
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
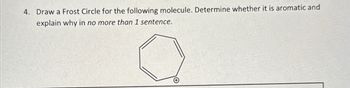
Transcribed Image Text:4. Draw a Frost Circle for the following molecule. Determine whether it is aromatic and
explain why in no more than 1 sentence.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hello I am stuck on this question, can I get help please? A CLEAR explanation with Drawings and the correct answer would be helpful. Thank you!arrow_forwardCircle the hydrogens to show where the hydrogens are and also what is the IHD of this molecule Narrow_forwardAromaticity and Properties Identify the properties that describe aromatic compounds. Aromatic Answer Bank planar all single bonds flexible rigid twisted alternating double and single bonds electrons fully delocalized in a ring all bond lengths between double and single bond lengths all double bonds reactive unpaired electrons very unstable very stablearrow_forward
- Molecule A Molecule B Molecule A Molecule C Molecule D H₂C: Molecule C Which of the compounds shown is aromatic? CH₂ Molecule B Molecule Darrow_forwardWhich one of the following statements from Chapter 8 and 18 is FALSE? O For a compound to be classified as aromatic, it must have an odd number of pairs of r-electrons and must be fully conjugated, cyclic and planar. O Inclusion of heteroatoms as part of the conjugated ring system renders the molecule to be considered non-aromatic. O Benzene is a six-membered ring where the r-electrons are equally shared across all six carbons in the ring and thus it possesses 36 kcal/mol of resonance stabilization energy. O All EAS reactions follow the same three mechanistic steps: (1) generate the electrophile, (2) capture the electrophile to give a carbocation intermediate, and (3) loss of a proton to regain aromaticity.arrow_forwardDraw both resonance structures of the anion formed by the reaction of the most acidic C-H bond of the compound below with base. • Include all valence lone pairs in your answer. . For structures having different hydrogens of comparable acidity, assume that the reaction occurs at the less-substituted carbon. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate resonance structures using the symbol from the drop-down menu. 0- O Bi % 5 T G ▾ 99-85 A 6 SCH₂CH3 ChemDoodleⓇ Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support Y H F6 On [F & 7 O U J F7 * 8 PrtScn | K Home 9 83°F Sunny O L A End 0 F10 P IN Previous Next> C 4x PgUp F11 J Save and Exit 9:38 AM 7/18/2022 PgDn + = F12 80arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forwardHow many H-types do each of the following compounds have and label them. Circle the one that expected to be the most downfield.arrow_forwardDraw both resonance structures of the anion formed by the reaction of the most acidic C-H bond of the compound below with base. a Include all valence lone pairs in your answer. . For structures having different hydrogens of comparable acidity, assume that the reaction occurs at the less-substituted carbon • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate resonance structures using the symbol from the drop-down menu. . O CParrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY