
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
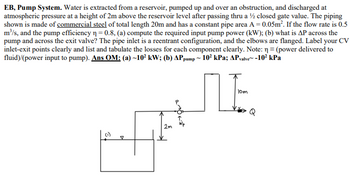
Transcribed Image Text:**EB, Pump System**
In this setup, water is extracted from a reservoir, elevated over an obstruction, and then released at atmospheric pressure 2 meters above the reservoir level after flowing through a half-closed gate valve. The piping system, shown in the diagram, is made of commercial steel with a total length of 20 meters and a constant cross-sectional pipe area of 0.05 square meters. The system operates with a flow rate of 0.5 cubic meters per second, and the pump's efficiency (η) is 0.8.
Tasks:
- **(a)** Compute the required input pump power in kilowatts (kW).
- **(b)** Determine the pressure drop (ΔP) across the pump and the exit valve.
The pipe inlet is configured as reentrant, and the elbows in the system are flanged. Label the control volume's inlet and exit points, and clearly list and tabulate the losses for each component.
**Note:**
η = (power delivered to fluid) / (power input to pump).
**Answers:**
(a) Required input pump power is approximately 10² kW.
(b) Pressure drop across the pump (ΔP_pump) is approximately 10² kPa; Pressure drop across the valve (ΔP_valve) is negative and approximately -10² kPa.
---
**Diagram Explanation:**
- The diagram illustrates a side view of the piping system.
- Water moves from a reservoir (initial level indicated) to an elevated pipe section (10 meters high) and through the system.
- A gate valve is visible right before the water is discharged at 2 meters above the reservoir level.
- The flow direction is marked, and key points such as the entry (P) and exit points are labeled.
This description helps readers understand the basic components and flow pathways within this engineering system and offers a foundation for analyzing the hydraulic performance and efficiency.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q6. A pump moves water horizontally at a rate of 0.02m /s. Upstream of the pump where the pipe diameter is 90mm, the pressure is 100kPa. Downstream of the pump where the pipe diameter is 30mm, the pressure is 350KP.. If the loss in energy across the pump due to fluid friction effects is 170N.m/kg, determine the hydraulic efficiency of the pump. (Pwater = 999 kg/m³)arrow_forward0105 Water at 40 °C is pumped from an open tank through 200 m of 50-mm-diameter smooth horizontal pipe as shown in Figure 1 and discharges into the atmosphere with a velocity of 3 m/s. Minor losses are negligible. (a) If the efficiency of the pump is 70%, how much power is being supplied to the pump? (b) What is the NPSHA at the pump inlet? Neglect losses in the short section of pipe connecting the pump to the tank. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. Note: for smooth pipe, friction factor, f = 0.0152 and at 40 °C. kinematic viscosity Temperature (°C) Water vapor pressure (N/m²) Specific weight (N/m³) (m²/s) 6.58 x 10-7 40 7.376 x 10³ 9.731 x 10³ T 3 m ! PUMP 9.731* Diameter = 50 mm Length 200 m e Figure 1arrow_forwardTwo 32-in pumps from Fig. are to be used in seriesat 1170 r/min to lift water through 500 ft of vertical castiron pipe. What should the pipe diameter be for most effi -cient operation? Neglect minor losses.arrow_forward
- Two identical pumps are connected in series and deliver water through an 45cmdiameter, 2.2km long, commercial steel pipe from reservoir A (surface elevation = 50m) to reservoir B(surface elevation = 100m). Consider minor losses of a square-edged inlet, exit, and swing-type checkvalve. Determine the discharge, the total head added by the pumps, and the total power output. The pumpcharacteristics for a single pump is tabulated below. Assume that the kinematic viscosity is 1x10-6 m 2/s and a specific weight of 9.79kN/m 3 . Plot the system and pump characteristic curves on a single plot. Besure to label the axes appropriately (i.e., include units). Be sure to include a legend to demark the systemhead curve and the pump characteristic curve.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 5: In Lake Geneva (Switzerland), there is a water jet (called the Jet d’Eau) that is discharged 130 m straight upward (measured from the surface of the lake). The exit of the discharge pipe is 20 cm in diameter.arrow_forwardA pump delivering water at a temperature of 400 F (204.4 C) and a rate of 12,000 GPM (757 lit/s) to a pressurized vessel at 1000 psia. The discharge piping is 135 ft (41.15 m) long schedule 40 stainless steel, and nominal pipe size of 20 in (7.874 cm). Find the total dynamic discharge head.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY