Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:ail
O Maps
O Web design tutori.
W MATH180: HW08-.
Update
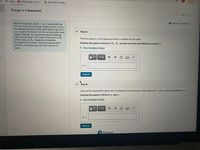
Energy of a Spacecraft
< 2 of 7
I Review I Constants
Very far from earth (at R = 00), a spacecraft has
run out of fuel and its kinetic energy is zero. If only
the gravitational force of the earth were to act on it
(i.e., neglect the forces from the sun and other solar
system objects), the spacecraft would eventually
crash into the earth. The mass of the earth is M.
and its radius is Re. Neglect air resistance
throughout this problem, since the spacecraft is
primarily moving through the near vacuum of
space.
Part A
Find the speed s. of the spacecraft when it crashes into the earth.
Express the speed in terms of Me, Re, and the universal gravitational constant G.
• View Available Hint(s)
>
Se =
Submit
Part B
Now find the spacecraft's speed when its distance from the center of the earth is R = a Re, where the coefficient a > 1.
Express the speed in terms of s, and a.
• View Available Hint(s)
Sa =
Submit
P Pearson
MacBook PrO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- (a) What is the gravitational potential energy of a two-particle system with masses 6.8 kg and 3.0 kg, if they are separated by 1.7 m? If you triple the separation between the particles, how much work is done (b) by the gravitational force between the particles and (c) by you?arrow_forwardneed help on attatched questionarrow_forwardA 2 kg ball rolls off a 26 m high cliff, and lands 28 m from the base of the cliff. Express the displacement and the gravitational force in terms of vectors and calculate the work done by the gravitational force. Note that the gravitational force is , where g is a positive number (+9.8 N/kg). (Let the origin be at the base of the cliff, with the +x direction towards where the ball lands, and the +y direction taken to be upwards.) Displacement 7 = Gravitational Force F= Work W = Additional Materials. Narrow_forward
- A satellite in Earth orbit has a mass of 91 kg and is at an altitude of 2.04 x 10° m. (Assume that U = 0 as r→ o.) (a) What is the potential energy of the satellite-Earth system? (b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by the Earth on the satellite? (c) What force, if any, does the satellite exert on the Earth? (Enter the magnitude of the force, if there is no force enter 0.) Narrow_forwardThere exista a spherical planet with a mass of M and a radius of R. How much energy is required to take a rocket of a mass m from rest on the surface of the planet to a circular orbit a height h above the surface?Find using the Energy Difference Ef -Ei where Ef is the energy in orbit and Ei is the energy at rest on the surface. h is not smallarrow_forwardHow much work would be required to move the moon (7.36 E 22 kg) from its current obit of 385 E 6 m to an orbit of 504 E 6 m. Assume the mass of the earth to be 6.00 E 24 kg and G = 6.67 E -11. Include the correct sign. This would be work external to the earth/moon system, not gravitational work. Think of it as the energy that would have to be added or removed from the system to allow the calculated change in gravitational potential energy.arrow_forward
- A 986-kg satellite orbits the Earth at a constant altitude of 101-km. (c) What is the change in the system's potential energy?arrow_forwardA satellite in Earth orbit has a mass of 103 kg and is at an altitude of 1.91 106 m. (Assume that U = 0 as r → ∞.) (a) What is the potential energy of the satellite–Earth system? (J) (b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by the Earth on the satellite? (N) (c) What force, if any, does the satellite exert on the Earth? (Enter the magnitude of the force, if there is no force enter 0.) (N)arrow_forwardSSM (a) What is the escape speed on a spherical asteroid whose radius is 500 km and whose gravitational acceleration at the surface is 3.0 m/s2? (b) How far from the surface will a particle go if it leaves the asteroid’s surface with a radial speed of 1000 m/s? (c) With what speed will an object hit the asteroid if it is dropped from 1000 km above the surface?arrow_forward
- A satellite has a mass of 94 kg and is located at 2.04 106 m above the surface of Earth. (a) What is the potential energy associated with the satellite at this location? J(b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force on the satellite?arrow_forwardHow much energy AE would be required to move the Moon from its present orbit around Earth to a location that is twice as far away? Assume the Moon's orbit around Earth is nearly circular and has a radius of 3.84 × 10° m. ΔΕ= Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios