
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
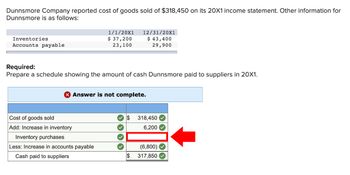
Transcribed Image Text:Dunnsmore Company reported cost of goods sold of $318,450 on its 20X1 income statement. Other information for
Dunnsmore is as follows:
Inventories
Accounts payable
Cost of goods sold
Add: Increase in inventory
1/1/20X1
$ 37,200
23,100
Required:
Prepare a schedule showing the amount of cash Dunnsmore paid to suppliers in 20X1.
12/31/20x1
$ 43,400
29,900
Inventory purchases
Less: Increase in accounts payable
Cash paid to suppliers
Answer is not complete.
✓$ 318,450
6,200
(6,800)
$ 317,850
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Questions # 21-23 are based on the information below: Wicker Inc. has the following transactions during March: March 3 March 5 March 6 March 12 March 29 Purchases inventory on account for $3,500, terms 2/10, n/30. Pays freight costs of $200 on inventory purchased on March 3. Returns inventory with a cost of $500. A. $60 B. $70 C. $56 D. $84 Pays the full amount due to supplier. Sells all inventory purchased on March 3 (less those returned on March 6) for $5,000 on account. 21. On March 12, how much is the purchase discount? 22. How much cash does Wicker pay to the supplier on March 12? A. $2,936 B. $2,930 C. $2,940 D. $3,000 23. How much will Wicker record as cost of goods sold on March 30? A. $5,000 B. $3,000 C. $3,200 D. $3,140arrow_forwardThe cost of goods sold computations for Bridgeport Company and Sarasota Company are as follows. Bridgeport Company Sarasota Company Beginning inventory $ 46,500 $ 74,000 Cost of goods purchased 199,000 290,075 Cost of goods available for sale 245,500 364,075 Ending inventory 54,680 74,500 Cost of goods sold $190,820 $289,575 (a1) Compute inventory turnover for each company. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.25.) Bridgeport Company Sarasota Company Inventory turnover enter inventory turnover rounded to 2 decimal places enter inventory turnover rounded to 2 decimal placesarrow_forwardCompute the inventory turnover ratio based on the following data: Sales revenue $275,000 Cost of goods sold 168,000 Beginning inventory 35,000 Ending inventory 45,000arrow_forward
- Jake Thomas Corporation uses the conventional retail method for financial reporting. The company's inventory records are summarized below. Description Cost Retail Beginning inventory $31,800 $53,000 Purchases 127,540 197,900 Additional markups 9,600 Markup cancellations 3,500 Markdowns 5,100 Markdown cancellations 4,000 Sales 230,000 Complete the partial table below to determine the cost-to-retail ratio. In the following step, complete the table by selecting the labels and entering the amounts needed to estimate Jake Thomas' ending inventory using the conventional retail method. (If an input field is not used in the table, leave the input field empty; do not enter a zero. Round the cost-to-retail ratio to two decimal places, X.XX%. Round all currency amounts to the nearest whole dollar.) Cost-to-Retail Description Cost Retail Ratio…arrow_forwardRichard Company's financial records report beginning inventory of $543,000; ending inventory of $699,000; and cost of goods sold of $1,387,000. What is the amount of purchases? Group of answer choices $1,543,000 $1,242,000 $844,000 $2,086,000arrow_forwardBioware Company reports cost of goods sold of $42,200. Its comparative balance sheet shows that inventory decreased $7,200 and accounts payable increased $5,200. Compute cash payments to suppliers using the direct method. Cash Payments to Suppliers (Direct) Cash paid for inventoryarrow_forward
- Solve it on excel onlyarrow_forward. Ebasan Company used the average cost retail inventory method. The entity provided the following information for the current year: Cost Retail 1,500,000 2,200,000 Beginning inventory Net purchases 3,875,000 4,950,000 Departmental transfer -credit 200,000 300,000 Net markup 150,000 Inventory shortage at sales price 100,000 Employee discounts 200,000 Sales, including sales of P400,000 of items which were marked down from P500,000 4,000,000 What amount should Ebasan report as cost of ending inventory? 61.950.000arrow_forwardMasthead Company's comparative balance sheets included an inventory of $180,400 at December 31, 2009, and $241,200 at December 31, 2010. Masthead's comparative balance sheets also included accounts payable of $85,400 at December 31, 2009, and $78,400 at December 31, 2010. Masthead's accounts payable balances are composed solely of amounts due to suppliers for purchases of inventory on account. Cost of goods sold, as reported by Masthead on its 2010 income statement, amounted to $1,200,000. What is the amount of cash payments for inventory that Masthead will report in the Operating Activities category of its 2010 statement of cash flows assuming that the direct method is used?arrow_forward
- Cost of Goods Sold Section, Multiple-Step Income Statement Based on the information that follows, prepare the cost of goods sold section of a multiple-step income statement. Merchandise Inventory, January 1, 20-- $36,000 Estimated Returns Inventory, January 1, 20-- 3,000 Purchases 102,000 Purchases Returns and Allowances 4,200 Purchases Discounts 2,040 Freight-In 800 Merchandise Inventory, December 31, 20-- 30,500 Estimated Returns Inventory, December 31, 20-- 2,500arrow_forwardPlease provide correct solutionarrow_forwardMetlock's Market recorded the following events involving a recent purchase of inventory: Received goods for $78200, terms 2/9, n/30. Returned $1700 of the shipment for credit. Paid $700 freight on the shipment. Paid the invoice within the discount period. As a result of these events, the company's inventory increased by $74970. increased by $75670. increased by $77200. O increased by $75656. O Oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education