
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
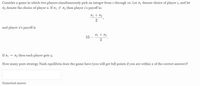
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a game in which two players simultaneously pick an integer from 1 through 10. Let s1 denote choice of player 1, and let
S2 denote the choice of player 2. If s1 7 82 then player 1's payoff is:
Si + 82
2
and player 2's payoff is
10 – ,*.
Si + 82
2
If s1 = 82 then each player gets 5.
How many pure strategy Nash equilibria does the game have (you will get full points if you are within 2 of the correct answer)?
Numerical answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following game. You will roll a fair, 6-sided die either once or twice. You decide whether to do the second roll after you see how the first one lands. The payoff is $n, where n is the outcome of the last roll. For example, if the first roll lands 4 and the second lands 2, you win $2. If you only do one roll and it lands 4, you win $4. Suppose you make your decision about whether to go for a second roll based on expected monetary value. Then you will go for a second roll if (and only if) the first roll lands x or lower. What is x?arrow_forwardIf the players play pure strategies, the game has no Nash equilibrium. But what if they choose their moves randomly? Let each player instead opt for a mixed strategy instead of a pure strategy. The first will play action Z with probability p, and the second will play action L with probability q. At which pair (p, q) are the mixed strategies of the players in equilibrium? At which pair (p, q) does neither player want to change strategy? When are both strategies simultaneously the best response?arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Refer to Table Left-Right-ZigZag. How many pure strategy Nash equilibria does this game have? Table: Left-Right-ZigZag Player 1 Drive left Driver right Zigzag 1) 1 2) 2 3) 3 4) 4 5) None of the above. Drive left (1,1) (-1,-1) (0,0) Player 2 Driver right (-1,-1) (1,1) (0,0) Zigzag (0,0) (0,0) (0,0)arrow_forwardThe count is three balls and two strikes, and the bases are empty. The batter wants to maximize the probability of getting a hit or a walk, while the pitcher wants to minimize this probability. The pitcher has to decide whether to throw a fast ball or a curve ball, while the batter has to decide whether to prepare for a fast ball or a curve ball. The strategic form of this game is shown here. Find all Nash equilibria in mixed strategies.arrow_forwardConsider the following two player game. In each cell the first number refers to the payoff to Player 1 while the second number refers to the payoff to Player 2. Suppose the two players move simultaneously (at the same time). Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? Player #1 Player #2 Top Bottom Left 7.7 4.0 Right 0,4 4,4 O There are three equilibria in this game: two pure strategy equilibria at [Top, Left] and [Bottom, Right) and al third equilibrium in mixed strategies. In the mixed strategy equilibrium of this game. Player 1 should play Top with probability 2/5 and Bottom with probability 3/5; Player 2 should play Left with probability 2/5 and Right with probability 3/5. O There are three equilibria in this game; two pure strategy equilibria at (Top. Left) and (Bottom, Right) and a third equilibrium in mixed strategies. In the mixed strategy equilibrium of this game, both players should randomize over the strategies with probability and %. O There is a unique dominant…arrow_forward
- Please help with #1arrow_forwardPlease help with #2arrow_forwardConsider a simultaneous move game with two players. Player 1 has three possible actions (A, B, or C) and Player 2 has two possible actions (D or E.) In the payoff matrix below, each cell contains the payoff for Player 1 followed by the payoff for Player 2. Identify any pure strategy Nash Equilibria in this game. If there are none, state this clearly.arrow_forward
- 1.a) If the three executives of a fraudulent organization report nothing to the authorities, each gets a payoff of 100. If at least one of them blows the whistle, then those who reported the fraud get 28, while those who didn’t get -100. Suppose they play a symmetric mixed-strategy Nash equilibrium where each is silent (does not report fraud) with probability p. What is p?A, 0.1B, 0.28C, 0.5D, 0.8 b) In a two-player game, with strategies and (some known and some unknown) payoffs as shown below, suppose a mixed-strategy equilibrium exists where 1 plays C with probability 3/4, and Player 2 randomizes over X, Y, and Z with equal probabilities. What are the pure-strategy equilibria of this game? A, (A, Y) and (B, X)B, (A, Z) and (C, Y)C, (B, X) and (C, X)D, (C, X) and (C, Y)arrow_forwardHello, please help me to solve this Game Theory question. Thanks in advance! Hobby hunter Jack decides what to do the next weekend. He can either stay at home and watch movies (Movies), or call his friend Katherine to go hunting (Hunt). If he stays in, both Jack and Katherine get a payoff of 2. If he decides to hunt, he knows the situation with his friend will resemble a classic stag hunt game with simultaneous moves: Hunting a stag is better than hunting a rabbit, but it only works if they cooperate. The hunting subgame is captured as: Katherine Stag Rabbit Jack Stag 3 , 3 0 , 1 Rabbit 1 , 0 1 , 1 Draw the entire game as an extensive form (game tree), capturing both Jack’s initial decision (M or H) and the subsequent hunting game. Make sure to correctly label all players, actions, and information sets.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education