
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The two children (fig shown) are balanced on a seesaw of negligible mass. (This assumption is made to keep the example simple—more involved examples will follow.) The first child has a mass of 26.0 kg and sits 1.60 m from the pivot.(a) If the second child has a mass of 32.0 kg, how far is she from the pivot? Use the second condition for equilibrium (net τ = 0) to calculate Fp
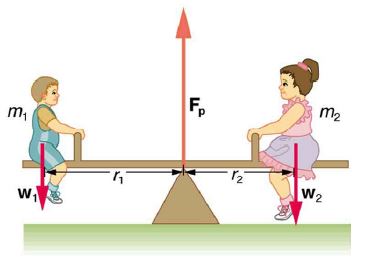
Transcribed Image Text:F,
m2
m,
W2
w,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object has its center of mass 7.25 cm from the pivot point of a servo. Assuming that the servo has a maximum torque of 1.75 kg - cm (based on a stall torque of 2.5 kg - cm, reduced by 30% to provide a buffer), what is the maximum mass that the object can be to not exceed the 1.75 kg - cm limit? Round your response to the second decimal place (i.e., #.##).arrow_forwardIn the figure, a nonuniform bar is suspended at rest in a horizontal position by two massless cords as shown in the figure here. One cord makes the angle 8 = 34.4 with the vertical; the other makes the angle o = 55.6 with the vertical. If the length L of the bar is 3.4 m, compute the distancex from the left end of the bar to its center of mass. comarrow_forwardA sign for a pizza restaurant hangs from a 2.60-m long rod extended out from a building. A cable, attached to the building, is attached to the rod at a point that is 2.10 m from the hidge. (See the figure.)The mass of the rod is 4.80 kg. The mass of the sign is 7.10 kg. The angle between the building and the rod is 50.0 degrees. The angle between the cable and the horizontal is 38.0 degrees. The tension in the cable is 90.27 N.What is the vertical component of the reaction force from then hinge on the rod?arrow_forward
- For two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them? Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick. The mass of the meter stick is 120 g. sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point. For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3arrow_forwardComputation A 6-kg bowling ball rests on a uniform beam of length L and mass M, as in the figure. The beam is supported at two points separated by a distance BL where ß = 0.59 and the bowling ball is a distance d from support point 1. Find the largest distance dmax such that the beam does not tip if M = 17 kg and L = 4.9 m. [Note: To keep the bowling ball on the beam, report an answer of dmax ≤ L. For some values, a correct calculation gives dmax > L. That means the bowling ball can be placed anywhere on the beam without tipping and, in that case, the correct answer is dmax = L = 4.9 m.) 2 dmax m L BL- d M Report your numerical answer below, assuming three significant figures. Remember to include a "-" as necessary. O Search 1arrow_forwardTwo blocks, each of mass 2 kg are suspendedfrom the ends of a rigid massless rod of lengthL. The rod is held horizontally on the fulcrumand then released. The length L1 is 15 cm andthe length L2 is 85 cm. Draw the force diagram for the rod. Clearly label all forces. Write Newton’s 2nd Law equation: (for F of y) Write Newton’s 2nd Law equation: (for net torque) What is the magnitude of the linear acceleration of the block closest to the fulcrum? What is the magnitude of the linear acceleration of the block furthest from the fulcrum?arrow_forward
- The uniform seesaw shown below is balanced on a fulcrum located d1 = 3.5m from the left end. The bigger boy on the left end has a mass m1 =75 kg. The smaller boy on the right end has a mass of m2 = 55 kg and is a distance d2 = 4.5 m from the fulcrum. The mass of the board is mb. Draw all forces acting on the seesaw board showing their directions and locations. Where would you draw the weight of the board? Identify and show the direction of rotations caused by the torques provided by all forces about the fulcrum. If the seesaw is in static equilibrium, write down the two conditions of static equilibrium symbolically using the forces and distances in the figure. Solve for the mass of the board. Calculate the force of fulcrum on the board.arrow_forwardA 1 490-kg automobile has a wheel base (the distance between the axles) of 2.70 m. The automobile's center of mass is on the centerline at a point 1.05 m behind the front axle. Find the force exerted by the ground on each wheel. each front wheel _______kN each rear wheel _______kNarrow_forwardThe diagram above shows a 3.00 m long uniform beam. The left end of the beam is attached to a wall by a frictionless pivot. The beam is supported by a string that keeps the beam horizontal. The string makes an angle of 35.0° relative to vertical. The beam has a mass of 7.00 kg. A 2.00 kg mass is located at the end of the beam. A 6.00 kg mass is located 1.00 m from the 2.00 kg mass, as shown in the diagram. a. What is the tension in the string? b. What is the y-component of force applied to the beam by the pivot?arrow_forward
- For two existing torques, what third force at a given distance from the pivot will balance them? Imagine a meter stick set up as in the figure. It hangs from a central bracket, and two hanging masses can hang from it from each of their brackets. At a third location, a force probe can either pull up or pull down on the stick, depending on what is needed to balance the stick. The mass of the meter stick is 120 g. sketch the situation (drawing r1, r2, r3, F1, F2, and F3) and determine the magnitude (value) and direction (+ or -) of each torque. Don't include the mass of a bracket that would hold the hanging mass in place; assume the mass listed is the entire mass hanging at that point. For each trial, use the principle of equilibrium (where the sum of torques is zero) to calculate the third, unknown force acting at x3arrow_forwardThe center of mass of the arm shown in the figure is at point A. Find the magnitudes (in N) of the tension force F and the force F which hold the arm in equilibrium. (Let 8 = 24.0°.) Assume the weight of the arm is 48.3 N. IF 8.00 cm 29.0 cm 1₂ 354 X Draw a diagram showing the forces and distances. Find the sum of the torques about point O, and set this equal to zero. Solve your equation for F₁. N 340.30 X Apply Newton's second law in the x and y directions, and solve for F Sx Pythagorean theorem to calculate F. . N and F You will need your value of F. Then use the sy'arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON