
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
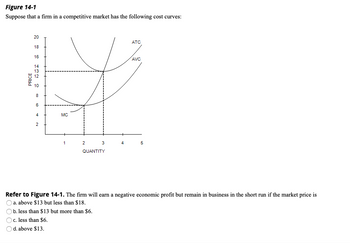
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 14-1
Suppose that a firm in a competitive market has the following cost curves:
PRICE
20
18
16
4 13 12 10
14
8
6
4
2
MC
1
2
3
QUANTITY
b. less than $13 but more than $6.
c. less than $6.
d. above $13.
4
ATC
AVC
5
Refer to Figure 14-1. The firm will earn a negative economic profit but remain in business in the short run if the market price is
a. above $13 but less than $18.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- do fast i will 5 upvotes.arrow_forwardQuestion 14 Figure 1 Use this figure for questions 14-20. This figure shows costs for a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Price MC 175 ATC AVC 125 100 80 270 322 515 Quantity Referring to Figure 1, suppose the price of the good is $175. If the firm produces and sells 515 units of output, its total revenue is (leave out the dollar sign)arrow_forwardam. 122.arrow_forward
- 1: 2 (N 2: 4 > 3: sa 4: 5: 6 8 10 ✓ 6: Question 16 Listen Figure 12-2 $60 $45 $40 $30 $10 200 Marginal Cost Average Total Cost 450 800 650 Refer to Figure 12-2. If the market price equals $45, the maximum profit that the firm can earn is: approximately $29,250. approximately $19,500. approximately $9,750. zero dollars. Average Variable Costarrow_forwardTable 1 shows the total cost schedule for a competitive firm. Price per unit of output is £7. Quantity 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total Cost 15 25 30 34 38 45 55 70 100 Table 1 D) Assume that the firm's minimum average variable cost is £6.5. Should the firm continue operating in the market in the short run? In the long run? Explain. E) If the firm is typical of other firms in the market, what price will it charge in the long run? Explain.arrow_forwardThe perfectly competitive farmer's profit maximizing level of output when price is $2 is ___ units of output Cost per unit 296 O 700 200 700 1000 200 0 MC 1000 ATCarrow_forwardPrice MC $5.50 ATC $5.00 $4.50 $3.00 $2.00 $1.75 55 110 MR 165 a. If this firm wants to maximize profits or minimize losses, be produced. (4 Points) b. The price charged would be (4 Points) c. The profit or loss incurred would be (4 Points) AVC Demand Quantity units of output should d. Is this firm likely to continue producing in the long run? Why? (4 Points)arrow_forwardAt the marketplace $8 per bushel.....please answerarrow_forwardThe cost curves below are for a firm competing in a perfectly competitive industry. If the market price is $7.50, a profit-maximizing firm would: Price and cost 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 2 MC y A A 1 B a 10 11 12 ATC AVC 13 Quantity Produce between 10 and 11, for a positive economic profit Produce about 9, for an economic profit of over $9 Produce between 10 and 11, for an economic profit of about $0 Produce about 9, for an economic profit of less than $9 Produce about 10, for an economic profit of about $20arrow_forwardPrice and costs (dollars) 20 16 12 8 4 0 5 10 MC ATC 20 15 Quantity (per day) The figure above shows short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the price of the product is $8, in the short run the firm will Select one: O a. incur an economic loss O b. earn an economic profit O c. earn a normal profit O d. None of the provided answers is correct because more information is needed to determine the firm's profit or lossarrow_forwardThe figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm. Figure 10.2 Price 50 35 30 20 10 $450 $700 10 $500 15 MC 20 MR AVC Refer to Figure 10.2. Compute the profit earned by the firm at the profit-maximizing level of output. $300 ATC Quantityarrow_forwardUse the figure below to answer the following questions. Price and cost (dollars per unit) 100 90 85 80 70 55 40 0 MR₂ MC ATC La MR₁ 100 140 200 220 250 Quantity (units per week) Figure 13.2.3 Refer to Figure 13.2.3. Assume this firm faces demand curve D2. If the firm produces the efficient quantity, it makes zero economic profit. makes an economic profit. will face competition from new firms entering the industry. is in a long-run equilibrium. incurs an economic loss.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education