
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The steps of the chymotrypsin mechanisms are listed below (1-7). Put the steps of chymotrypsin mechanism in the correct order. Figure representing chymotrypsin mechanism is given for reference.
a.The portion (N-terminal end) of original substrate with the new C terminus diffuses away
b. Substrate binding
c. His 57 catalyzes removal of H from Ser 195 hydroxyl; Ser 195’s nucleophilic O attacks carbonyl C of substrate; tetrahedral intermediate is formed
d. Water binding; water is deprotonated by His 57; resulting OH nucleophilically attacks carbonyl of remaining substrate; tetrahedral intermediate is formed
e. His 57 donates H to N of peptide bond and tetrahedral intermediate decomposes; the portion of original substrate (the C-terminal end) with the new amino terminus diffuses away
f. The portion (N-terminal end) of original substrate with the new C terminus is formed
g. His 57 protonates O from Ser 195, leading to collapse of tetrahedral intermediate
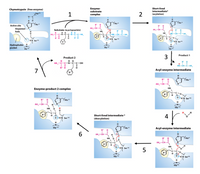
Transcribed Image Text:Enzyme-
substrate
complex
Short-lived
intermediate
(acylation)
Chymotrypsin (free enzyme)
Asp
1
2
H
YHis"
His
Active site
R'
AA
Охуanion
hole
Substrate (a polypeptide)
AA-CH -C
HN
H H
-N-C-C-N-C-C-AA
HH
HN
AA
HN
oHN Ser
HN Ser
HN Ser
Hydrophobic H
pocket
Gly
Gly
Product 1
3
Product 2
H H
-C-C-N-C-C-OH
AA
HN-CH-C-AA
Acyl-enzyme intermediate
R
R'
AA-CH
HN
Enzyme-product 2 complex
R
H.
R'
YHis
Ser
H.
AA-CH -C
Gly
HN
R'
Short-lived intermediate*
OHN Ser19
(deacylation)
H
N-
Gly
YHis "
Acyl-enzyme intermediate
R'
AA-CH
YHis"
HN
HN
HN Sers
5
R
Gly
OHN Seras
Gly
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- From the complete oxidation of glucose (glucose → 6CO2), how many total nucleotide triphosphates are yielded (be sure to deduct payback) as part of substrate level phosphorylation?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast the c4 pathway and the malate–aspartate shuttle in bullet format, meaning list the similarities and differences.arrow_forwardThe purified OXA-M290 enzyme can now be tested to determine which β-lactamase inhibitor is most effective. This inhibitor could be prescribed in combination with a β-lactam antibiotic to treat the infection caused by the E. coli KGH1 strain. Before testing inhibitors against OXA-M290, the kinetic activity of this enzyme must first be measured. The activity of OXA-M290 is measured using nitrocefin, a chromogenic β-lactam antibiotic. When nitrocefin is hydrolyzed by a β-lactamase, it changes from yellow to red in colour. The nitrocefin hydrolysis product has an extinction coefficient of 20,500 M-1 cm-1 at 486 nm. The hydrolysis of 60 μM nitrocefin by 1 nM OXA-M290 is monitored using a microplate reader. The absorbance of the wells in the plate is measured at 486 nm every 30 seconds. This experiment is carried out with three replicates, generating the following data: Time (min) Absorbance of Replicate 1 Absorbance of Replicate 2 Absorbance of Replicate 3 0.5 0.0984…arrow_forward
- The diagram below shows the substrate binding cleft for a protease, providing the substrate structure, and indicating the residues (using one-letter code) that line the four specificity pockets. 1 M F H₂N K R IZ 2 3 P F S W оо E 4 The protease is known to cleave the amide linkage between W and E residues for substrates containing the WEFD sequence. Using 3-letter code with amino acids linked by a "dash" (ex. GLY-ALA), the N-terminal product is A and the C-terminal product is Aarrow_forwardThe enzymatic activity of PFK1 is generally measured by set- ting up a coupled enzyme assay system whereby aldolase, triose phos- phate isomerase, and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase are added to the assay mixture. For the latter enzyme, NADH is added and its change in concentration is readily monitored at 340 nm. Write the chain of reactions catalyzed by these enzymes using structural formulas, label substrates and products, and explain why the coupled en- zyme assay system leads to oxidation of NADH. While the chain of reac- tions is similar to those in glycolysis, there is a critical difference because of the dehydrogenase enzyme. Describe how this enzyme causes the chain of reactions to differ from those in glycolysis.arrow_forwardWhy is de novo biosynthesis of purines markedly elevated in patients with a deficiency in hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT)? 5-Fluoruracil is converted to methotrexate by a DPD deficiency, leading to increased purine biosynthesis. HGPRT deficiency prevents purine salvage, leading to increased purine biosynthesis to make up for it. HGPRT increases pyrimidine salvage and thereby increases purine biosynthesis as a result. Increased purine biosynthesis is the result of ATP hydrolysis during the production of cyclic AMP.arrow_forward
- Proteases are one of the main drug targets. Choose the False statement regarding proteases. A. Proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds. B. Water is a reactant in the reaction catalyzed by proteases. C. Proteases, like all enzymes show substrate specificity, meaning they cleave only substate that fit the bonding product. D. Proteases rely on the proton transfer from NADH to the substrate. E. Protease mechanism involves only acid-base catalysis.arrow_forwardA child with coarse facies, corneal clouding, joint stiffness and mental retardation is found to have a Damage to this enzyme directly affects which of partial defect in N-acetylglucosaminotransferase. the following biochemical functions? A. Formation of polysomes B. Microtubule attachment to centrioles C. Synthesis of ribosomal RNA D. Targeting of enzymes for lysosomes E. Transport of sugars into mitochondriaarrow_forwardWithin the body, CoQ 10 can be found in an oxidized or reduced form (also known as ubiquinone and ubiquinol). Describe how these structures differ and the biochemical role of coenzyme Q10.arrow_forward
- PLP can catalyze both \alpha, \beta elimination reactions and \beta, \gamma - elimination reactions. Propose a mechanism for the following PLP - catalyzed \beta, \gamma eliminationarrow_forwardAnswer the following using the picture attached: A. How does pepsin differ from chymotrypsin in terms of its active site residues and mechanism? B. How do these changes permit pepsin to operate at such a low pH?arrow_forwardComplete the paragraph describing the fate of glutamate, labeled at the Cγ position with 14C, once it has been introduced to the TCA cycle. In the second round (A.) 50%,B.) 25%, C.)or NONE of the label is lost) , however, in each subsequent cycle (25%,50%, or NONE of the label is lost). This occurs becuase at the end of the second round the label is (A.)Equally dsitributed among all carbons B.) part of the carboxylate group C.) Positioned on the erminal Carbon) of oxaloacetate and each cycle (A.) releases a carbon B.) Releases two carbons C.) adds a carbon) from oxaloacetate.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON