
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
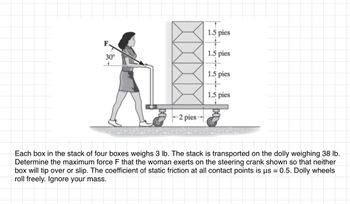
Transcribed Image Text:30°
-2 pies--
1.5 pies
+
1.5 pies
1.5 pies
+
1.5 pies
Each box in the stack of four boxes weighs 3 lb. The stack is transported on the dolly weighing 38 lb.
Determine the maximum force F that the woman exerts on the steering crank shown so that neither
box will tip over or slip. The coefficient of static friction at all contact points is us = 0.5. Dolly wheels
roll freely. Ignore your mass.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- only HANDWRITTEN answer needed ( NOT TYPED)arrow_forwardConsider the system as shown below. The 45-kg disk rests on the surface for which thecoefficient of static friction is 0.2. Determine the largest moment M that can be applied to the barwithout causing motion. Mass of the bar BC is negligible. Joints B and C are frictionless hinges. Please solve the questionarrow_forwardDetermine the distance s that the 90 kg draftsman can climb without causing the 4-meter ladder to slip at its lower end A. The top of the ladder weighing 15 kg has a small pulley, and on the ground the coefficient of static friction is 0.25. The painter's center is directly above her feet. Answer. S 2.55 m% 3d by 4 m by 1.5 marrow_forward
- Hello good evening, Permission, i have a question in my homework. The following bellow is question. Please advice. Thank you Regards,Irfan A 132-lb cabinet is mounted on casters that can be locked to preventtheir rotation. The coefficient of static friction between the floor and each caster is 0.30. Assuming that the casters at both A and B are locked, determine :(a) the force P required to move the cabinet to the right, (b) the largest allowable value of h if the cabinet is not to tip over.arrow_forwardI need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardAI The block D weighs 200 lbs and is connected to the block B by a cable. Block B has a weight of 160 lb acting at its center of gravity, CG,8, and Block B has a weight of 100 lb acting at its center of gravity, CG,A. The coefficient of friction between blocks A and B is uAB = 0.85. 1,15m 1.15m The coefficient of friction between block A and the ground is HAG = 0.4. a) Determine if slipping will occur between block B and block A. b) Determine if blocks A and B will tip on the ground (assume no slipping at A-B for this scenario).arrow_forward
- solve it quick and correctly includes FBD. Don't copy any wrong solutionarrow_forwardin the figure, the coefficient of friction between the blocks and the planes is 0.2 and the two blocks are moving along the plane as shown. What is the unbalance force equations for each object.arrow_forwardNeed help finding the second part of the question.arrow_forward
- Help!!! Answer it correctly!!! Pleasearrow_forwardProblem 4: A truck is towing a car. mtruck move. The truck is 4-wheel drive vehicle with the coefficient of static friction between the tires of the truck and the ground of µ. The = 3mcar. Draw the Kinetic FBD’s of the car and the truck at the instant the car begins to car wheels are free to roll.arrow_forwardThe man pushes on the roller with force P through a handle that connects to the central axle of the roller. If the coefficient of static friction between the 49-lb roller and the floor is s = 0.22, determine the maximum force Pthat can be applied to the handle, so that roller rolls on the ground without slipping. Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s2. 1.5 ft 30° Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY