
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
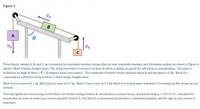
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 1
В
А
Three blocks, labeled A, B, and C, are connected by essentially massless strings that run over essentially massless and frictionless pulleys (as shown in Figure A
above). Block A hangs straight down. The string from block A connects to block B which is sliding up and to the left along an inclined plane. The plane is
inclined at an angle of theta = 0 = 52 degrees away from vertical. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block B and the plane is 0.38. Block B is
connected by a different string to block C which hangs straight down.
Block A has a mass of 4.1 kg. Block B has a mass of 3.7 kg. Block C has a mass of 2.5 kg. Block A is moving down and block C is moving up (the strings do not
stretch).
The only significant forces acting on the blocks are friction acting on block B, normal forces, tension forces, and gravity (with g = 9.81 m/s²). Calculate the
%3D
acceleration (in units of meters per second squared) of block A. For block A, a downward acceleration is considered positive, and the sign of your answer is
important.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Early test flights for the space shuttle used a "glider" (mass of 980 kg including pilot). After a horizontal launch at 600 km/h from a height of 3600 mm , the glider eventually landed at a speed of 210 km/h. part a What would its landing speed have been in the absence of air resistance? Part b What was the average force of air resistance exerted on it if it came in at a constant glide of 12 degrees to the Earth? can you please help with part b?arrow_forwardPlease answer parts a -carrow_forwardA block of mass m₁ is attached to a massless, ideal string. This string wraps around a massless pulley and then wraps around a second pulley that is attached to a block of mass m2 that is free to slide on a frictionless table. The string is firmly anchored to a wall and the whole system is frictionless. Use the coordinate system indicated in the figure when solving this problem. (Figure 1) Figure m1 m₂ Frictionless table 1 of 1arrow_forward
- A 65 kg person running at 2.0 m/s jumps onto the skim board at right. The skim board is 50 cm wide and 120 cm long, with an area of 0.60 m². Part A Draw a sketch of this situation. Part B If the person jumps onto the board on sand with a coefficient of friction of f=0.50, what force will resist the forward movement of the board [N]? Recall the friction force is the normal force times the coefficient of friction. Part C Now assume the person jumps onto the board on a 0.50 cm film of fresh water at 30°C. Use Newton's law of viscosity to estimate the force resisting the forward movement of the board.arrow_forwardTwo blocks are connected by a massless rope. The rope passes over an ideal (frictionless and massless) pulley such that one block with mass m1 = 12.25 kg is on a horizontal table and the other block with mass m2 = 7.5 kg hangs vertically. Both blocks experience gravity and the tension force, T. Use the coordinate system specified in the diagram. a.) Assuming friction forces are negligible, write an expression, using only the variables provided, for the acceleration that the block of mass m1 experiences in the x-direction. Your answer should involve the tension, T. b.) Under the same assumptions, write an expression for the acceleration, a2, the block of mass m2 experiences in the y-direction. Your answer should be in terms of the tension, T and m2. c.) Carefully consider how the accelerations a1 and a2 are related. Solve for the magnitude of the acceleration, a1, of the block of mass m1, in meters per square second. d.)Find the magnitude of the tension in the rope, T, in newtons.arrow_forwardYou're driving home from the grocery store at 12 m/s with a 7.0 kg bag of groceries on the front seat when the light ahead turns red. Part A What is the shortest distance in which you can stop, after the brakes are applied, without the groceries sliding off the seat? The static and kinetic coefficients of friction are, respectively, 0.65 and 0.45. Assume that the surface of the seat is horizontal. Express your answer with the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) Ax= HÅ Value Units ?arrow_forward
- A sledge loaded with bricks has a total mass of 18.7 kg and is pulled at constant speed by a rope inclined at 19.5° above the horizontal. The sledge moves a distance of 19.4 m on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sledge and surface is 0.500. Find parts a-c.arrow_forwardTHIS QUESTION IS NOT GRADED.arrow_forwardA 1,040-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 390 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. Two figures show a side view of a crate positioned upon a horizontal surface. Figure (a): An arrow pointing downward and to the right is labeled vector F and forms an angle of 20° below the horizontal as it approaches the upper left edge of the crate. Figure (b): An arrow pointing upward and to the right is labeled vector F and forms an angle of 20° above the horizontal as it extends from the upper right edge of the crate. (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.)(b) If the 390-N force is instead pulling the block at an angle of 20.0° above the horizontal, as shown in the figure b, what will be the acceleration of the crate? Assume that the coefficient of friction is the same as that found in part (a).arrow_forward
- An 8.00 kg crate sits on an inclined plane that is inclined at 33.0 above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the surface of the plane is 0.300. A constant horizontal force F = 28.0 N is applied to the crate (Figure 1), and the crate moves down the plane. Part A If the crate is initially at rest, find its speed 2.00s after the force is applied? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA Value Units Figure 1 of 1> Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback F 33.0°arrow_forwardB In the figure, block A has a mass of 9.06 kg. It rests on a smooth (assume frictionless) horizontal table and is connected by a very light horizontal string over an ideal pulley to block B, which has a mass of 2.80 kg. When block B is gently released from rest, how long does it take block B to travel 76.7 cm? Report your answer in seconds.arrow_forwardC?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON