
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079373
Author: William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
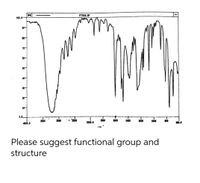
Transcribed Image Text:F77612.SP
100.0
90-
80-
70-
60-
50-
40-
30-
20
10-
0.0.
3500
3000
2500
1800
1600
1400
1200
1000
4000.0
2000.0
-1
cm
Please suggest functional group and
structure
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A. Draw structure of compound. B. Label base peak and molecular ion peak.arrow_forwardmacollege.instructure.com/courses/352/pages/covid-proteins-lab-manual?module_item_id=D44333 A = abc Where "A" is absorbance, "a" is molar absorptivity, "b" is the path length (length of the cuvette in units of cm), and "c" is concentration (mol/L). The molar absorptivity is an intrinsic property of a molecule which tells us how intensely it will absorb at a particular wavelength. If "A" is a unitless quantity, "b" is in units of cm, and "c" is in units of mol/L, then what are the units of molar absorptivity? Do a little research to learn how alpha-helices and beta-sheets are drawn in protein structures. If most of the absorption properties are coming from the alpha-helices in these proteins, and many alpha-helices have similar absorbance properties across different proteins, which protein would you predict would have the highest molar absorptivity? Your job is to use the following data table to determine the molar absorptivity for each of the following proteins at their respective…arrow_forwardDon’t know how to do thisarrow_forward
- Question 2. While internal cysteine amino acid sidechains in proteins undergo oxidation to produce disulfide crosslinks that stabilize the protein structure after folding, solvent-exposed cysteine sidechains can remain in their reduced thiol form and serve as reactive nucleophiles (recall for instance Acyl Carrier Proteins involved in fatty acid biosynthesis or various oxidoreductase enzymes). The reactive thiol groups in proteins can be detected using Ellman's test, wherein the protein is reacted with a disulfide Ellman's reagent to form a new mixed disulfide and a 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate (TNB) byproduct. Upon addition of base, TNB is deprotonated to form a dianion, which absorbs light in the visible region and can be detected using UV-Vis spectroscopy. Ellman's Reagent CO₂H -NO₂ internal disulfide crosslink O₂N- HO₂C SH solvent- exposed thiol UV Absorbance at 412 nm O₂N- -S TNB²- alkaline pH O₂N- SH HO₂C 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate (TNB) -NO2 mixed disulfide CO₂H a) Provide a detailed…arrow_forward8-9 are together could you briefly explainarrow_forwardMatch the following amino acids with their chemical properties H -N-CIC- A -A ✓ B но с D VE ✓ F ✓ G / CH3 CH3 CH B H но -N-C-C- feed C но -N-C-C- H CH₂ D HO -N-CIC- 1 H CH₂ OH E но ||| -N-C-C- II H CH₂ I CH₂ CH₂ CH₂ T NH3 I. Acidic II. Nonpolar III. Polar uncharged IV, Basic + F O HO -N-C-C- H CH₂ NH₂ G но | || -N-C-C- I H CH₂ 1arrow_forward
- Biological Macromolecules Identifying and drawing peptide bonds Draw the structure of threonylmethionine, a dipeptide made from threonine and methionine, as it would appear at physiological pH. $ 4 Explanation % 5 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Check 6 MacBook Pro & 7 * 00 8 ( 9 X O 0:0 3 0 è D ▬▬ Ⓒ2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | O + 11 Ⓡ 2/5 =arrow_forwardPlease solvearrow_forwardSort the agents according to the way they disrupt the structure of proteins: denaturation or hydrolysis. Drag each item to the appropriate bin.arrow_forward
- 9) I have circled six different species in the attachment table of standard reduction potentials. Just consider the half-reaction that involve the circled species. Which of the circled species are oxidizing agents? Which is the strongest oxidizing agent? Which is the weakest oxidizing agent? Which of the circled species are reducing agents? Which is the strongest reducing agent? Which is the weakest reducing agent?arrow_forwardA 1.00-mg sample of a pure protein yielded on hydrolysis 0.0165 mg of leucine and 0.0248 mg of isoleucine. What is the minimum possible molar mass of the protein? (MMleucine=MMisoleucine=131g/mol)arrow_forwardHow many of the -amino acids shown in Table 26-1 contain aromatic rings? How many contain sulfur? How many contain alcohols? How many contain hydrocarbon side chains?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning