
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please draw substitution and elimination major products
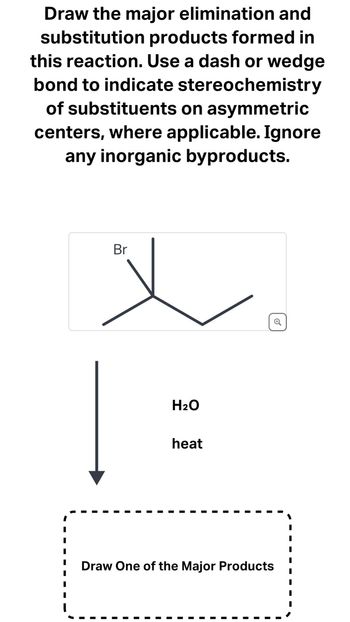
Transcribed Image Text:## Organic Chemistry Reaction Exercise
**Objective:**
Draw the major elimination and substitution products formed in the following reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.
### Reaction Scheme
1. **Reactant Structure:**
- The reactant is a brominated molecule, illustrated as follows:
```
Br
\
C
/ \
C C
```
2. **Conditions for the Reaction:**
- The reactant is treated with **H₂O** under **heat**.
3. **Instruction:**
- Draw one of the major products resulting from either an elimination or substitution reaction.
### Step-by-Step Guide
1. **Identify possible elimination and substitution pathways:**
- **Elimination Reaction:** This typically leads to the formation of an alkene by removing a hydrogen (H) from one carbon and a bromine (Br) from an adjacent carbon.
- **Substitution Reaction:** Here, the bromine (Br) is replaced by a hydroxyl group (OH) from the water, resulting in an alcohol.
2. **Determine the stereochemistry:**
- When applicable, use wedge and dash bonds to show the 3D placement of substituents around any asymmetric carbon atoms.
### Example of a Major Product (Elimination Pathway):
- Form an alkene by removing H and Br:
```
C=C
```
- Incorporate stereochemistry if the product has asymmetric centers.
### Example of a Major Product (Substitution Pathway):
- Form an alcohol by replacing Br with OH:
```
OH
\
C
/ \
C C
```
- Include appropriate 3D bonds (wedge, dash) for any chiral centers.
Draw the structure within the provided frame and ensure the stereochemistry is clear where necessary.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Please complete the following reaction and draw a step wise mechanism. A1C13arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when attached compound is treated with HNO3 and H2SO4. State whether the reaction occurs faster or slower than a similar reaction with benzene.arrow_forward10. Draw a complete curved arrow mechanism for the following reaction sequence. CC13H + KOt-Bu +arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of the organic product of the following transformation. cat. ACOH NHarrow_forwardExplain why benzaldehyde is less reactive than cyclohexanecarbaldehyde towards nucleophilic attack.arrow_forwardHello, I do not understand these questions and I am stuck. May I get help please?? Question: Draw the curved arrow mechanism for the following reactionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY