
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
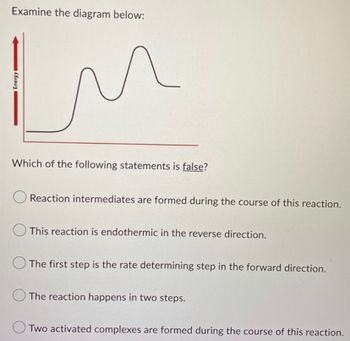
Transcribed Image Text:Examine the diagram below:
In
Energy
Which of the following statements is false?
Reaction intermediates are formed during the course of this reaction.
This reaction is endothermic in the reverse direction.
The first step is the rate determining step in the forward direction.
The reaction happens in two steps.
Two activated complexes are formed during the course of this reaction.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a) The two copper atoms in R have the ability to bind one molecule of O2 (Cu–O–O–Cu). If, at equilibrium, O2 is bound to 60% of the R, what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction R + O2 ⇌ RO2 ? b) Hemoglobin, abbreviated Hb, is the oxygen carrier protein in mammals. The equilibrium constant for the reaction of Hb with O2(g) under the same conditions, Hb + O2 ⇌ HbO2, is 225. What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction HbO2 + R ⇌ RO2 + Hb ?arrow_forward33. What property of a reaction can we use to predict the effect of a change in temperature on the equilibrium constant? lowing re 1217 estamararrow_forwardHemoglobin (Hb), carries oxygen from our lungs to the rest of out body. The figure below shows oxygen binding to the active site of Hb.ONON Fe NNN NCarbon monoxide is poisonous because it binds to Hb in a similar fashion and can displace oxygen and block O2 from binding to Hb.a) The reaction below describes the equilibrium for the displacement of O2 in the HbO2 complex by CO to form HbCO. Write an equilibrium expression for this reaction.HbO2 + CO HbCO + O2Kdisp = ______________b) The equations below describe the equilibrium for O2 and CO binding to Hb. Using the information provided determine the value of KdispHb +O2 HbO2?"#= [???#]=3.2 [??][?#] Hb + COHbCO ?$"= [????]=750 [??][??] 16 Initials __________c) Use your Kdisp to calculate ΔGo for the displacement reaction at 298 K.d) The kinetics of CO displacement of O2 were studied under equal concentrations of each gas at a variety of temperatures. A plot of lnkdisp vs 1/T is shown below, use this information to calculate the…arrow_forward
- Table 11.7 (data) Color Change Relative to Reference Test performed Add Fe(NO3)3 Add KSCN Add AgNO 3 Cool Solutionarrow_forwardWhile all different types of physical states can be present in a chemical equation, the incorporation of, are not expressed in the equilibrium constant expression. gases aqueous solution solid and liquids O none of the abovearrow_forwardIn an aqueous chloride solution cobalt(II) exists in equilibrium with the complex ion CoCl42-. Co2+(aq) is pink and CoCl42-(aq) is blue. ... At Low Temperature the pink color predominates. ... ... At High Temperature the blue color is strong. ... If we represent the equilibrium as:... CoCl42-(aq) Co2+(aq) + 4Cl-(aq)We can conclude that: fill in the blank 1 1. This reaction is: A. Exothermic B. Endothermic C. Neutral D. More information is needed to answer this question. fill in the blank 2 2. When the temperature is increased the equilibrium constant, K: A. Increases B. Decreases C. Remains the same D. More information is needed to answer this question. fill in the blank 3 3. When the temperature is increased the equilibrium concentration of CoCl42-: A. Increases B. Decreases C. Remains the same D. More information is needed to answer this question.arrow_forward
- 1. The shape of boron trihydride, BH3, is 2. In an exothermic reaction, the potential energy of the products is than the potential energy of the reactants. 3. A system at equilibrium always has forward and reverse reaction rates which are 4. A solution at 25°C with a pOH of 3.45 has a pH of 5. When nitric acid is titrated to an end point by lithium hydroxide, two products are and O 6. The standard reduction potential table lists the Evalues of half-cell reactions measured in combination with the standard half-cell.arrow_forwardNeed help wit this, please explain all the steps.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant is given for one of the reactions below. Determine the value of the missing equilibrium constant. N2O4(g) = 2NO2 (g) Kc = 1.46 5N2O4(g) = 10NO2 (g) K. = ? %3D 0.322 O 5.40 O 1.46 O 1.13 O 6.63arrow_forward
- Is the energy of the compounds higher or lower before the formation of an activated complex?arrow_forwardWhen solid lead(II) phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of lead(II) ions to phosphate ions is which of the following? 2:1 3:2 1:1 2:3 1:2arrow_forward5. Consider the following reaction: 2A+B C A kinetics study on this reaction yielded the following data: [A] mol/L [B] mol/L Rate = mol/L/s 0.0250 0.0400 4.06 x 10-3 0.0250 0.0800 4.06 x 10-3 0.0500 0.0800 4.06 x 10-3 Calculate the K constant for the above reaction: ()+(p) 28 a a. 0.025 mol/L.s evods A b. 0.0010 mol/L.s c. 0.0020 mol/L.s d. 0.00406 mol/L. s e. None of the above (p) 2 + (p) OS (2):82 svods evil to onait evods all bris ang wond 6. Calculate AG° for the following reaction: Thiog 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) AGf in kJ/moles for SO2(g) is -300.2, for SO3(g) is -371.1 and for O2 is 0.0. a. +141.8 kJ b. +70.9 kJ c. #70.9 kJ enimmeted d. -141.8 kJ lom EL 7. Consider the following reaction for the production of SO3: 18.8 XC70 b 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g) Which of the following expressions best illustrates the rate of the product? a. rate = 2A[SO3] / At b. rate = A[SO3]/2At c. rate = 2A[SO3]/2At プラ FRASERarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY