
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:PM - XA dxA
PB
@M + XA dxB
M
(23)
d@M
since dxA 3D —-dxв 3D Фв
B
M
Since dx, = -dxB, Equation 19 can be also rewritten as:
4
dộM
= dộm = (@B – Pa)dxB =
Фв — ФА
(24)
dxB
dộm = -Padxg + @gdxa
Combining Equations 17 and 24 gives:
dộm
— фм — Хв
(25)
(d@m +
+ (Хд + Хв)ФА
dxB
PA
PM = XAPA + xB
dxB
(26)
since dxA 3D -dхв — ФА%3D Фм + хв
dxB
dxA
PA = PM – XB
А
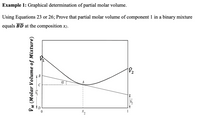
Transcribed Image Text:Example 1: Graphical determination of partial molar volume.
Using Equations 23 or 26; Prove that partial molar volume of component 1 in a binary mixture
equals BD at the composition x2.
A
1
VM (Molar Volume of Mixture)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Estimate the solubility of carbon dioxide (species 2) in water(species 1) at 323 K and 3.65 bar. Assume that the vapor phase can be represented by the truncated virial equation of state (equation 3.36 in your textbook). Data: B11 = - 834.2 cm³/mol Henry's law constant for carbon dioxide in water = 2939 bar at 323K. 4. B22 = - 104.2 cm³/mol B12 = - 153.4 cm³/mol ation beng used.arrow_forward1. How many grams of C are present in 4.98 grams of carbon tetrafluoride ? grams C. 2. How many grams of carbon tetrafluoride contain 2.68 grams of F ? grams carbon tetrafluoride.arrow_forwardThis problem is (13.8) from a book "Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics An Integrated Approach by M. Scott Shell"arrow_forward
- Problem 1: You are in charge or analyzing the following continuous process containing hexanol, octanol and decanol. hexanol octanol decanol hexanol decanol Unit 1 Unit 3 hexanol Unit 2 octanol And the following stream table and information are provided. Streams Component H: hexanol 1 2 3 4 5 6 1.00 O: octanol D: decanol 1.00 Molar flowrate 125 50 [mol/min] The molar flow rate of stream 5 is equal to 3 times the molar flow rate of stream 6. REMINDER: Make sure you clearly indicate your assumptions and the equations you use. a) What is the function of this process (what is it used for)? b) What assumptions can be made for this process? c) Write the different mole balances for unit 3.arrow_forwardNeed asaparrow_forward2. Consider the P-x-y diagram at 300 K for A-B mixtures at right. (a) What are the vapor pressures of A and B at 300 K? (b) A 25 mol-% A vapor mixture is isother- mally compressed from 1.5 to 2.0 bar. Does a 2-phase mixture form, and if so, what is the mole fraction of A in each resulting phase? (c) Using data at the azeotrope, compute the van Laar parameters a and 3 for A-B mix- tures at this temperature. P (bar) 2.8 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 XA or YAarrow_forward
- 1. Draw the gas absorption tower with N = 10 (similar to the figure below, but you should draw your own; instead of n or N, you should have actual numbers). Label EACH AND EVERY liquid and vapor streams – flowrates and mole fractions with correct subscripts. 2. Write definitions for the following terms in your own words: V, y, L, x, L, x, V, y., VYNU n-1⁹ n-19 Xa I V₂ Y₂ = YN+1 V₁ = V₁ Ya = y1 Ln-1 Xn-1 Yn Ln Xn +Plate 1 Plate n- Plate n Vn+1 Yn+1 Plate n + 1 Plate N = LN Xb = XNarrow_forwardPlease not Ai generated, show all steps in need to understand. Use table vaules thermodynamics engineering aprproch 10th.arrow_forwardQ3. The following information on the pressure-temperature diagram of nitrogen: P (atm) T(K) 0.123 33.3978 1.0 Triple point Critical point Normal boiling point Density of N₂(s): 1.03g/cm-³ N₂(1): 0.808g/cm-³ 63.15 126.19 77.35 Using this information, sketch a phase-equilibrium diagram of nitrogen and mark each point. Then, describe why the slope of each phase/phase equilibrium is positive or negative.arrow_forward
- 3. Fig. 3-1 shows z as function of mole fraction of butane in a nitrogen/butane mixture. The figure shows line for various pressures. Explain why z for pure butane behaves so differently from z for pure nitrogen as P increases, in particular, why is the butane z non-monotonic in pressure.arrow_forwardComplete the property table for water below. Use only the Thermodynamic Property Table for Water referring to the Smith, Van Ness and Abbot Thermodynamics textbook. P [kPa] V [m³/kg] H[ kJ/kg] T[°C] Phase Description X 500 Saturated liquid 171 2044.5 300 0.8 Note that x refers to the "quality" or the mass fraction of the water in vapor phase. If the system is composed of pure liquid water, x = 0. If the system is composed of pure gaseous steam, x = 1. The volume of a liquid/vapor system can be determined using the following equation. V = Vj + x(Vg-Vj) V - volume of saturated liquid water Va - volume of saturated gaseous steam Similar calculation can be done for other properties such as internal energy, entropy, and enthalpy. H = HỊ + x(Hg-H) Under phase description, indicate whether the system is composed of saturated liquid, saturated vapor, superheated vapor, or liquid-vapor mixture. Also note that when pressure is given, it is more advisable to use the Superheated Steam Table than…arrow_forward25.Simplify the following expressions using the Laws of Boolean Algebra, please specify which Law you have used. Y= AB(A+B) (B+B)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The