
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
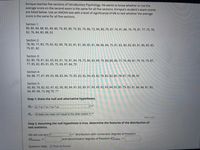
Transcribed Image Text:Enrique teaches five sections of Introductory Psychology. He wants to know whether or not the
average score on the second exam is the same for all five sections. Enrique's student's exam scores
are listed below. Use an ANOVA test with a level of significance of 6% to test whether the average
Score is the same for all five sections.
Section 1:
80, 80, 84, 88, 85, 89, 80, 79, 85, 80, 70, 82, 76, 86, 72, 84, 80, 79, 87, 74, 81, 86, 74, 79, 81, 77, 75, 76,
82, 76, 84, 80, 88, 92
Section 2:
78, 90, 77, 83, 79, 82, 82, 89, 78, 82, 81, 81, 80, 85, 81, 84, 86, 84, 75, 81, 82, 80, 83, 83, 81, 86, 85, 82,
79, 81, 82
Section 3:
82, 80, 78, 81, 82, 83, 83, 81, 76, 81, 84, 78, 75, 86, 83, 89, 79, 84, 80, 80, 77, 76, 80, 81, 79, 76, 79, 87,
77, 85, 82, 85, 81, 85, 75, 83, 87, 84, 79
Section 4:
84, 88, 77, 87, 89, 83, 88, 83, 84, 70, 85, 82, 82, 84, 83, 82, 78, 83, 82, 85, 78, 81, 78, 86, 87
Section 5:
83, 85, 78, 82, 82, 87, 82, 90, 80, 84, 87, 83, 89, 81, 80, 89, 82, 83, 84, 92, 85, 79, 83, 91, 84, 84, 81, 82,
84, 89, 88, 73, 86 78, 77
Step 1: State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Ho: P1 = P2 = µ3 = H4 = Ps
Ha: At least one mean isn't equal to the other means v
Part 2 of 4
Step 2: Assuming the null hypothesis is true, determine the features of the distribution of
test statistics.
We will use a(n) F
vv distribution with numerator degrees of freedom
d fbetween =
and denominator degrees of freedom d fwithin
Question Help: D Post to forum
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Read the statements and decide whether it is true or false. The number of degrees of freedom for a test of independence is equal to the sample size minus one. The test to use when determining if the college or university a student chooses to attend is related to his or her socioeconomic status is a test for independence.arrow_forwardCharlie isinterested in whether elementary school students, middle school students, or high school students spend more time reading in the summer. In the beginning of the school year he asks 20 elementary school students, 15 middle school students and 40 high school students to report the number of pages they read over the summer. What statistical test should Charlie use to test his research question?arrow_forwardHow often do you go out dancing? This question was asked by a professional survey group on behalf of the National Arts Survey. A random sample of 95 single men showed that 24% went out dancing occasionally. Another random sample of 92 single women showed that 21% went out dancing occasionally. Is the proportion of single men who go out dancing occasionally higher than the proportion of single women? Use a 5% level of significance. If men are group 1 and women are group 2, what is the p-value for this hypothesis test? 0.656 0.688 0.344 0.217 0.242arrow_forward
- I need help with something regarding this problem. The National Sleep Foundation recommends that adults aged 18 to 64 get an average of 8 hours of sleep per night. A survey of sleep hours was taken during a Statistics class. The data is listed below: 4, 5, 5, 5, 5.5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10 Do we have enough evidence at the 0.05 significance level to say that statistics students tend to get less sleep than the recommended average of 8 hours per night? How would I get the degrees of freedom?arrow_forwardTwenty years ago, 47% of parents of children in high school felt it was a serious problem that high school students were not being taught enough math and science. A recent survey found that 293 of 900 parents of children in high school felt it was a serious problem that high school students were not being taught enough math and science. Do parents feel differently today than they did twenty years ago? Use the a = 0.01 level of significance. ... Find the test statistic. Zn = (Round to two decimal places as needed.) %3Darrow_forwardAnswer and explain your answer corectly. i ll rate accordingly.arrow_forward
- Please apply table to question. Thanks!arrow_forwardth Last year over 8000 students took an entrance exam at a certain state university. Tom's score was at the 55 percentile. Leila's score was at the 86 percentile. (a) Which of the following must be true about Tom's and Leila's scores? O Tom scored higher than Leila. O Both Tom and Leila scored higher than the median. O Leila answered 31 more questions correctly than Tom. O Tom's and Leila's scores were both in the bottom half of all scores. (b) Which of the following must be true about Tom's score? O Tom scored lower than about 55% of the students who took the exam. O Tom got about 55% of the questions correct. Tom scored higher than about 55% of the students who took the exam. Tom got about 55% of the questions wrong. Submit Assignme Continue iert 144 %23 4. 6. 8 R Y U H K L A. D paus V. B M alt ctri alt USE YOUR Dew de LLarrow_forwardThe Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that the official unemployment rate for Black people was 10.4% and 4.7% for White people in February 2015. Select all correct answers for this question. O The samples of white and black people are independent. The explanatory variable is the unemployment rate. The response variable is the unemployment rate. The response variable is race.arrow_forward
- Please answer all the questions in literal barrow_forwardThe first picture is the question and the second is the ones that I need help with. Thanks!arrow_forwardYou collect data on number of hours spent studying, on average, throughout the Fall 2019 semester for all Stonehill students. You have a colleague at the College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA who collects the same data at Holy Cross. You want to compare the average number of hours spent studying during the Fall 2019 semester for male students at Stonehill, female students at Stonehill, male students at Holy Cross and female students at Holy Cross. Which statistical test would you use to compare the students at Stonehill and Holy Cross to look for significant differences in study time? a. one sample t test b. two sample t test c. repeated measures t test d. ANOVAarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman