
-
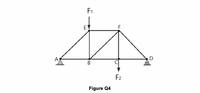
a) The truss structure in Figure Q4 is supported at A and D with downward vertical load F1 acting at joint E and a downward vertical load F2 acting at joint C. The length of each truss member AB, BE, BC, CD and CF is 1.25 m. If F1 = 95 kN and F2 = 225 kN, determine the reaction force RA and RD at the supports A and D. Give your answers in kilonewtons (kN) to two decimal places.
-
-
b) For the truss structure in Figure Q4, determine the forces FAE, FAB and FCF acting in members AE, AB & CF and clearly state if each member is in compression or in tension. Give your answers in kilonewtons (kN) to two decimal places.
-
-
c) A solid homogeneous truss tie-rod has a diameter of 9.52 mm and an original length of 1.75 m experiences a stress of 600 MPa when placed under tension. If the material used for the truss tie-rod has a Young’s Modulus, E, of 5.8 x 1011 N/m2, calculate: (i) the tie-rod’s extension in millimetres (mm); (ii) the strain energy (U) in Joules; and (iii) the strain energy per unit volume (U/V) in Joules per cubic metre (m3). Give your answers to two decimal places.
-
-
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images



- From the given figure Solve the following: Let P = 30 Find: Vertical reaction at CHorizontal reaction at CAxial force at member ABarrow_forwardDetermine the support reactions and joint forces on the compound beam in the figure. There is a hinge at point Barrow_forwardCompound axial member ABC has a uniform diameter of d = 1.2 in. Segment (1) is an aluminum [E₁ = 10,000 ksi] alloy and segment (2) is a copper [E₂ = 17,000 ksi] alloy. The lengths of segments (1) and (2) are L₁ = 80 in. and L2 = 140 in., respectively. Determine the force P required to stretch compound member ABC by a total of 0.10 in. LI L2 A d Aluminum Copper Answer: P = i B kipsarrow_forward
- SITUATION 2: The steel truss supports a 6000-lb load. The cross-sectional areas of the members are 0.5 in.2 for AB and 0.75 in.? for BC. E = 29 x 106 psi. 15 ft 7. Compute the elongation of bar AB 8. Compute the elongation of bar BC 9. Compute the strain energy of the two bars 10. Compute the horizontal displacement of B 11. Compute the vertical displacement of B 9 ft B 12 ft C 6000 lbarrow_forward2. There is structure (see the figure below) under two external loadings: 20 N horizontal and 10 N vertical at D and E, respectively. The structure consists of 4 members, AB, CD, DE, and CE. The structure is supported by two grounded pins at C and A. The lengths are shown in the figure. The cross-section areas are l cm² everywhere in AB and 10 cm? everywhere in CE. Find the support reactions at C. Find the internal force(s) in AB. Find the normal stress in AB. Find the normal force in DE. 1) Find the normal stress at a-a in CE. Find the shear force and shear stress at a-a. 20 N 45° 1m 45° C E 30 В 10 N 0.5 m 0.25 m' 0.25 marrow_forwardSet P1= 6.3 kN and P2 = 9 kN A) Determine the force in member AB of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. B) Determine the force in member AE of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression. C) Determine the force in member BC of the truss and state if the member is in tension or compression.arrow_forward
- a) The truss structure in Figure Q4 is supported at A and D with downward vertical load F1 acting at joint E and a downward vertical load F2 acting at joint C. The length of each truss member AB, BE, BC, CD and CF is 1.25 m. If F1 = 95 kN and F2 = 225 kN, determine the reaction force RA and RD at the supports A and D. Give your answers in kilonewtons (kN) to two decimal places. F1 E A В F2 Figure Q4 b) For the truss structure in Figure Q4, determine the forces FAE, FAB and FCF acting in members AE, AB & CF and clearly state if each member is in compression or in tension. Give your answers in kilonewtons (kN) to two decimal places. c) A solid homogeneous truss tie-rod has a diameter of 9.52 mm and an original length of 1.75 m experiences a stress of 600 MPa when placed under tension. If the material used for the truss tie-rod has a Young's Modulus, E, of 5.8 x 1011 N/m², calculate: (i) the tie-rod's extension in millimetres (mm); (ii) the strain energy (U) in Joules; and (ii) the strain…arrow_forwardA P = 10 kip 1.5 ft B C 2 ft The bars in the structure to the left are pinned and have circular cross-sections. The diameter of the cross- section is 1.5 inches. The bars are made of steel, which has an elastic modulus of 29,000 ksi. A point force of 10 kips is applied at point C, as shown. What is the change in length of member BC? Is the bar getting longer or shorter?arrow_forwardDetermine the bending moment (M) in kNm at the point x = 4.5 m from point A for the beam as loaded in Figure 3.2b6. Given a = 2, b = 5 and w4 = 6. Wą kN/m C В a m b marrow_forward
- use force method Consider the beam shown below. The structure is subjected to two concentrated loads. If all three supports settle the following amounts: A = 4.0 in., B = 2.0 in., and č = 3.5 in., determine the support reactions and draw the bending moment and shear force diagrams. 60k 90k 10 ft 10 ft 10 ft 10 ft Note: E = 4,000 ksi, / = 1200 in"; select the reaction at Support B to be the redundant.arrow_forwardSolve B Please fastarrow_forwardQuestion 4(a) The uniform bar shown in Figure 4 weighs 428 N. It is supported by a pin at A and a cable that runs around the pulley, D. It is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 17.7 N/m and 12.5 Nm clockwise moment at E. Beam is in equilibrium position as shown in the Figure. Take a = 0.41 m and b = 2.5 m. Determine the tension in the cable and the reaction force at A, both in Newtons. w N/m 75° A ▼▼ ▼ ▼ 12.5 Nm B E 1 m 0.5 m m b Figure 4 Question 4(b) Find a truss from your neighborhood where you can take a photo safely. It does not have to be taken from the perfect angle and as long as we can see the complete truss that is good enough. One photo would be ideal but upto 3 photos can be used. Include these photos in your solutions for this question and based on these photos draw this 2D truss (exact dimensions are not required) with the supports too. Comment on the possible loads and their locations that may be applied to the truss. Discuss the assumptions that you have to…arrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





