
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Civil engineering Resultant of general coplanar forces
Q- Determine the resultant of the four forces acting on a plate shown in given figure, analytically
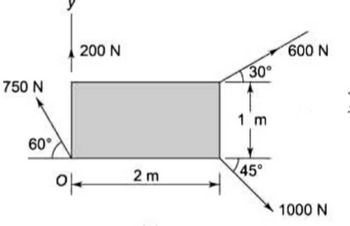
Transcribed Image Text:750 N
60°
200 N
아
2 m
30°
1m
45°
600 N
1000 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mechanics of Materialsarrow_forwardThe equation of motion of GVUF differs from the differential equation of GVF by one essential term. This term isarrow_forwardA uniform beam of weight Wis supported by the two rods, the lower ends of which are at the same level just before the beam is supported, as shown in figure. The ratio of the areas Aluminium (E = 70 GPa) 2 m 1.5 m W 3 m 3m Aaluminium Asteel Steel (E = 200 GPa) 0.5 m of the rods so that the beam will be horizontal after it is attached to the rods isarrow_forward
- This is a much needed Problem, Kindly solve it carefully Include all the steps (diagram, formula)arrow_forwardThere is no force on a beam, but the beam is subjected to a very large temperature difference above and below. As shown in the figure below, try to calculate the vertical displacement of the midpoint of the beam, assuming that the temperature coefficient of the entire beam is a = 11.7×10^-6 °F. Tip: See Mechanics of Materials for Beam Deformation Geometryarrow_forwardQUESTION 3 UWE The figure below shows the cross section of unsymmetric Bristol I-beam. The I-beam experiences a maximum M=4 kNm sagging bending moment. And the beam is pulled apart with end-loading forces of 20 kN. Calculate the maximum tensile stress the beam experiences. (State your answer to the nearest whole number Mega-Pascals.) 120 mm 60 mm I 40 mm 30 mm 220 mm 30 mmarrow_forward
- The channel shape cross-section and the rectangular cross-section shown in the Figure Q4 are made of materials with elastic-perfectly plastic behaviour. The yield stress of the material used for the channel shape cross-section is y=405 MPa, whereas that used for the rectangular cross- section is 0.850y. Compute the thickness of the web, t, of the channel shape section if the two cross sections have identical plastic bending moment about the z-axis. In Figure 4, h= 74 mm, b=52 mm, a-8 mm, H=74 mm, d= 52 mm Z b h Figure Q4 Z d Harrow_forwardProvide solution and explain also with stepsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning