
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Instructions for Analyzing Mass Spectrometry Data**
A. Draw the structure of the compound.
B. Label the base peak and the molecular ion peak.
**Explanation:**
In mass spectrometry, the structure of a compound can be determined by analyzing its mass spectrum. The mass spectrum provides crucial information, including various peaks that represent the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of ionized fragments.
- **Base Peak**: The base peak is the tallest peak in the mass spectrum, representing the most abundant fragment ion.
- **Molecular Ion Peak**: The molecular ion peak, also known as the parent peak, indicates the ion of the entire molecule before fragmentation. This peak helps identify the molecular weight of the compound.
**Note**: Ensure you understand the molecular structure in order to accurately identify and label these peaks, as they are critical for deducing the compound's identity.
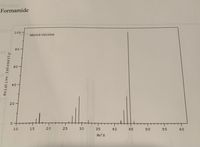
Transcribed Image Text:**Formamide**
This graph represents the mass spectrometry data for Formamide.
- **Y-Axis (Vertical):** Relative Intensity
- **X-Axis (Horizontal):** m/z (mass-to-charge ratio)
The graph indicates several peaks at different m/z values:
1. Small peaks around the m/z values of 15, 30, and 45.
2. A significant peak at the m/z value close to 45.
These peaks represent the different fragments of the formamide molecule as it is analyzed in the mass spectrometer, showing how the molecule breaks apart and the relative abundance of each fragment. The highest peak, also known as the base peak, can be used to identify the compound and assess its molecular structure.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Refer to the bar graph below, Explain why the n→π* interactions contributes more to the overall stabilization of the protein than all the other interactions(C-H-O hydrogen bond,π-π interactions, C5 Hydrogen Bonds, Cation-π interactions, Sulfur-arene interactions, Anion-π interactions, Chalcogen bonds, X-H-π interactions) even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Explain why that's the case for EACH of the bonds. I.e Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than C-H-O hydrogen bonds, even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than π-π interactions even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than C5 Hydrogen Bonds, even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than Cation-π interactions, even though…arrow_forwardRefer to the bar graph below, Explain why the n→π* interactions contributes more to the overall stabilization of the protein than all the other interactions(C-H-O hydrogen bond,π-π interactions, C5 Hydrogen Bonds, Cation-π interactions, Sulfur-arene interactions, Anion-π interactions, Chalcogen bonds, X-H-π interactions) even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Explain why that's the case for EACH of the bonds. I.e Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than C-H-O hydrogen bonds, even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than π-π interactions even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than C5 Hydrogen Bonds, even though n→π* is the weaker interaction. Why n→π* interactions contribute more to the overall stabilization of the protein than Cation-π interactions, even though…arrow_forwardBenzocaine has been tested as an anaesthetic for inhibition of m1 muscarinic acetylcholine signalling. Using the data below, plot a graph and determine the IC50. Concentration (M) 1 x 10-6 10 x 10-6 100 x 10-6 1000 x 10-6 10000 x 10-6 100000 x 10-6 % of control response 97 93 78 56 42 36arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardQ3- We wish to synthesize all possible dipeptides containing the amino acids tyrosine, lysine, phenylalanine, and leucine. Identify the number of possible dipeptides and explain how we would carry this out using combinatorial techniques.arrow_forwardYou obtained the following raw data when setting up a Bradford standard curve: BSA (mg/ml) Absorbancy 595nm 0 0.155 1 0.287 2 0.420 3 0.523 4 0.651 5 0.756 6 0.878 7 0.918 8 0.954 9 10 0.982 0.990 After blanking against a bradford-dH2O sample, the protein concentration of an unknown sample was determined using the same method and an absorbancy of 0.566 was obtained. Set up a standard curve, excluding outliers (experimental and statistical) and determine the protein concentration in the unknown sample in mg/ml (up to 3 decimal places).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY