
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please show all steps and answer
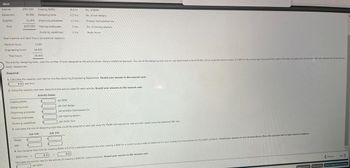
Transcribed Image Text:eBook
Salaries
$507,000
Creating BOMS
0.4 hr.
No. of BOMs
Equipment
Supplies
92,000
Designing tools
3.2 hrs.
No. of tool designs
31,000
Improving processes
1.1 hrs.
Process improvement hrs.
Total
$630,000
Training employees
Studying capabilities
2 hrs.
No. of training sessions
2 hrs.
Study hours
Total machine and labor hours (at practical capacity):
Machine hours
2,000
Engineering hours
Total hours
18.000
20,000
The activity, designing tools, uses the number of tools designed as the activity driver. Using a traditional approach, the cost of the designing tools activity was determined to be $178,000 with an expected activity output of 1,000 for the coming year. During the first week
tools, respectively.
Required:
1. Calculate the capacity cost rate for the Manufacturing Engineering Department. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
1.5 per hour
2. Using the capacity cost rate, determine the activity rates for each activity. Round your answers to the nearest cent.
Activity Rates
Creating BOMs
Designing tools
E
Improving processes
Training employees
per BOM
per tool design
per process improvement hr.
per training session
Studying capabilities
per study hour
3. Calculate the cost of designing tools that would be assigned to each job using the TDABC-derived activity rate and then repeat using the traditional ABC rate.
Job 150
TDABC
5
ABC
Job 151
the year, two jobs (Job 150 and Job 151) had a demand
10 and 210 new
4. Now suppose that time for creating BOMs is 0.4 for a standard product but that creating a BOM for a custom product adds an additional 0.2 hour. Express the time equation for this added complexity. Round your answers to two decimal places. Place the amounts left to right, lowest to highest.
BOM time
=
0.4
=
0.2
Calculate the activity rate for the activity of creating a BOM for custom products. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
per BOM
Email Instructor
Save and Ent
Next
>
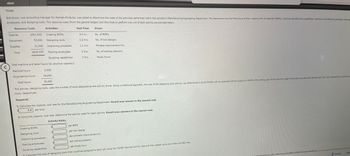
Transcribed Image Text:TDABC
Bob Russo, cost accounting manager for Hemple Products, was asked to determine the costs of the activities performed within the company's Manufacturing Engineering Department. The department has the following activities: creating bills of materials (BOMs), studying manufacturing capabilities, improving manufacturing processes, training
employees, and designing tools. The resource costs (from the general ledger) and the times to perform one unit of each activity are provided below.
Resource Costs
Activities
Unit Time
Driver
Salaries
$507.000
Creating BOMs
0.4 hr.
No. of BOMs
Equipment
Supplies
92.000
Designing tools
3.2 hrs.
No. of tool designs
31,000
Total
$630,000
Improving processes
Training employees
Studying capabilities
1.1 hrs.
Process improvement hrs.
2 hrs.
2 hrs.
No. of training sessions
Study hours
Total machine and labor hours (at practical capacity):
Machine hours
2,000
Engineering hours
18,000
Total hours
20,000
The activity, designing tools, uses the number of tools designed as the activity driver. Using a traditional approach, the cost of the designing tools activity was determined to be $178,000 with an expected activity output of 1,000 for the coming year. During the first week of the year, two jobs (Job 150 and Job 151) had a demand for 10 and 20 m
tools, respectively.
Required:
1. Calculate the capacity cost rate for the Manufacturing Engineering Department. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
1.5 per hour
2. Using the capacity cost rate, determine the activity rates for each activity. Round your answers to the nearest cent.
Creating BOMs
Designing tools
Activity Rates
per BOM
per tool design
Improving processes
Training employees
Studying capabilities
per process improvement hr.
per training session
per study hour
2. Calculate the cost of designing tools that would be assigned to each job using the TDABC-derived activity rate and then repeat using the traditional ABC rate.
ecimal alene Blaen the amount Infm right
Pervcoust
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Task 2: CLO4 OBJECTIVE: To enable learners to identify the relevant costs and benefits from costs and revenue information available in the financial database to aid decision making on time. REQUIREMENT: Short term decision making Question Selma Corporation uses Part PB7 in one of its products. The company's Accounting Department reports the following costs to produce 7,000 units of the PB7 that are needed every year. $ per unit Direct materials 7.00 Direct labour 6.00 Variable overhead 5.60 Supervisor's salary Depreciation of special equipment Allocated general overhead 4.70 1.50 5.40 An outside supplier has offered to make the part and sell it to the company for $28.30 each. If this offer is accepted, the supervisor's salary and all of the variable costs, including direct labor, can be avoided. The special equipment used to make the part was purchased many years ago and has no salvage value or other use. The allocated general overhead represents fixed costs of the entire company. If…arrow_forwardBusinessE b My Questi Reference Chapt X enccinstructure.com/courses/3788/assignments/35967?module ite 0 In the month of June, a department had 19000 units in beginning work in process that were 65% complete. During June, 89000 units were started into production. At the end of June there were 9000 units in ending work in process that were 35% complete. Materials are added at the beginning of the process, while conversion costs are incurred uniformly throughout the process. How many units were transferred out of the department in June? O 89000 units. O 99000 units. O 108000 units. O 80000 units.arrow_forwardeBook Show Me HowPrint Item Question Content Area Costs per Equivalent Unit The following information concerns production in the Baking Department for August. All direct materials are placed in process at the beginning of production. ACCOUNT Work in Process—Baking Department ACCOUNT NO. Date Item Debit Credit Balance Debit Balance Credit August 1 Bal., 36,000 units, 3⁄4 completed 207,360 31 Direct materials, 200,000 units 450,000 657,360 31 Direct labor 207,900 865,260 31 Factory overhead 680,400 1,545,660 31 Goods finished, 196,000 units 1,361,660 184,000 31 Bal., ? units, 1⁄2 completed 184,000 a. Based on the above data, determine each cost listed below. Round "cost per equivalent unit" answers to the nearest cent. Line Item Description Amount 1. Direct materials cost per equivalent unit $fill in the blank 1 2. Conversion cost per equivalent unit $fill in the blank 2 3. Cost of the beginning work in process completed during…arrow_forward
- Graded Practice i Saved Activity Budgeted Cost Activity Cost Driver Usage Machine hours (MH) 7,400 Setups 180 Activity Machining Process Assembly Setups $ 310,600 24,000 $ 334,600 Finishing Inspecting $ 226,000 Support Purchasing $ 132,000 Inspections 760 Purchase orders 480 Additional production information concerning its two models follows. Units and Activities Units produced ces Machine hours Setups Inspections Purchase orders 3 Model X Model Z 1,600 3,200 2,200 5,200 60 120 480 280 320 160 Per Unit Selling price per unit Model X $ 410 Model Z $ 390 Direct materials cost per unit 145 115 Direct labor cost per unit 130 145 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity using activity-based costing. 2. Using activity-based costing, compute the overhead cost per unit for each model. 3. Compute the total product cost per unit for each model. 4. For each model, compute the gross profit per unit (selling price per unit minus product cost per unit). 40 % 4 5 A- +4 < Prev 4 of 4 Next no f O…arrow_forwardQ. 2 Índigo manufacturing has five activity cost pools and two products ( a budget tape vacuum and a deluxe tape vacuum). Information is presented below:arrow_forwardhelp please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forward
- Please explain how you get the answer. Thanksarrow_forwardhelp please answer in text form with proper working and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no ai no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardHello tutor answer the accounting questionarrow_forward
- eBook Show Me How Support department cost allocation-reciprocal services method Davis Snowflake & Co. produces Christmas stockings in its Cutting and Sewing departments. The Maintenance and Security departments support the production of the stockings. Costs from the Maintenance Department are allocated based on machine hours, and costs from the Security Department are allocated based on asset value. Information about each department is provided in the following table: Machine hours Asset value Department cost Maintenance Department Security Department Cutting Department Sewing Department 800 2,000 8,400 9,600 $2,000 $29,520 $1,430 $13,120 $3,000 $67,000 $5,000 $78,000 Determine the total cost of each production department after allocating all support department costs to the production departments using the reciprocal services method. Sewing Department Cutting Department < Production departments' total costs 83,976 X 117,184 X Feedback Check My Work The reciprocal services method…arrow_forwardPoF bussiness stats bool.pdf cost accounting book.pdf E Chapter 1.pdf x + PRE PDF O File | C:/Users/RASAB/Downloads/Chapter%201%20.pdf P1-8 Job order cost; journal entries; ending work in process; inventory analysis Hidalgo Company manufactures goods to special order and uses a joh order cost system. During its first month of operations, the following selected transactions took place: LO7 a. Materials purchased on account $37,000 b. Materials issued to the factory: Job 101 $ 2,200 Job 102 5,700 Job 103 7,100 Job 104 1,700 For general use in the factory 1,350 c. Factory wages and salaries earned: Job 101 $ 2,700 Job 102 6,800 Job 103 9,200 Job 104 ..... 2,100 For general work in the factory 2,250 d. Miscellaneous factory overhead costs on account ... $ 2,400 e. Depreciation of $2,000 on the factory machinery recorded. f. Factory overhead allocated as follows: Job 101 $ 1,200 Job 102 2,000 Job 103 3,800 Job 104 ... 1,000 g. Jobs 101, 102, and 103 completed. h. Jobs 101 and 102 shipped to…arrow_forwardeBook Given the following information, prepare a production report with materials added at the beginning and ending work in process inventory being 20% complete with regard to conversion costs. Costs to Account for Units to Account for Beginning inventory: materials $5,000 Beginning work in process 3,000 Beginning inventory: conversion 1,100 Units started into production 85,000 Direct material 25,620 Transferred out 83,000 Direct labor 35,000 Applied overhead 12,500 Transferred-in materials 8,100 Transferred-in conversion 10,200 Total costs to account for $97,520 Enter all amounts as positive values. If required round "Cost per unit" answers to two decimal places. Production Report Completed and transferred out fill in the blank 1 Ending work in process fill in the blank 2 Total units to account for fill in the blank 3 Work in process completion percent 100% 20% Material Units…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education