
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:E2B.3(b, The constant-pressure heat capacity of a sample of a perfect gas
was found to vary with temperature according to the expression C/(JK") =
20.17 + 0.4001(T/K). Calculate q, w, AU, and AH when the temperature is
raised from 25°C to 100°C (i) at constant pressure, (ii) at constant volume.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
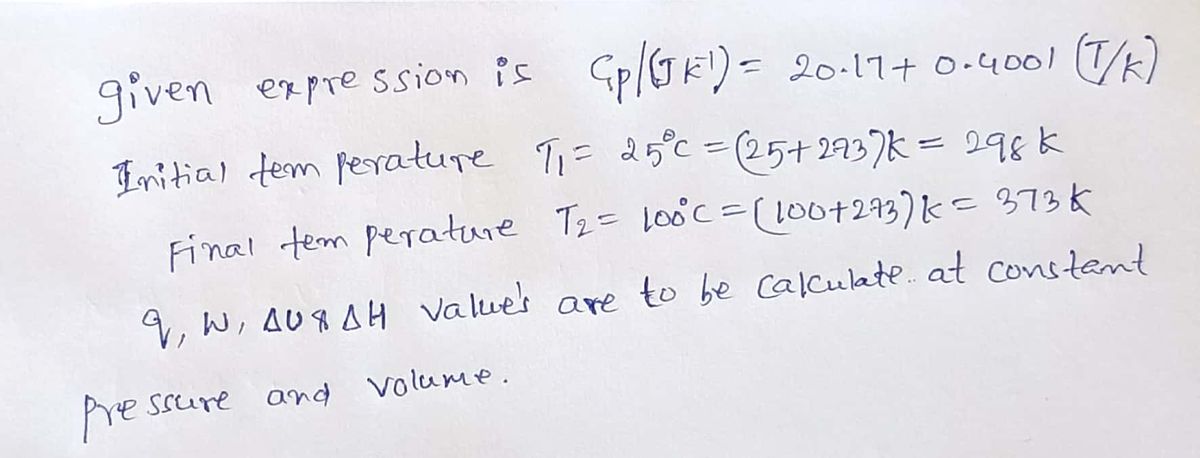
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Indicate the true option about calorimetry.(A). Internal energy is an intensive quantity.(B). The enthalpy does not depend on p, since this variable is the amount of heat put into play during an isobaric transformation.(C). The superscript ° added to the thermodynamic functions indicates that it is operated at p = 1 atm and T = 298.15 K.(D). The heat exchanged between a system and the medium is not a state function.arrow_forwardE2B.3(a) The constant-pressure heat capacity of a sample of a perfect gas was found to vary with temperature according to the expression CJ(JK*") = 20.17+ 0.3665(T/K). Calculate q, w, AU, and AH when the temperature is raised from 25°C to 100°C (i) at constant pressure, (ii) at constant volume.arrow_forward1. (a) In reaching equilibrium, how much heat transfer occurs from 1.2 kg of water at 40°C when it is placed in contact with 1.2 kg of 20°C water? Specific heat of water c=4186 J/(kg°C) Hint: If the masses of water are equal, what is the equilirium temperature of the water mixture? Q= ✓ J (b) What is the change in entropy due to this heat transfer? AS total ✔J/K (c) How much work is made unavailable, taking the lowest temperature to be 20°C? = W unavailable ✓ Jarrow_forward
- 3. Derive the thermodynamic equation of state for an ideal gas starting from internal energy then express this equation in a form without differentials. = -P +T| T LƏT.arrow_forwardBenzoic acid, C;HsO:H, is typically used as a çalibrant for determining the specific heat of bomb calorimeters. It combusts via the following unbalanced chemical reaction: C,H5O2H (s) + 02(g) → CO2 (g) + H2O(1) 3. For this experimental setup and reaction, the constant volume heat flow is known to be gy = -26.979 kJ. Over the course of the reaction, the temperature rose from 19.863 °C to 22.540 °C. Calculate the heat capacity, Cou, for this calorimeter in kJ °C-!.arrow_forwardSuppose a piece of solid lead weighing 41.3 g at a temperature of 312 °C is placed in 413 g of liquid lead at a temperature of 374 °C. Calculate the temperature after thermal equilibrium is reached, assuming no heat loss to the surroundings. The enthalpy of fusion of solid lead is AH fus = 4.77 kj mol¹ at its melting point of 328 °C, and the molar heat capacities cp of solid and liquid lead are 26.9 and 28.6 J K¹ mol-¹, respectively. (Enter your answer to three significant figures.) T₁= Jc Submit Answer Try Another Version 1 item attempt remainingarrow_forward
- 1. The specific heat capacities (in units of J/g-K) of V, W, and Zn are 0.489, 0.132, and 0.388, respectively. What is the order of the molar heat capacities? Formula weights: V 50.94; W 183.8; Zn 65.4 (c) W>V>Zn (a) V>W>Zn (d) W>Zn>V (b) V>Zn>W (e) Zn>V>Warrow_forwardQ3) Thermodynamic Processes- 2.0 mol of a diatomic ideal gas undergoes a process in which it is compressed very slowly from state a (V. = 3.0 m³, P, = 1000 Pa) to state b (V, = 1.0 m³), in such a way that the system maintains thermal equilibrium with its surroundings at all times. P (Pa) 3000 2000 A. Find the change in internal energy during the process. 1000 B. Find the final pressure of the gas. 1 3 4 V(m³) C. Find the work done by the piston on the gas during this process. (Hint: Since Pis not constant during this process, it doesn't come out of the integral. Use the ideal gas law to find an expression for Pin terms of constants and the integration variable V) D. So what's the work done by the gas on the piston during this process? E. How much heat – if any - was transferred between the gas and surroundings during this process? Did heat flow from the gas to the surroundings or from the surroundings to the gas? Explain your reasoning. F. At the end of the process, is the average…arrow_forward(a) Suppose that attractions are the dominant interaction between gas molecules, and the equation of state is p = nRT/V – n2a/V2. Determine the work (W(non-ideal gas)) of reversible, isothermal expansion of such a gas from initial volume V (initial) = 20.0 L to final volume V(final) = 40.0 L if n = 2.00 mol, T = 300 K, and a = 3.621 atm-L2/mol2. Watch your units. (b)Determine the work (W(ideal gas) of reversible, isothermal expansion of an ideal gas from initial volume V (initial) = 20.0 L to final volume V(final) = 40.0 L if n = 2.00 mol and T = 300 K. (c) Show the difference W(non-ideal) – W(ideal). If all your calculations are done correctly, this result shows you the effect of attractive interaction between gas particles on the work done by the system.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY