
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
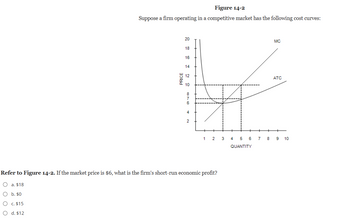
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 14-2
Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves:
a. $18
b. $0
c. $15
d. $12
PRICE
20
18
16
14
878
4
2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
QUANTITY
Refer to Figure 14-2. If the market price is $6, what is the firm's short-run economic profit?
8
MC
ATC
9 10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following table shows data for quantity (Q), price (P), fixed cost (FC), and variable cost (VC) for a hypothetical firm in a perfectly competitive market. Q FC VC TC MC TR MR P/L $72 $100 $0 1 72 100 64 72 100 84 3 72 100 114 4 72 100 184 72 100 270 a) Fill the table for total cost (TC), marginal cost (MC), total revenue (TR), marginal revenue (MR), and profit or loss (P/L). Make sure to show your work for at least one line of Q. b) What is the profit maximizing quantity? Justify your answer. NOTE: this is a FILE UPLOAD question. Work your solution in an excel file and upload it, or write down your solution in a piece of paper, take a picture with your smartphone and upload the picture. 2.arrow_forwardCOSI MC АТС AVC MR 15 14 11 750 1,100 1,350 1,800 Quantity Figure 12-5 shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant-cost, perfectly competitive industry. Refer to Figure 12-5. to answer the following questions, assuming market price is $20. a. What is the profit maximizing quantity produced by the firm? 1350 b. What is the average total cost incurred by the firm at that quantity? 15 20arrow_forwardSuppose that a firm in a competitive market has the following cost curves: PRICE 20 18 16 4 13 12 10 14 8 6 4 2 MC 1 2 3 QUANTITY ATC AVC 5 Refer to Figure 14-1. If the market price is $5, the firm will earn a. negative economic profits in the short run but remain in business. b. negative economic profits and shut down. c. zero economic profits in the short run. O d. positive economic profits in the short run.arrow_forward
- Figure 14-2 Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves: 20 MC 18 16 14 12 ATC 10 8 7 4 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 QUANTITY Refer to Figure 14-2. If the market price is $10, what is the firm's total revenue? a. $35 b. $30 C. $15 d. $50 PRICEarrow_forwardSuppose that a firm in a competitive market has the following cost curves: 13- 12 11 10 Price +++ 9- 8. $3. Refer to Figure 14-1. The firm's short-run supply curve is its marginal cost curve above $4.50. MC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Quantity $6.30. O $1 ATC AVCarrow_forwardFigure 14-1 Suppose that a firm in a competitive market has the following cost curves: PRICE 20 18 16 14 432 10 8 6 4 2 MC 2 3 QUANTITY ATC AVC 5 Refer to Figure 14-1. If the market price is $5, the firm will earn a. negative economic profits in the short run but remain in business. O b. negative economic profits and shut down. c. zero economic profits in the short run. O d. positive economic profits in the short run.arrow_forward
- 1. The following figure shows the marginal cost curve and the average total cost curve of a firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry. Price ($) 14 12 10 MR =8 6 4 2 10 20 30 MC ATC Quantity (units) a. What price does the firm face in the market? b. At what level of output does the firm maximize profits? c. What is the revenue of the firm when it sells the profit-maximizing level of output? d. What is the total cost of the firm when it produces the profit-maximizing level of output? e. What is the maximum profit that the firm can make? f. Discuss the implications if the level of production is 10. g. Discuss the implications if the price is 2.arrow_forward22 In the above figure, at a price of RO 7, the firm's output would be units and it Would a. 16; cam an economic profit b. 0; shutdown 16; incur an economic loss d. 10; incur an economic lossarrow_forward3. Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves Suppose Yakov runs a small business that manufactures teddy bears. Assume that the market for teddy bears is a competitive market, and the market price is $25 per teddy bear. The following graph shows Yakov's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for teddy bears quantities zero through seven (inclusive) that Yakov produces. Yakov's profit is maximized when he produces teddy bears. When he does this, the marginal cost of the last teddy bear he produces is , which is ___ than the price Yakov receives for each teddy bear he sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional teddy bear (that is, one more teddy bear than would maximize his profit) is , which is than the price Yakov receives for each teddy bear he sells. Therefore, Yakov's profit-maximizing quantity corresponds to the intersection of the…arrow_forward
- Question 21 please solvearrow_forward7. Working with Numbers and Graphs Q8 The following graph illustrates the demand and marginal revenue curve (D-MR) of a perfectly competitive firm. Suppose that when the firm produces 70 units, its average variable cost equals $30 per unit and its average total cost equals $55 per unit. Use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to plot the total cost of producing 70 units. Next, use the grey rectangle (star symbols) to plot the total variable cost of producing 70 units. Then, use the tan rectangle (dash symbols) to plot the total revenue at 70 units. Finally, use the purple rectangle (diamond symbols) to plot the profit or loss at 70 units. PRICE AND COST (Dollars) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 10 30 40 50 60 QUANTITY (Units) + ATC +AVC 70 80 D=MR 90 100 Total Cost Total Variable Cost Total Revenue Profit or Loss ? Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for…arrow_forwardQuestion 25 Use the graph below to answer the following question: MC AVC # Q5 P4 P3 Ⓡ P2 ↑Price P1 Q1Q2 Q3 Q4 ATC Quantity If the market price is less than P3 and greater than P2, in the short run, the perfectly competitive firm will earn O positive economic profit zero economic profit. O negative economic profit and shut down. O negative economic profit but continue to produce output.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education