
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
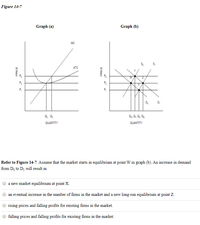
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 14-7
Graph (a)
Graph (b)
MC
ATC
1.
D,
Q, a, 0, 0:
QUANTITY
QUANTITY
Refer to Figure 14-7. Assume that the market starts in equilibrium at point W in graph (b). An increase in demand
from Do to Di will result in
a new market equilibrium at point X.
an eventual increase in the number of firms in the market and a new long-run equilibrium at point Z.
rising prices and falling profits for existing firms in the market.
falling prices and falling profits for existing firms in the market.
PRICE
PRICE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a purely competitive market at its long-run equilibrium, which of the following is not true? a The marginal benefit of the last unit of the product equals the marginal cost of producing that unit. b The maximum willingness of buyers to pay for the last unit of the product equals the minimum acceptable price for the seller of that unit. c Price equals marginal cost, and they are equal to the lowest attainable average cost of production. d The combined amount of consumer and producer surpluses is at its minimum possible.arrow_forwardM/c question - Micro 31) Refer to Figure 14-13. When a firm in a competitive market, like the one depicted in panel (a), observes market price rising from P1 to P2, what is most likely the cause? A. the exit of existing firms in the market B. an increase in market supply from Supply0 to Supply1 C. the entrance of new firms into the market D. an increase in market demand from Demand0 to Demand1 30) A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market discovers that, at its current level of production, price is greater than marginal cost. What should it do? A. It should increase its output. B. It should reduce its output but continue operating. C. It should shut down. D. It should keep output the same.arrow_forwards 1, 12 & 13 Assignment Saved Help Save & Exit Assume a purely competitive increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium. If a decline in demand occurs, firms will Multiple Choice leave the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will rise. enter the industry and price and quantity will both rise. leave the industry and price and quantity will both rise. leave the industry, price will fall, and quantity produced will fall.arrow_forward
- If there were 10 firms in this market, the short-run equilibrium price of steel would be $______per ton. At that price, firms in this industry would ______(shut down/operate at a loss/ earn a positive profit/ earn zero profit). Therefore, in the long run, firms would__________(enter/ exit/ neither enter nor exit) the steel market. Because you know that competitive firms earn______(zero/ negative/ positive) economic profit in the long run, you know the long-run equilibrium price must be $_____per ton. From the graph, you can see that this means there will be_____(10/20/30) firms operating in the steel industry in long-run equilibrium.arrow_forwardQ27arrow_forwardQUESTION 6 Which of the following is a necessary condition for a firm to be able to bundle a new product with an existing one? consumers' willingness to pay for the two products are inversely related. the firm must operate in a perfectly competitive market. consumers must have a higher willingness to pay for the new product than for the older existing product. the two goods must be substitute products.arrow_forward
- 10 The industry in the figure given below on the left consists of many firms with identical cost structures, and the industry experiences constant returns to scale. a. Draw the short-run market supply curve up to 4,000 units of output. Instructions: Use the tool provided (SRMSC) to draw the short-run market supply curve. Plot three points total. b. Draw the long-run market supply curve from zero to 4,000 units of output. Instructions: Use the tool provided (LRMSC) tool to draw the long-run market supply curve. Plot only the endpoints across the entire output range (0 to 4,000). Price ($) 50 40 40 Typical Firm Market Price ($) 50 MC ATC 40 30 AVC 20 20 10 0 10 20 20 30 Quantity 40 40 50 50 30 20 20 10 0 D Tools / LRMSC SRMSC 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Quantityarrow_forwardThe diagram to the right shows the long-run equilibrium for a competitive market for three different levels of demand (Do, D₁, and D₂). Assume that firms earn a normal level of profits at each market equilibrium. Illustrate the long-run industry supply curve. Using the line drawing tool, draw the long-run industry supply curve. Label this curve 'LRIS'. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required object. C Price per unit ($) 18.00- 16.00- 14.00- 12.00- 10.00- 8.00- 6.00- 4.00- 2.00- 0.00+ 0.0 Po -So 0.4 P₁ P₂ 0.8 1.2 1.6 2.0 Units of output, q (millions) 2.4 2.8arrow_forwardLooking to see how to resolvearrow_forward
- 10. In a competitive market, the current equilibrium price is $200 per unit. A firm that produces Q units of output in this market has a short-run Total Cost (TC) given by TC = 8000 + 40Q + Q². What is the marginal cost for this firm? How many units should the firm produce?arrow_forwardAnswer the questions based on the table below - Complete the table below. - In which market does this firm operate? Explain your reasons. - Determine the equilibrium output. Calculate whether the firm will it be earning a profit or suffering a loss at equilibrium. Quantity(unit) Total Revenue($) Average Revenue($) MarginalRevenue($) TotalCost($) MarginalCost($) 1 10 5 2 18 11 3 24 16 4 28 20 5 30 23 6 30 25arrow_forwardSuppose that the jackfruit industry is initially operating in long-run equilibrium at a price level of $5 per pound of jackfruit and quantity of 75 million pounds per year. Suppose a leading foodie video blogger raises awareness for a scholarly article that links jackfruit consumption to premature hair loss and unhealthy skin. The viral video is expected to cause consumers to demand Shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both on the following graph to illustrate these short-run effects of the viral video. PRICE (Dollars per pound) 10 9 8 7 co 01 2 1 0 0 15 Supply Demand jackfruit at every price. In the short run, firms will respond by 30 45 60 75 90 105 120 135 150 QUANTITY (Millions of pounds) Demand Supply ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education