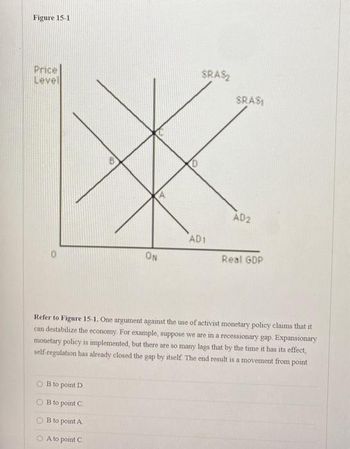
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 15-1
Price
Level
ON
OB to point D
B to point C
B to point A
O A to point C
0
SRAS₂
AD1
SRASI
AD2
Real GDP
Refer to Figure 15-1. One argument against the use of activist monetary policy claims that it
can destabilize the economy. For example, suppose we are in a recessionary gap. Expansionary
monetary policy is implemented, but there are so many lags that by the time it has its effect,
self-regulation has already closed the gap by itself. The end result is a movement from point
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Answer quickly please fastarrow_forwardhow to calculate the equilibrium price.....arrow_forwardConsidering how monetary policy affects the market, which of the following statements is most accurate? There is an indirect impact on aggregate demand by monetary policies. O There is more of an impact on consumption than investments by monetary policies. There is a direct impact on aggregate demand by monetary policies.arrow_forward
- Which of the following scenarios below BEST matches an inflationary monetary policy aka a “loose money” policy? a.Buying bonds increases the money supply, which lowers the interest rate b.Increasing taxes increases the reserve requirements, which decreases investment c.Increasing the discount rate lowers the real interest rate, which raises investment d.Selling bonds decreases the money supply which increases the interest rate e.Decreasing government spending lowers the interest rate, which lowers consumptionarrow_forwardWhat is a monetary rule? What is its purpose? Illustrate and explain the implementation of a monetary rule.arrow_forwardHow do changes in interest rates impact consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity, and how does the central bank use interest rates as a tool of monetary policy? A) Changes in interest rates have no effect on economic activity. B) Lower interest rates typically encourage consumer borrowing and business investment, stimulating economic activity. The central bank uses interest rate adjustments as a tool to influence borrowing and spending. C) Higher interest rates boost economic activity by increasing consumer savings. D) Changes in interest rates only affect government spending.arrow_forward
- Why do Keynesian economics believe increasing the money supply is a good idea? Use the equation of exchange in this answer.arrow_forwardThe answer choices for the blanks are Blank 1: fall, remain the same, rise Blank 2: remain the same, rise, decline Blank 3: international trade, real balance, interest-ratearrow_forwardAn example of a tight monetary policy isarrow_forward
- "If a central bank's desired intermediate target is a monetary aggregate (money supply), then its policy instrument will most likely be a reserve aggregate variable like the monetary base." Explain this based on the conduct of monetary policy in practice.arrow_forwardwhat is a fiscal policy what is a monetary policy -give an example in todays economy. thanks for your timearrow_forwardHow does the federal government reduce interest rate? What happens to interest rate and quantity of money as a result of expansionary monetary policy? Please explain using a diagram of interest rates vs quantity of money. showing the relevant shifts in the supply and demand curve.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education