
Concept explainers
A certain ideal gas (unknown) inside a close piston-cylinder assembly undergoes a set of processes
that composed of Isothermal expansion from State point 1 to state point 2, Isometric heat rejection
from state point 2 to state point 3, and Isentropic compression from state point 3 back to the initial
condition. If the maximum pressure is 3000kPa and maximum and minimum volume is 200cm3
and
50cm3
, analyze the problem and perform the following:
a. Draw and label the graph of this set of processes in the P-V and T-S diagram showing the state
point numbers and energy directions.
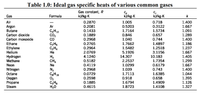
b. From the known ideal gases as shown in Table 1.0, select the best suited ideal gas to attain the
processes stated if the lowest pressure is limited to 629.8kPa. Assume a constant specific heat.
c. For the selected ideal gas from b, compute the work of compression (kJ/kg), work of expansion
(kJ/kg), and heat rejected (kJ/kg)
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- 2.1 A well-insulated, frictionless piston-cylinder assembly is connected by a valve to an air supply line at 8 bar, as shown in the figure. Initially, the air inside the cylinder is at 1 bar and 300°K and the piston is located 0.5 m above the bottom of the cylinder. Atmospheric pressure is 1 bar and the diameter of the piston face is 0.3 m. The valve is opened and air is admitted slowly until the volume of air inside the cylinder has doubled. Calculate a) the work done in kJ, and b) the final mass in kg of the air inside the cylinder for a supply temperature of 300°K. Air supplv linearrow_forwardHeat Transfer question In order to cool down a hot steel sphere (its diameter is 5 cm), CO2 gas is blown over it through a pipe with a diameter of 10 cm. The CO2 gas is kept at atmospheric pressure while moving through a smooth pipe at a speed of 6 m/sec. The gas temperature entering the pipe is 300K and exiting the pipe is 340 K. The pipe temperature at the entrance is 350K and at the exit is 550K. The sphere is located just about the pipe exit. Find the convective heat transfer coefficient of the gas moving in the pipe, the heat transfer rate at the pipe and the pipe length. What is the surface temperature of the sphere if the heat transfer rate between the sphere and the gas is 7W and its surface temperature is higher than the gas?arrow_forwardd²u d²u u(x,t) is solution to steady state 2-D heat equation, + dx² ду2 -=0,with following parameters for numerical approximation: u = u(0,0), u(0,y)=0, u(1,y)=y(1-y), 0arrow_forward
- An electrically heated process is known to exhibit second-order dynamics with the following parameter val-ues: K = 3 °C/kW, T = 3 min,~ = 0.7. If the process initially is at steady state at 70 oc with heater input of 20 kW and Exercises 89the heater input is suddenly changed to 26 kW and heldthere,(a) What will be the expression for the process temperatureas a function of time?(b) What will be the maximum temperature observed?When will it occur?arrow_forwardBmbxarrow_forward9arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





