
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
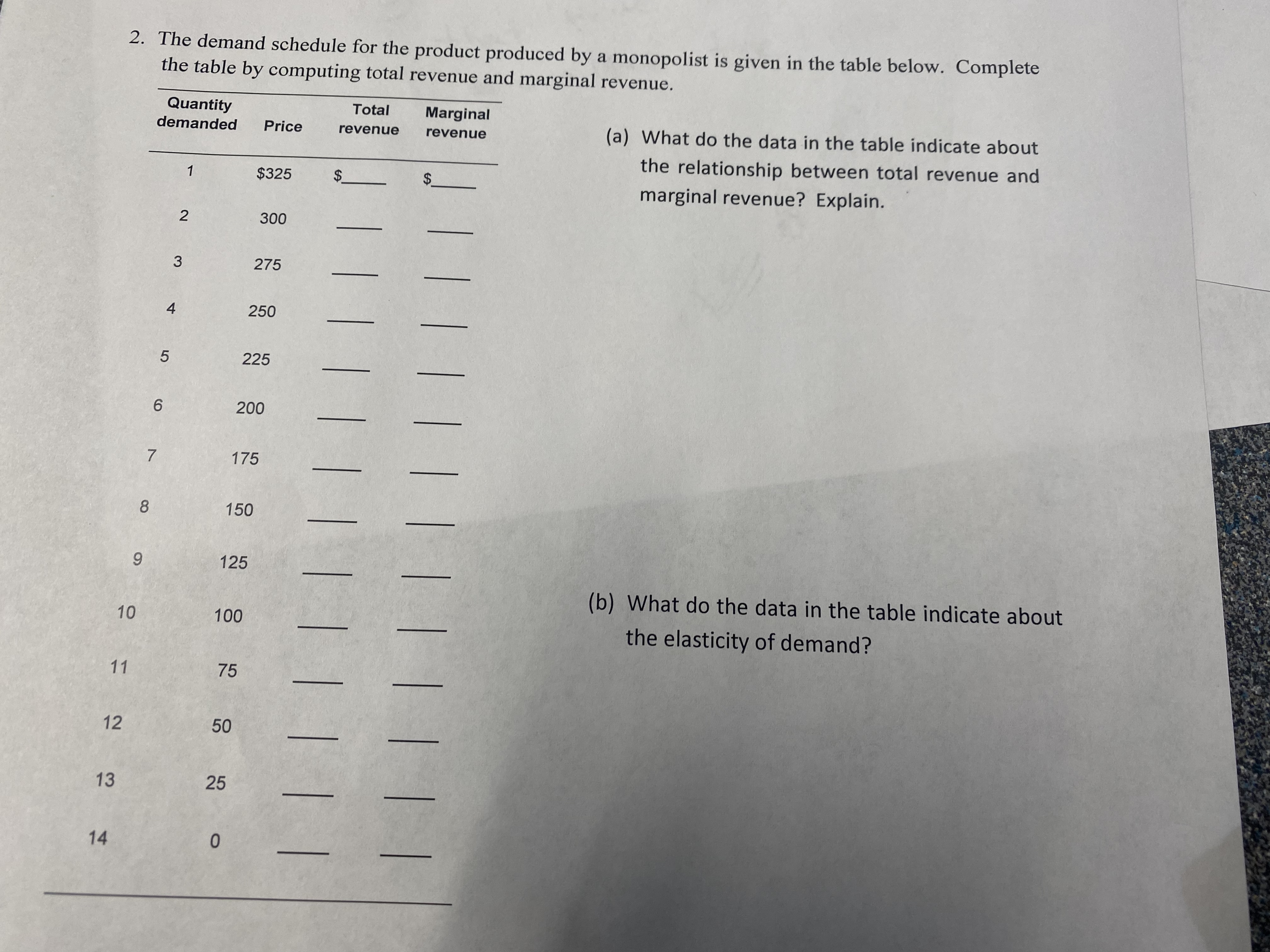
Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Website Content: Analyzing Demand and Revenue**
**Table Analysis**
The demand schedule for a product produced by a monopolist is presented below. Students are tasked with completing the table by computing total revenue and marginal revenue. Here's a transcription of the table:
| Quantity Demanded | Price | Total Revenue | Marginal Revenue |
|-------------------|-------|---------------|------------------|
| 0 | $25 | | |
| 1 | $24 | | |
| 2 | $23 | | |
| 3 | $22 | | |
| 4 | $21 | | |
| 5 | $20 | | |
| 6 | $19 | | |
| 7 | $18 | | |
| 8 | $17 | | |
| 9 | $16 | | |
| 10 | $15 | | |
| 11 | $14 | | |
| 12 | $13 | | |
| 13 | $12 | | |
| 14 | $11 | | |
**Questions for Analysis**
1. **(a) Relationship between Total and Marginal Revenue:**
- What do the data in the table indicate about the relationship between total revenue and marginal revenue? Explain.
2. **(b) Elasticity of Demand:**
- What do the data in the table indicate about the elasticity of demand?
**Instructions for Students:**
- Calculate the total revenue by multiplying the quantity demanded by the price.
- Calculate the marginal revenue by finding the change in total revenue as quantity demanded increases by one unit.
- Analyze how changes in quantity and price affect both total and marginal revenue to determine the elasticity of demand and the implications for pricing strategy in a monopolistic market.
This exercise encourages students to explore the fundamentals of economics, particularly the concepts of elasticity, demand, and revenue in monopoly contexts.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. The graph attached represents a monopoly firm. Answer the questions below. a. Briefly explain three ways in which pricing can be set with a regulated monopoly and the intended objective of each pricing method.b. Based on the diagram, if this monopoly firm is unregulated, what will be its profit? Show your calculations.c. Based on the diagram, if this firm is regulated based on social interest theory, what will be its profit? Show and explain your calculations.d. Based on the diagram, if this monopoly is subject to rate of return regulation, what will be the new price, output and profit of the firm? Show your calculations with explanations.e. Based on the diagram, if this is a natural monopoly that is allowed to set its price, what will be the minimum it should set in order to make a profit or break even? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardoutline the monopolist profit rectangle. on the graph, label the price the monopolist will charge, the quantity the monopolist will produce, the TR and TC. Calculate the profit. A profit-maximizing monopolist will charge a price of ___, produce a quantity of ___ units per hour, and earn a profit of ____?arrow_forward29 $55 $50 $45 MC АТС I of $40 $35 $30 $25 $20 Demand = P $15 $10 $5 MR $0 40 80 120 160 200 240 Output (Q) The diagram above shows the Demand, MR, and cost curves for a monopolist in the short-run. The monopolist will maximize its profit by choosing Output (Q) level and charging Price. Select one: а. 120; $20 b. 160; $30 С. 120;B $35 d. 160; $25 $$arrow_forward
- Answer the given question with a proper explanation and step-by-step solution.arrow_forwardFigure 94 Monopolist (dollars) 10 8 6 0 Quantity MC Refer to Figure 94. Suppose that the profit-maximizing/loss minimizing level of output is 40 units per day and the average fixed cost and average variable cost of producing this amount is $4 $7, respectively. (a) What is the total cost of producing 40 units per day? Show your work. (b) What is the total profit earned/loss incurred by producing 40 units per day? Show your work. (c) What price will the firm charge to maximize profit or minimize loss? (d) Should the firm shut down or continue to produce in the short run? Explain.arrow_forward46. If a monopolist sells 100 units at $9 per unit and realizes an average total cost of $8 per unit, what is the monopolist's profit? Group of answer choices $200 $50 $900 $100arrow_forward
- Do you agree or disagree with each of the following statements? Explain your reasoning. a. For a monopoly, price is equal to marginal revenue because a monopoly has the power to control price. b. Because a monopoly is the only firm in an industry, it can charge virtually any price for its product. c. It is always true that when demand elasticity is equal to –1, marginal revenue is equal to 0.arrow_forwardanswer typing i will give 5 upvotesarrow_forwardIV.arrow_forward
- Please solve part C & Darrow_forward5arrow_forward(Table: Profit-Maximizing Monopolist) Refer to the table. When this monopolist sells 8 units, its average cost and marginal cost per unit levels are: Price ($) Quantity (Units) Total Cost ($) Average Cost ($) Average Revenue ($) Marginal Cost ($) Marginal Revenue ($) 11 6 17 10 7 19 9 8 21 8 9 23 7 10 25 $2.63 and $2, respectively. $2.63 and $4, respectively. $2.56 and $4, respectively. $2.56 and $2, respectively.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education