
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Draw the structure of product, substrate, or condition in the following reactions (clearly show the stereochemistry).
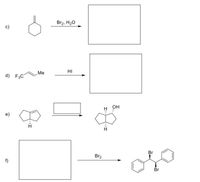
Transcribed Image Text:The image contains a series of chemical reactions represented by structural formulas and reagents that lead to various organic transformations. Here's a detailed transcription and explanation:
### Reaction Scheme
**c)**
- **Starting Compound:** Cyclohexene
- **Reagent:** Br₂, H₂O
- **Product:** The product box is blank, indicating an expected outcome of a bromohydrin formation, where bromine (Br) and a hydroxyl group (OH) are added across the double bond of cyclohexene.
**d)**
- **Starting Compound:** 1,1,1-Trifluoro-3-methylbut-2-ene
- **Reagent:** HI (Hydrogen Iodide)
- **Product:** The product box is blank, indicating an expected outcome of an addition reaction where iodine is added across the double bond, and possibly the fluorine atoms remain unaffected.
**e)**
- **Starting Compound:** Norbornane with a hydrogen at a bridgehead
- **Reagent:** Not specified (blank reagent box)
- **Product:** A norbornenol structure, indicating an alcohol (OH) group addition, suggesting that the unspecified reagent could be an oxidizing agent or involves an hydroxylation reaction.
**f)**
- **Reagent:** Br₂
- **Product:** The product is a dibromo compound with two phenyl rings, indicating that the starting compound (blank in the image) was likely a diphenylethylene structure. The product shows bromine atoms added on the carbon chain between the two benzene rings.
### Explanation:
Each section of the diagram involves different organic reactions demonstrating typical transformations such as halogenation, addition of halogens and water (bromohydrin formation), and possibly hydroxylation. Each reaction is marked by a blank space for certain reagents or products, indicating these are likely exercises or examples where one is expected to deduce the missing components based on knowledge of organic chemistry transformations.
This content is educational, aiming to instruct students or readers on how to anticipate the products of given reactions typical in synthetic organic chemistry.
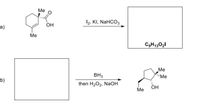
Transcribed Image Text:### Organic Reaction Pathways
#### Reaction Pathway A
**Reactant:**
- A molecule with a cyclohexene ring, containing one double bond.
- It has two methyl groups (Me) and a hydroxyl group (OH).
- An additional carbonyl group (C=O) is present.
**Reagents:**
- Iodine (I₂)
- Potassium iodide (KI)
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃)
**Product:**
- A compound with the molecular formula C₉H₁₃O₂I.
**Reaction Description:**
- This is a halogenation reaction involving iodine. The presence of sodium bicarbonate suggests a basic environment, which may aid in the reaction's progress.
#### Reaction Pathway B
**Reagents:**
- Borane (BH₃)
- Followed by hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
**Product:**
- A molecule with a cyclopentane ring, featuring one alcohol group (OH) and two methyl groups (Me) on adjacent carbon atoms.
**Reaction Description:**
- This process is likely a hydroboration-oxidation, which typically converts alkenes into alcohols, with borane acting first to add BH₂ and then the alcohol formation via oxidation with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of sodium hydroxide.
### General Concepts
- **Halogenation Reactions:** These involve the addition of halogens like iodine to unsaturated bonds, usually facilitated by catalysts or solvents.
- **Hydroboration-Oxidation:** A two-step process that adds a hydroxyl group across an alkene, converting it into an alcohol. The borane acts as a reducing agent, and subsequent oxidation yields the alcohol.
Understanding these reactions is crucial in synthetic organic chemistry for creating varying functional groups and structural motifs in complex molecules.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed..don't give Handwritten answerarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ...arrow_forwardTo the presence of hexane HBr addition PEROXIDE leads to the output: subject to O Citzv base Opposite of Marconikov's rule ● Marconikov basearrow_forward
- Give detailed Solution with explanation needed..no need handwritten answer..give mechanismarrow_forwardAbove each arrow, supply the reagent(s)/reaction conditions that is(are) needed for each of the followingtransformations.arrow_forwardGive detailed mechanism Solution with explanation needed..don't give Handwritten answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY