
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
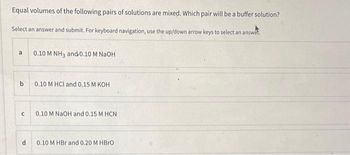
Transcribed Image Text:Equal volumes of the following pairs of solutions are mixed. Which pair will be a buffer solution?
Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answe
a
b
с
d
0.10 M NH3 and 0.10 M NaOH
0.10 M HCl and 0.15 M KOH
0.10 M NaOH and 0.15 M HCN
0.10 M HBr and 0.20 M HBrO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Buffer solution
VIEW Step 2: Why Ammonia and NaOH combination can not act like a buffer?
VIEW Step 3: Why HCl and NaOH combination can not act like a buffer?
VIEW Step 4: Why HBr and HBrO combination can not act like a buffer?
VIEW Step 5: Why HCN and NaOH combination will act like a buffer?
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A solution containing H2CO3 and HCO3- is a buffer (in blood). Which of the two would be consumed if a small increment of a dilute solution of the following is added.i) HCl (aq)ii) NaOH (aq)arrow_forwardSome soluble compounds are listed in the table below. Complete the table by filling in the name or chemical formula of each compound, whichever is missing. (If there is more than one way to name the compound, choose the name used when the compound is dissolved in water.) Also classify the compound using the checkboxes. compound 0 HCH₂ CO₂ NH3 HCIO4 name barium hydroxide 0 0 type of compound (check all that apply) strong weak strong weak acid base base acid ionic molecular 0 0 0 0 X Sarrow_forwardConsider the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.100 M HCl with 0.050 M NaOH. At what volume of added NaOH is the solution a buffer solution?arrow_forward
- 25.0 mL of a weak base is titrated with 0.708 M solution of HCl. The equivalence point is reached when 13.0 mL of HCl is added. What is the concentration of the original 25.0 mL weak base solution?arrow_forwardA 18.8 mL sample of a 0.424 M aqueous acetic acid solution is titrated with a 0.331 M aqueous potassium hydroxide solution. What is the pH at the start of the titration, before any potassium hydroxide has been added? pH =arrow_forwardA 39.0 mL sample of a 0.540 M aqueous hypochlorous acid solution is titrated with a 0.390 M aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide. How many milliliters of sodium hydroxide must be added to reach a pH of 7.176? mLarrow_forward
- Can you help me answer this questions!arrow_forwardA 48.3 mL sample of a 0.492 M aqueous hypochlorous acid solution is titrated with a 0.229 M aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide. How many milliliters of potassium hydroxide must be added to reach a pH of 7.241? mLarrow_forwardA 0.658 g sample of a diprotic acid is dissolved in water and titrated with 0.130 M NAOH. What is the molar mass of the acid if 38.4 mL of the NaOH solution is required to neutralize the sample? Assume the volume of NaOH corresponds to the second equivalence point. 10 11 12 13 molar mass: g/mol 18 19 20 21 22 23 24arrow_forward
- The titration of a 5.00 mL sample of an HCl solution of unknown concentration requires 4.90 mL of a 0.1000 M NaOH solution to reach the equivalence point. What is the concentration of the unknown HCl solution in M?arrow_forwardI don’t know how to do this questionarrow_forwardMixing which of the following pairs will make a buffer solution? O CsF, HF O KBr, HBr O Nal, HI RbCl, HC1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY