
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
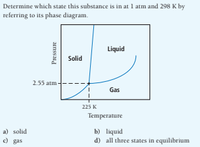
Transcribed Image Text:Determine which state this substance is in at 1 atm and 298 K by
referring to its phase diagram.
Liquid
Solid
2.55 atm -
Gas
225 K
Temperature
b) liquid
d) all three states in equilibrium
a) solid
e) gas
Pressure
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the pressure at which the melting point of X is - 173. °C. 1.6- solid liquid 0.8- gas 100 200 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 0.1 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm pressure (atm)arrow_forwardAn unknown liquid has a heat of vaporization of 9.14 kJ/mole. If the vapor pressure of this liquid at -174 degrees C is 92 torr, what is the normal boiling point of this liquid in degrees C? HINT: Normal boiling point occurs when the vapor pressure of the liquid is the same as atmospheric pressure (1 atm or 760 mm Hg).arrow_forwardStudy the following phase diagram of Substance X. pressure (atm) A F B -E- H temperature (K) D C Which line must the temperature and pressure have crossed if a solid sample of X is observed to melt? If a sample of pure X is observed to be a mixture of solid, liquid and gas, which point marks the temperature and pressure? A U O O C O O O O E G A E O O O O B F H B F Harrow_forward
- Answer the following questions concerning vapor pressure. a) Why doesn't a change in the surface area of a liquid cause a change in the equilibrium vapor pressure? b) What effect does increasing the temperature have on the equilibrium vapor pressure of a liquid? Explain!arrow_forwardWhich statement is correct about the boiling? select the correct answer. O a. a dynamic equilibrium exists between the liquid and vapor phase. O b. the molecular bonds in the liquid are broken rapidly. O c. the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the external pressure above the liquid surface. O d. the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the pressure exerted by its vapor phase. O e. the vapor pressure of the liquid is less than the external pressure above the liquid surface. A Moving to another question will save this response. 234 44,461 23 APR 13 étvarrow_forwardREFER TO IMAGEarrow_forward
- d• Using the phase diagram to the right, select all of the statements that are false. f Te Temperature (not to scale) Point G is the Critical Point. The substance is a supercritical fluid at Point F Decreasing the pressure of the substance at constant Temperature from point A, will result in vaporization Cooling the substance at Point F will induce condensation There is an equilibrium in the gaseous and liquid states at Point E. Increasing the temperature at constant pressure from Point A will results in two phase changes in the substance. Pressure (not to scale)arrow_forwardAn unknown liquid has a heat of vaporization of 9.40 kJ/mole. If the vapor pressure of this liquid at -193 degrees C is 111 torr, what is the normal boiling point of this liquid in degrees C? HINT: Normal boiling point occurs when the vapor pressure of the liquid is the same as atmospheric pressure (1 atm or 760 mm Hg).arrow_forwardREFER TO IMAGEarrow_forward
- In what phase is CO₂ at 72 atm and 0 °C? 2 liquid gas solid Starting from the same point, 72 atm and 0 °C, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? O melting O freezing O deposition sublimation O vaporization condensation Pressure (atm) 5.11 1.0 solid -78.5 -56.4 liquid Temperature (°C) gas 1 31.1arrow_forwardBelow is the phase diagram for iodine. If you start with a sample of iodine at 150°C and 1.0 atm and you increase the temperature, what phase change will you observe? a. boiling b. melting c. sublimation d. melting, then boilingarrow_forward5.What happens when the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the external pressure? A) An equilibrium exists between the liquid and the solid state. B) The liquid freezes. C) The intermolecular forces become stronger in the liquid. D) The liquid boils. E) Dispersion forces become weaker in the liquid.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY