
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:$
4
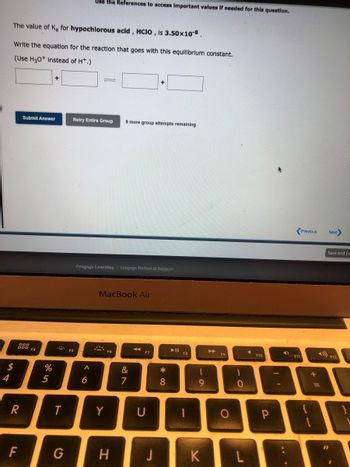
The value of K, for hypochlorous acid, HCIO, is 3.50x10-8.
Write the equation for the reaction that goes with this equilibrium constant.
(Use H3O+ instead of H*.)
000
000 F4
R
F
Submit Answer
%
+
5
T
G
FS
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining
A
Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support
6
MacBook Air
Y
F6
H
87
&
+
F7
U
*
8
F8
9
K
>>
F9
O
0
F10
P
F11
Previous
+
Next>
Save and Ex
F12
11
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Most naturally occurring acids are weak acids. Lactic acid is one example. CH3CH(OH)CO2H(s)+H2O(l)H3O+(aq)+CH3CH(OH)CO2(aq) If you place some lactic acid in water, it will ionize to a small extent, and an equilibrium will be established. Suggest some experiments to prow that this is a weak acid and that the establishment of equilibrium is a reversible process.arrow_forwardFor a chemical reaction to take place, some or all chemical bonds in the reactants must break, and new chemical bonds must form among the participating atoms to create the products. Write a simple chemical equation of your own choice, and list the bonds that must be broken and the bonds that must form for the reaction to lake place.arrow_forwardWhen a mixture of hydrogen and bromine is maintained at normal atmospheric pressure and heated above 200. °C in a closed container, the hydrogen and bromine react to form hydrogen bromide and a gas-phase equilibrium is established. Write a balanced chemical equation for the equilibrium reaction. Use bond enthalpies from Table 6.2 ( Sec. 6-6b) to estimate the enthalpy change for the reaction. Based on your answers to parts (a) and (b), which is more important in determining the position of this equilibrium, the entropy effect or the energy effect? In which direction will the equilibrium shift as the temperature increases above 200. °C? Explain. Suppose that the pressure were increased to triple its initial value. In which direction would the equilibrium shift? Why is the equilibrium not established at room temperature?arrow_forward
- Nitrogen and hydrogen are placed in a high temperature reaction vessel to form ammonia according to the equation Irthe equilibrium.concentration of N. Hy and NHg were each 2.0 M, the value of Ke would be 0:05 O-0.25 2.0 O:40arrow_forwardPlease help answer these questions 30 A solution of H2504(ag) (sulfuric acid, a weak acid) was prepared with 10.75g of H2SO4() added to 950.0 mL of water. Determine/calculate and report the following components in the text box below: a) Write out all of the reactions present in this solution (phases may be omitted; write any charges in brackets formatting tools are unavailable; use any arrow style if the equilibrium arrow is unavailable) b) Report the concentration (in mol/L) of H2SO4(aq) at equilibrium. c) Determine the pH of this solution.arrow_forwardQuestion is attached.arrow_forward
- Part3: Based on your ICE table and equilibrium expression Kb, determine the initial moles of NaClO added to this solution.arrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. In an aqueous solution of a weak acid, HA, the assumption is often made that [HA]equilibrium = [HA]nitial: This approximation is reasonable if the initial concentration of the acid is sufficiently large compared to Ka. What multiple of K, must the initial concentration of a weak acid exceed, for the initial concentration and the equilibrium concentration to be within 9.98 percent of each other?arrow_forwardCalculate the Ka from the following data. + 2 H₂O 2 H3O+ H₂S 1.000 M 0 start: equil: 0.9923 M 0.0154 M 0.0077 M The amount of H₂S that was converted into product is The stoichiometry tells us that 1 mol H₂S will give us mol of H30+1 M H₂S will give Thus, M H30+1 [ ][ Ka = [ ] x [ Ka the concentration of [H3O+¹] is squared because its coefficient is 2 a. acetic b. hydrochloric c. phosphoric d. Al+3 g. HF (aq) h. CaCO3(s) i. OH-1 k. SO4² -1 n. HPO4² 0. H₂PO4¹ p. CO3-² r. H₂S u. H₂O(liq) aa. 0.9923 hh. 1.84 x 10-6 v. H₂CO3 W. PO4³ bb. 0.0077 CC. 3 y. C₂H30₂-1 ee. 1 kk. 0.05656 ii. 0.01250 = 5 [] j. H30+1 q. HCO3-1 x. HC₂H3O2 dd. 2 jj. 0.22100 + S-² 0 0.0077 M 1² 1² = e. CO₂ M S-² and 1. Mg+2 S. HS-1 M mol of S-² and ff. 0.0154 f. CaF2(aq) m. Cl-1 t. S-² z. 1 x 10-14 gg. 3.95 x 10-3arrow_forward
- Kinetics and Equilibrium Calculating an equilibrium constant from a heterogeneous equilibrium... Try Again Try again... Bis 2/5 Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations. Fluoride anion and hydronium cation react to form hydrofluoric acid and water, like this: F (aq)+H3O (aq)→HF (aq) + H2O(l) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 9.9 L reaction vessel containing an aqueous solution of fluoride anion, hydronium cation, hydrofluoric acid, and water at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount F 0.146 g H₂O 0.364 g HF 4.96 g 892. g H₂O Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K 8.4 x 10 Carrow_forwardConfusing please help?arrow_forward1. H;Og) 2 H;SO41) + At equilibrium [S0;] = 0.400M [H;O] = 0.480M [H;SO4] = 0.600M Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:9781559539418
Author:Angelica Stacy
Publisher:MAC HIGHER

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning