
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
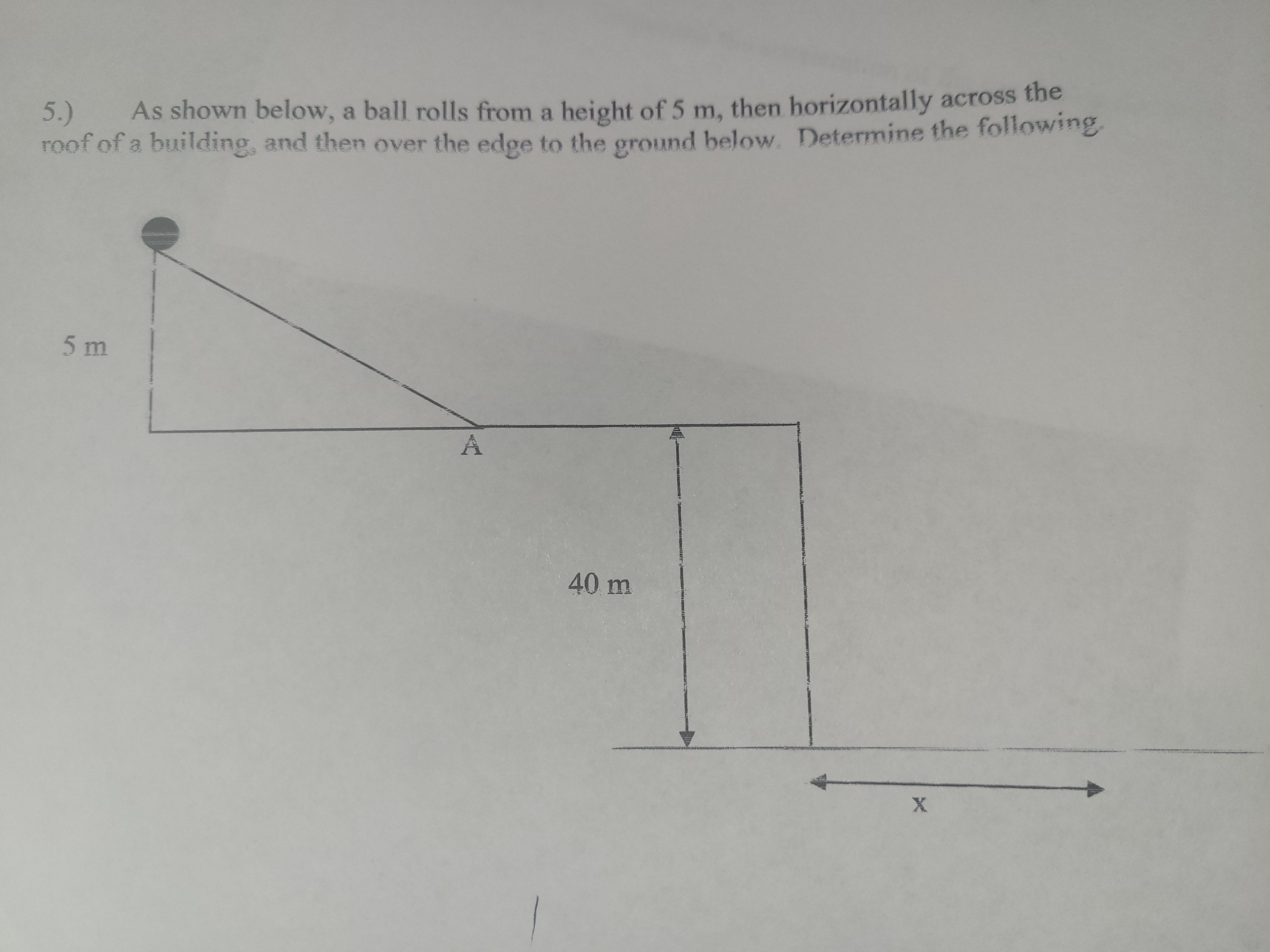
Determine the velocity of the ball at point A
Determine how far the ball will land from the edge of the table (x)
If the ball lands on a small bug, which will have the greater force: the bug or the ball? Explain fully
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A vehicle collides with an immoveable concrete embankment. Estimate the number of 'gs' the occupant experiences when the front end of the vehicle collapses 0.93 m when bringing the vehicle to rest from a speed of 85 km/hr. Assume uniform (constant) deceleration. Ref. 2.11 Express algebraic solution in terms of ds, vo and g. As 0.93 VO 85arrow_forwardThe door is made in one piece, the ends of which move along the horizontal guides and vertical. If the door is in the open position, θ = 0◦ , and then released, determine the speed (this is already solved Vinpact = 31.9 ft / s) at the that its outer A hits the stop C. Suppose the door is a 180-lb thin plate that has a width of 10 ft. Determine the impulsive force with which point A hits point C in an instant of 5 thousandths of a second.arrow_forwardA student on the ground fires a pebble from a catapult with a velocity of 30 m/s at an angle of 30° above the horizontal. If the pebble’s flight is interrupted by a vertical wall 12 m away from the student, at what height above the ground does the pebble hit the wall?arrow_forward
- A particle P of mass m = 3 kg arrives at point O with a horizontal velocity vo and starts rolling down a circle with radius R = 3.5 m. The particle is attached to the point O by means of a linear spring of stiffness k = 60 N/m that is unstretched when the particle is at O. Assume that during the motion of P along the circle, the spring follows the circle. Let N = {î, îy} be a fixed reference frame as shown in the figure and let B = {b, by} be a reference frame attached to P so that ba is tangent to the circular path and by is perpendicular to the circular path. For convenience, take g = 10 m/s² in this question. ny nx IParrow_forwardQ3. A body is released from a great height falls freely towards earth. Another body is released from the same height exactly two second later. Find the separation between both bodies after 3 second of the release of the second body.arrow_forwardcan you pls also draw a picture/representation of the scenario described? Thanks so much!arrow_forward
- A marksman fires a practice round from A toward a target B. If the target diameter is 180 mm and the target center is at the same altitude as the end of the rifle barrel, determine the range of "shallow" launch angles for which the round will strike the target. Neglect aerodynamic drag and assume that the round is directed along the vertical centerline of the target. (Note: The word "shallow" indicates a low-flying trajectory for the round.) A 950 m/s Answers: i 0.393 0 1270 m °≤e≤ i 0.402 B Oarrow_forwardplease answer the question below and include explination. many thanksarrow_forwardA projectile is shot directly away from Earth's surface. Neglect the rotation of the Earth. What multiple of Earth's radius RE gives the radial distance (from the Earth's center) the projectile reaches if (a) its initial speed is 0.325 of the escape speed from Earth and (b) its initial kinetic energy is 0.325 of the kinetic energy required to escape Earth? (Give your answers as unitless numbers.) (c) What is the least initial mechanical energy required at launch if the projectile is to escape Earth? (a) Number i (b) Number i (c) Number i Units Units Units ✪ îarrow_forward
- A marksman fires a practice round from A toward a target B. If the target diameter is 160 mm and the target center is at the same altitude as the end of the rifle barrel, determine the range of "shallow" launch angles for which the round will strike the target. Neglect aerodynamic drag and assume that the round is directed along the vertical centerline of the target. (Note: The word "shallow" indicates a low-flying trajectory for the round.) Answers: A i 950 m/s 0 1270 m °≤0≤ i Barrow_forwardA marksman fires a practice round from A toward a target B. If the target diameter is 170 mm and the target center is at the same altitude as the end of the rifle barrel, determine the range of "shallow" launch angles for which the round will strike the target. Neglect aerodynamic drag and assume that the round is directed along the vertical centerline of the target. (Note: The word "shallow" indicates a low-flying trajectory for the round.) A Answers: i 890 m/s 0.5425 0 1540 m °≤0s i 0.5494 Barrow_forward2. Now consider the pulley problem shown below. In this problem, both blocks have mass m m m (a) At the instant shown, the block on the horizontal surface is moving to the right with speed v. At this instant, what is the velocity of the other block? (b) What is the acceleration of the block on the right?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY