
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
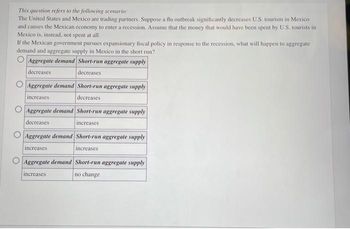
Transcribed Image Text:This question refers to the following scenario:
The United States and Mexico are trading partners. Suppose a flu outbreak significantly decreases U.S. tourism in Mexico
and causes the Mexican economy to enter a recession. Assume that the money that would have been spent by U.S. tourists in
Mexico is, instead, not spent at all.
If the Mexican government pursues expansionary fiscal policy in response to the recession, what will happen to aggregate
demand and aggregate supply in Mexico in the short run?
Aggregate demand Short-run aggregate supply.
decreases
decreases
Aggregate demand Short-run aggregate supply
decreases
increases
Aggregate demand Short-run aggregate supply
decreases
increases
Aggregate demand Short-run aggregate supply
increases
increases
Aggregate demand Short-run aggregate supply
increases
no change
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ? G The following graph shows a hypothetical economy in long-run equilibrium at an expected price level of 120 and a natural output level of $600 billion. Suppose the government increases spending on building and repairing highways, bridges, and ports. Using the graph, shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the increase in government spending. PRICE LEVEL 240 200 AS 160 120 80 40 0 0 200 400 600 AD 800 1000 1200 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) ŏ AD 一 AS (?) In the short run, the increase in government spending on infrastructure causes the price level to the quantity of output to the price level people expected and the natural level of output. The increase in government spending will cause the unemployment rate to the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows a hypothetical economy experiencing long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and natural output level of…arrow_forwardPlease Solve Fast I give upvote and good feedback.arrow_forward- family purchasing changed when Covid and the lock-downs hit, Name some details of both quantity of purchasing and types of purchasing. - Be sure to define demand and aggregate demand and how your purchasing is part of Agg. Demandarrow_forward
- An increase in taxes when the economy is above full employment OA. increases; falls B. increases; rises O C. does not change; does not change O D. decreases; falls aggregate demand and real GDP, and the price levelarrow_forwardWhich of the following scenarios would result in a decrease in Aggregate Demand? R A decline in investors confidence causes investment to fall. O Technology improvements lead to productivity gains O A rise in imports from Europe f5 O The congress passes a new income tax cut. 100 % 5 16 T e 6 6 3 Y ly 7 7 U 8 f10 num lk. 8 9 5 9 f12 Farrow_forward. Fill-in-the-Blank: A falling demand for investment goods results in a (n) _________ in aggregate demandarrow_forward
- 5 k es Price Level 170 150 130 110 90 The Economy of Morin 70 460 480 500 520 54535,75 580 600 Real GDP AD AS a. If potential GDP (LAS) is $550, and the economy is presently in equilibrium, then there is a(n) [recessionary b. In order to close this gap aggregate demand must increase by $ billion. gap of $ billion. c. If every $1 change in government spending leads to a $4 change in aggregate demand, government spending must increase by $ billion.arrow_forwardSuppose a tax cut affects aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Which of the shifts raise the price level? a. The shift of aggregate demand, but not the shift of aggregate supply b. Both the shift of aggregate demand and the shift of aggregate supply c. The shift of aggregate supply, but not the shift of aggregate demand d. Neither the shift of aggregate demand nor the shift of aggregate supplyarrow_forward170 Price 140 level 120 100 D AD5 AD4 AD 3 AD, AD2 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 Real GDP In Exhibit 20-8, if aggregate demand shifts from AD₁ to AD3, O a. real GDP will increase from $3.0 to $4.0, and the price level will increase from 100 to 140. Ob. real GDP will increase from $3.0 to $7.0, and the price level will increase from 100 to 120. Oc. real GDP will increase from $3.0 to $7.0, and the price level will increase from 100 to 140. Od. real GDP will increase from $3.0 to $4.0, and the price level does not change.arrow_forward
- 01 10 CO xp 381 In the figure, the economy is at an equilibrium with real GDP of $20 trillion and a price level of 110. As the economy moves toward its ultimate equilibrium, the curve shifts, because 0 0 0 0 0 A. aggregate demand; leftward; the money wage rate rises B. aggregate supply: rightward; the money wage rate falls OC. potential GDP; leftward; the money wage rate falls D. aggregate demand; rightward; the money wage rate falls OE. aggregate supply; leftward; the money wage rate rises 130- 120- 110- 100- Price level (GDP price Index, 2012 = 100) Potential GDP 90- AS AD 19.0 19.5 20.0 20.5 21.0 21.5 22.0 Real GDP (trillions of 2012 dollars) ✓ ✓ 5arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward✔ 2 Aplia Assignment Ch 20 4. Determinants of aggregate supply The following graph shows a decrease in short-ron aggregate supply (AS) in a hypothetical economy where the currency is the dollar Specifically, the short-un aggregate supply curve shifts to the left from AS, to AS, causing the quantity of output supplied at a price level of 100 to fall from $200 billion to $150 billion K 1 1 **### PRICE LEVEL 200 20 QUANTITY OF OUTPUT 380 400 The following table lists several determinants of short-run aggregate supply. Regulations on the firm Tax rates Input prices Complete the table by selecting the changes in each scenario necessary to decrease short-run aggregate supply Change Necessary to Decrease AS Grade It Now Save & Continue Continue without savingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education