
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577206
Author: Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
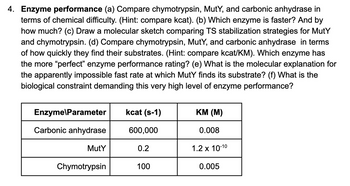
Transcribed Image Text:4. Enzyme performance (a) Compare chymotrypsin, MutY, and carbonic anhydrase in
terms of chemical difficulty. (Hint: compare kcat). (b) Which enzyme is faster? And by
how much? (c) Draw a molecular sketch comparing TS stabilization strategies for Muty
and chymotrypsin. (d) Compare chymotrypsin, Muty, and carbonic anhydrase in terms
of how quickly they find their substrates. (Hint: compare kcat/KM). Which enzyme has
the more "perfect" enzyme performance rating? (e) What is the molecular explanation for
the apparently impossible fast rate at which Muty finds its substrate? (f) What is the
biological constraint demanding this very high level of enzyme performance?
Enzyme\Parameter
Carbonic anhydrase
Muty
Chymotrypsin
kcat (s-1)
600,000
0.2
100
KM (M)
0.008
1.2 x 10-10
0.005
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 5.5 Explain the effect of each type of inhibitor on the apparent kinetic parameters: (1) Inhibitor binds only free enzyme does Km increase, decrease, not change? does Vmax increase, decrease, not change? (2) Inhibitor binds only ES complex does Km increase, decrease, not change? does Vmax increase, decrease, not change? (3)Inhibitor binds E and ES equally does Km increase, decrease, not change? does Vmax increase, decrease, not change?arrow_forward1. For enzyme catalyzed reaction: ki S + E=X (fast) k2 X -2> P + E (slow) derive the rate law and answer the following: a) What is meant by Michaelis-Menten constant km? (b) Prove that order of reaction in substrate changes from unity to zero at higher [S]. (c) What is the rate and value of km, if k2 >> k1. (d) Draw the potential energy diagram for enzyme catalyzed reaction.arrow_forward22. Describe the Induced fit of Hemoglobin, Hb (enzyme-like protein) which has quarternary structure and exhibits allosteric activation with cooperativity.arrow_forward
- 3. (a) ( The equilibria for release of molecular dioxygen (O2) and protons (H+) by human hemo- globin (HbA) are illustrated in the scheme below in which the ionization (Ka, Ka') and ligand binding (K02, Ko2') are given as dissociation constants. The proton ionizations are known to be due to Hisẞ146 and account for a major part of the Bohr effect. A mutant hemoglobin is found for which Ka = 6.6 E-9 (pKa =8.18), Ka= 2.0 E-10 (pKa' = 9.70) and Ko2 = 1.0. What is the value of Ko2' for this mutant hemo- globin? K 02 = 1.0 Κα pka = 6.3 E-7 = 6.2 H*Hb O₂ H* + НЬ 02 HHb 02 Ka' = 2.0 E-8 pKa = 7.7 H+ + Hb + 02 K 02' = 0.032 (b) (' For the mutant hemoglobin described above, illustrate the relative changes that will be observed for the oxygen dissociation curve of Y versus pO2 compared to that of normal hemoglobin where Y represents thefraction of heme sites bound by O2. Explain whether there will be a change in the Bohr effect under physiological conditions, considering the pH of normal arterial…arrow_forward3.18: An enzyme E binds a substrate S and a cofactor C. The equilibrium dissociation constantKd,S of the enzyme-substrate complex ES is 1 μM, for EC it is 10 μM. When the cofactor Cis present, K’d,S is decreased to 0.1 μM. What is the value for the dissociation constant K’d,C of the enzyme-cofactor complex in the presence of substrate S? Calculate the interactionenergy ΔΔGint for cofactor and substrate binding.arrow_forwardCalculate the rate enhancement for the enzyme pair: Enzyme 1: Kcat (sec-1)= 5.5 KM (µ M) = 1245 Kcat / KM = 0.00442 (µ M-1 sec-1) Enzyme 2: Kcat (sec-1)= 3.2 KM (µ M) = 1785 Kcat / KM = 0.00179 (µ M-1 sec-1)arrow_forward
- 3. (a) The beakers below represent different conditions for measuring the initial velocity (vo) of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction under the steady-state approximation. The gray "donut-shaped" struc- tures represent the enzyme. The blue, filled circles represent free substrate molecules. The red cir- cles represent substrate molecules bound in the active site of the enzyme forming the Michaelis (ES) complex. Indicate in the diagram of the double reciprocal plot which kinetic parameters or variables each of the three "beaker conditions" represent either alone or in combination with another. A B 455 C V₁™¹ [So]-¹arrow_forwardB) Uncompetitive inhibition: Where do these inhibitors bind? To what mechanistic form of the enzyme do these inhibitors bind? What are changes to Km and Vmax?arrow_forwardam. 206.arrow_forward
- Chemical scheme for enzyme catalysis (a) Write the chemical equations for enzyme,substrate, enzyme•substrate complex, and product as for a typical Michaelis-Mentenenzyme (b) At what condition is half of the enzyme expected to be saturated withsubstrate? (c) Plot the rate of product formation as a function of substrate concentration.(d) Indicate the KM parameter on your rate vs substrate plot.arrow_forward5. Shown below are the first steps in the mechanism of a cysteine protease, which catalyses amide bond hydrolysis in a similar manner as serine proteases. (a) Complete this mechanisms, and (b) sketch the approximate reaction coordinate diagram for this catalyzed reaction relative to the uncatalyzed proteolysis. HN N HN cysteine proteasearrow_forwardq41 please calculate the unknown concentration of the protein D wih an absorbance value of A412 given the standard curve indicated in the table. write your answers in numbers only with 2 decimals. protein concentration (ug/ml) absorbance 0 0.000 0.02 0.161 0.04 0.284 0.06 0.438 0.08 0.572 0.10 0.762arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College