
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
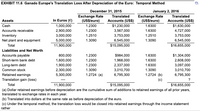
Transcribed Image Text:**EXHIBIT 11.6** *Ganado Europe's Translation Loss After Depreciation of the Euro: Temporal Method*
**December 31, 2015**
**January 2, 2016**
---
### Assets
| Description | In Euros (€) | Exchange Rate (US$/euro) | Translated Accounts (US$) |
|----------------------------|--------------|--------------------------|---------------------------|
| Cash | 1,000,000 | 1.2300 | 1,230,000 |
| Accounts receivable | 2,900,000 | 1.2300 | 3,567,000 |
| Inventory | 3,000,000 | 1.2510 | 3,753,000 |
| Net plant and equipment | 5,000,000 | 1.3090 | 6,545,000 |
| **Total** | 11,900,000 | | 15,095,000 |
### Liabilities and Net Worth
| Description | In Euros (€) | Exchange Rate (US$/euro) | Translated Accounts (US$) |
|----------------------------|--------------|--------------------------|---------------------------|
| Accounts payable | 800,000 | 1.2300 | 984,000 |
| Short-term bank debt | 1,600,000 | 1.2300 | 1,968,000 |
| Long-term debt | 1,900,000 | 1.2300 | 2,337,000 |
| Common stock | 2,300,000 | 1.3090 | 3,010,700 |
| Retained earnings | 5,300,000 | 1.2724 | 6,795,300 (a) |
| **Translation gain (loss)**| | 1.2724 (b) | (c) |
| **Total** | 11,900,000 | | 15,095,000 |
---
**January 2, 2016** Translated Accounts (US$):
- Cash: 1,630,000
- Accounts receivable: 4,727,
![**Ganado Europe (D).** Using facts in the chapter for Ganado Europe, assume that the exchange rate on January 2, 2016, in Exhibit 11.6 appreciated from $1.2300/€ to $1.6300/€. Calculate Ganado Europe's translated balance sheet for January 2, 2016, with the new exchange rate using the temporal rate method as shown in the popup window.
**a.** What is the amount of translation gain or loss?
**b.** Where should it appear in the financial statements?
*Enter a positive number for a gain and a negative for a loss.*
$ [___________] (Round to the nearest dollar.)](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/20bf0873-ce5f-49f4-a4c8-d91249e00b48/1d70d3e3-823e-4f03-b025-922afee7a83f/hj45r2w_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:**Ganado Europe (D).** Using facts in the chapter for Ganado Europe, assume that the exchange rate on January 2, 2016, in Exhibit 11.6 appreciated from $1.2300/€ to $1.6300/€. Calculate Ganado Europe's translated balance sheet for January 2, 2016, with the new exchange rate using the temporal rate method as shown in the popup window.
**a.** What is the amount of translation gain or loss?
**b.** Where should it appear in the financial statements?
*Enter a positive number for a gain and a negative for a loss.*
$ [___________] (Round to the nearest dollar.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Exercise 11-1 (Static) Exchange Rates LO 11-1 Suppose the direct foreign exchange rates in U.S. dollars are 1 British pound = 1 Canadian dollar = Required: a. What are the indirect exchange rates for the British pound and the Canadian dollar? b. How many pounds must a British company pay to purchase goods costing $8,000 from a U.S. company? c. How many U.S. dollars must be paid for a purchase costing 4,000 Canadian dollars? Required A $ 1.60 $ 0.74 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required B Required C What are the indirect exchange rates for the British pound and the Canadian dollar? Note: Round your answers to 4 decimal places. 1 USD 1 USD Answer is complete but not entirely correct. € 0.6250 British pounds $ 1.3510 Canadian dollarsarrow_forwardprovide correct answer need help!!arrow_forwardA3arrow_forward
- Qd 36.arrow_forwardVALUE OF EURO (U.S. dollars per euro) 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 QUANTITY OF EUROS (Billions) At an exchange rate of 1.5 per euro, the quantity of euros demanded is of euros demanded is + (?) billion euros, while at an exchange rate of 1.1 per euro, the quantity sloping. billion euros. This confirms that the demand curve for euros isarrow_forwardForeign currency transactions Melbourne Ltd purchased goods from France on 3 April 2022 on credit shipped FOB Paris. The cost of good is Euro 500,000 and outstanding as of 31 April 2021. On 3 April 2022, the exchange rate is A$1.00 = Euro 0.67. On 30 April 2022, exchange rate is A$1.00 = Euro 0.66 REQUIRED Provide the accounting entries necessary to account for the above purchase transaction for the month ending 30 April 2022.arrow_forward
- 1 points Clark Company, a U.S. corporation, sold inventory on December 1, 2022, with payment of 12,000 British pounds to be received in sixty days. The pertinent exchange rates were as follows: Date December 1 December 31 January 30 0000 Spot Rate $1.831 $1.976 $1.768 What amount of foreign exchange gain or loss should be recorded on December 317 $1,740 gain $1,740 loss $756 loss $756 gainarrow_forwardCanadian Denmark Euro S per Foreign Currency $.7800 $.2000 $.9900 Foreign Currency per $ 1.2821 5.0000 1.0101 a. How many Canadian dollars would you receive for $500? b. A Mercedes costs Euros 130,000. How many $ would you need? c. What is the cross rate of Canadian $ and Denmark?arrow_forwardA U.S. firm holds an asset in France and faces the following scenario: State 1 State 2 State 3 State 4 Probability 25% 25% 25% 25% Spot rate $ 2.10 per euro $ 2.00 per euro $ 1.90 per euro $ 1.80 per euro P* € 1,500 € 1,400 € 1,300 € 1,200 P $ 2,160 $ 1,900 $ 1,480 $ 1,260 In the above table, P* is the euro price of the asset held by the U.S. firm and P is the dollar price of the asset. Required: Compute the exchange exposure faced by the U.S. firm. What is the variance of the dollar price of this asset if the U.S. firm remains unhedged against this exposure? If the U.S. firm hedges against this exposure using a forward contract, what is the variance of the dollar value of the hedged position?arrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardQuestion 1/ chapter 2 An entity took out a bank loan for 12 million dinars on 1 January 20X1. It repaid 3 million dinars to the bank on 30 November 20X1. The entity has a reporting date of 31 December 20X1 and a functional currency of dollars ($). Exchange rates are as follows: What is the total loss arising (to the nearest $000) on the above transactions in the year ended 31 December 20X1?arrow_forwardQuestion 12 Given the following cross currency rates, identify an arbitrage trade and show the profit if you start with $1,000. (USD = U.S. dollar, SGD = Singapore dollar, CHF = Swiss franc) SGD:USD CHF:USD SGD:CHF 1,045.46 3.00 1.50 2.20arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education