
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
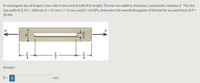
Transcribed Image Text:A rectangular bar of length L has a slot in the central half of its length. The bar has width b, thickness t, and elastic modulus E. The slot
has width b/3. If L = 400 mm, b = 51 mm, t = 11 mm, and E = 64 GPa, determine the overall elongation of the bar for an axial force of P =
32 kN.
b
Answer:
i
mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the vertical displacement of joint C. The length, L, of trusses AC, BC is 1,000 mm. The applied force at joint C, is 9.5 kN. The cross-sectional area of both trusses, A, is 370 mm2. The elastic modulus of truss AC, E1, is 115 GPa. The elastic modulus of truss BC, E2, is 155 GPa.arrow_forwardDetermine the horizontal displacement of joint C. The length, L, of trusses AC, BC is 1,300 mm. The applied force at joint C, is 5.0 kN. The cross-sectional area of both trusses, A, is 360 mm2. The elastic modulus of truss AC, E1, is 135 GPa. The elastic modulus of truss BC, E2, is 150 GPa.arrow_forwardA 0.525 in. diameter solid steel shaft supports two pulleys. The shaft has a length of L = 9.9 in., and the load applied to each pulley is P = 62 lb. The bearing at A can be idealized as a pin support and the bearing at D can be idealized as a roller support. Determine the magnitude of the maximum horizontal shear stress in the shaft. P A B D L Answer: Tmax = i psi 1//3arrow_forward
- Determine the vertical displacement of joint C. The length, L, of trusses AC, BC is 1,000 mm. The applied force at joint C, is 9.5 kN. The cross-sectional area of both trusses, A, is 370 mm2. The elastic modulus of truss AC, E1, is 115 GPa. The elastic modulus of truss BC, E2, is 155 GPa.arrow_forwardCompound axial member ABC has a uniform diameter of d = 1.2 in. Segment (1) is an aluminum [E₁ = 10,000 ksi] alloy and segment (2) is a copper [E₂ = 17,000 ksi] alloy. The lengths of segments (1) and (2) are L₁ = 80 in. and L2 = 140 in., respectively. Determine the force P required to stretch compound member ABC by a total of 0.10 in. LI L2 A d Aluminum Copper Answer: P = i B kipsarrow_forwardRigid bar ABCD is supported by two bars as shown in Figure P2.7. There is no strain in the vertical bars before load P is applied. After load P is applied, the normal strain in bar (2) is measured as –3,300 um/m. Use the dimensions L1 = 1,600 mm, L2 = 1,200 mm, a = 240 mm, b = 420 mm, and c = 180 mm. Determine:(a) the normal strain in bar (1).(b) the normal strain in bar (1) if there is a 1 mm gap in the connection at pin C before the load is applied.(c) the normal strain in bar (1) if there is a 1 mm gap in the connection at pin B before the load is applied.arrow_forward
- A P = 10 kip 1.5 ft B C 2 ft The bars in the structure to the left are pinned and have circular cross-sections. The diameter of the cross- section is 1.5 inches. The bars are made of steel, which has an elastic modulus of 29,000 ksi. A point force of 10 kips is applied at point C, as shown. What is the change in length of member BC? Is the bar getting longer or shorter?arrow_forwardRigid bar DB in the figure is supported at pin B by axial member ABC, which has a cross-sectional area of A1 = A2 = 85 mm², an elastic modulus of Ej = E2 = 1000 MPa, and lengths of L = 390 mm and L2 = 645 mm. Aload of Q = 555 N is applied at end Cof member (2), and a load of P = 1425 N is applied to the rigid bar at a distance of a = 85 mm from pin support D and b = 45 mm from pin B. Determine the magnitudes of the downward deflections of: (a) pin B. (b) pin C. A |(1) Rigid bar B a b. L2 (2) (a) VB = i mm (b) vc = i mmarrow_forward1. A Using E = 100 GPA. IN.A. = 1,500 x 10 mm², compute the SUPPORT REACTIONS of the loaded beam shown when: a. supports are unyielding. b. support at the midspan yields 4 mm. 4m 60 KN/m B 2m www 10 KN C D 2marrow_forward
- The force in DB of the truss shown in below figure is W A C O VW tension 5m √3 W compression 2 W compression 5 W tension E D 2W 5m Barrow_forwardThe fixed-end bar ABCD consists of three prismatic segments, as shown in the figure. The end segments have cross-sectional area A1 = 840 mm2 and length L1 = 200 mm. The middle segment has cross- sectional area A2= 1260 mm? and length L2 = 250 mm. Loads Pg and Pc are equal to 25.5 kN and 17.0 kN, respectively. (a) Determine the reactions RA and Rp at the fixed supports. (b) Determine the compressive axial force FBC in the middle segment of the bar. A1 - A2 A1 PB Pc A D B L -L1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning