
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:K
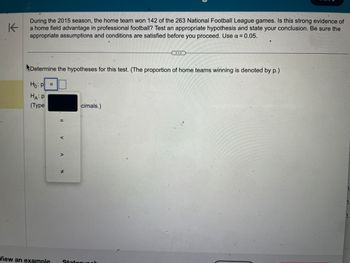
During the 2015 season, the home team won 142 of the 263 National Football League games. Is this strong evidence of
a home field advantage in professional football? Test an appropriate hypothesis and state your conclusion. Be sure the
appropriate assumptions and conditions are satisfied before you proceed. Use α = 0.05.
Determine the hypotheses for this test. (The proportion of home teams winning is denoted by p.)
Ho: P =
HA: P
(Type
11
V
V
#
cimals.)
…...
View an example Statorumah
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Test the claim below about the mean of the differences for a population of paired data at the level of significance a. Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed. Claim: <0; a=0.05. Sample statistics: d= 1.6. sy =3.7, n=12 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. OA Ho: 14=0 H₁₂-10 OC. Ho: Hy so H₁₂:0 OE HO H₂: P20 The test statistic is t= ☐ (Round to two decimal places as needed.) B. Ho: Hy 20 H: <0 D. Ho: Hy #0 H₂: H₁₂ =0 OF H₂: 10 H.: 150arrow_forwardUse technology to help you test the claim about the population mean, μ, at the given level of significance, α, using the given sample statistics. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: μ>1300; α=0.09; σ=207.09. Sample statistics: x=1326.58, n=275 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. A. H0: μ≥1326.58 Ha: μ<1326.58 B. H0: μ≤1300 Ha: μ>1300 C. H0: μ≥1300 Ha: μ<1300 D. H0: μ≤1326.58 Ha: μ>1326.58 E. H0: μ>1326.58 Ha: μ≤1326.58 F. H0: μ>1300 Ha: μ≤1300 Click to select your answer and then click Check Answer. 3 parts remainingarrow_forward52arrow_forward
- you did not answer this Let p be the true proportion of firms with a chief marketing officer currently on their top management team. To conduct the hypothesis test, the null and alternative hypotheses are formulated as: H₀: p̄ p̄ = 0.42'; Haa: p̄ p̄ ≠ 0.42 H₀: p ≥ 0.42; Haa: p < 0.42 H₀: p = 0.42; Haa: p ≠ 0.42 H₀: p ≤ 0.42; Haa: p > 0.42 If the null hypothesis is true, the sampling distribution of the sample proportion p̄ p̄ can be approximated by a _____ with a mean ______ and a standard deviation of ____ . The test statistic is _____ .arrow_forwardTeat the claim abouy the population mean, u, at the given level of significance, a, using the given sample statistics. Claim:u=50; a=0.05; o=3.11. Sample statistics: x=48.4, n=71. i) Identify the null and alternative hypothesis. (Do not forget to find the standardized test statistic and critical values) ii) Determine tge outcome and conclusion of the test.arrow_forwardA sample mean, sample size, and population standard deviation are provided below. Use the one-mean z-test to perform the required hypothesis test at the 1% significance level. x=34, n=20, σ=7, H0: μ=37, Ha: μ≠37 The test statistic is z=___________ (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the critical value(s). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box within your choice. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) A. The critical values are ±zα/2=±_________ B. The critical value is zα=____________ C. The critical value is −zα=____________ ________________ (Do not reject, Reject) the null hypothesis. The data ____________ ( provide, do not provide) sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean is ______________ (not equal to 37, less than 37, equal to 37, greater than 37)arrow_forward
- Use technology to find the P-value for the hypothesis test described below. The claim is that for a smartphone carrier's data speeds at airports, the mean is µ = 14.00 Mbps. The sample size is n= 20 and the test statistic is t= -2.174. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse technology to find the P-value for the hypothesis test described below. The claim is that for 12 AM body temperatures, the mean is µ> 98.6°F. The sample size isn=9 and the test statistic is t=2.568. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse technology to find the P-value for the hypothesis test described below. The claim is that for 12 AM body temperatures, the mean is u> 98.6°F. The sample size is n = 6 and the test statistic is t= 2.287. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- State whether the standardized test statistic z indicates that you should reject the null hypothesis. (a)z=2.374 (b)z=2.304 (c)z=−2.138 (d)z=2.544 z0=2.330 For z=2.374, should you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis?arrow_forwardUse technology to find the P-value for the hypothesis test described below. The claim is that for a smartphone carrier's data speeds at airports, the mean is u = 16.00 Mbps. The sample size is n = 19 and the test statistic is t= 1.798. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardSuppose are running a study/poll about the proportion of men over 50 who regularly have their prostate examined. You randomly sample 102 people and find that 87 of them match the condition you are testing. Suppose you are have the following null and alternative hypotheses for a test you are running: Ho:p = 0.86 Ha:p < 0.86 Calculate the test statistic, rounded to 3 decimal places. Z = Question Help: D Video Submit Question hp % & 3 4 7 8 5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman