
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
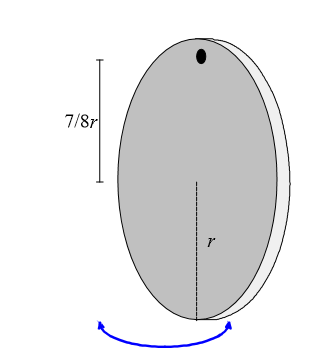
A coin having a mass of m = 12 g, a thickness of h = 0.17 cm, and a radius of r = 1.5 cm has a small hole drilled through it so that it can be suspended from a thin wire and worn as an earring or pendant. The hole is at a distance of 7/8 r from the center of the coin as shown above. When suspended from this hole, the coin is a physical pendulum that swings back and forth with this hole as its axis of rotation. Assuming that the hole does not appreciably change the center of mass of the coin, determine the period of this physical pendulum.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 500 mm 10.0 cm (hrw8c15p43) A pendulum consists of a uniform disk with radius 10 cm and mass 650 g attached to a uniform rod with length 500 mm and mass 235 g (see the figure). Calculate the rotational inertia of the pendulum about the pivot. Submit Answer Tries 0/5 What is the distance between the pivot and the center of mass of the pendulum? ( m) Submit Answer Tries 0/5 Calculate the period of oscillation. Submit Answer Tries 0/5arrow_forwardA spring with spring constant k and equilibrium length zero is attached tothe top of a frictionless hoop of radius R. The spring is stretched and connected to a bead of mass m at the bottom of the hoop. At t = 0 the bead is given an initial speed v0 and the bead moves up the hoop. Find the speed of the bead as a function of position on hoop v(θ).arrow_forwardA small ball is attached to one end of a spring that has an unstrained length of 0.230 m. The spring is held by the other end, and the ball is whirled around in a horizontal circle at a speed of 4.21 m/s. The spring remains nearly parallel to the ground during the motion and is observed to stretch by 0.0198 m. By how much would the spring stretch if it were attached to the ceiling and the ball allowed to hang straight down, motionless? Number i Units kgarrow_forward
- A 0.120kg, 50 cm long uniform bar has small 0.055 mass glued to its left end and small 0.110 kg mass glued to the other end. The two small masses can be treated as point masses. You want to balanced this system horizontally on a fulcrum placed just under its center of gravity. How far from the left end should the fulcrum be placed?arrow_forwardA 3.72 kg iron box is suspended from a spring with a spring constant of k=18 N/m. The mass is pulled 0.35 m downward from its equilibrium position and allowed to oscillate. a) what will the angular velocity be for this iron box? b) with what period will the iron box oscillate?arrow_forwardA thin rod of mass 0.800 kg and length 0.700 m has a fixed pivot at one end. The rod is held horizontally and released from rest. The rod swings downward and back up again like a pendulum. The rotational inertia of a thin rod rotating about one end is I=13ML2. Disregard friction and air resistance.(a) Determine the initial angular acceleration of the rod just as it is released.(b) Determine the maximum angular speed of the rod as it swings back and forth.arrow_forward
- The balance wheel of a watch oscillates with angular amplitude 1.0n rad and period 0.34 s. Find (a) the maximum angular speed of the wheel, (b) the angular speed of the wheel at displacement 1.0n/2 rad, and (c) the magnitude of the angular acceleration at displacement 1.0n/4 rad. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Unitsarrow_forwardA small ball is attached to one end of a spring that has an unstrained length of 0.222 m. The spring is held by the other end, and the ball is whirled around in a horizontal circle at a speed of 4.52 m/s. The spring remains nearly parallel to the ground during the motion and is observed to stretch by 0.0102 m. By how much would the spring stretch if it were attached to the ceiling and the ball allowed to hang straight down, motionless? Number i eTextbook and Media Units +arrow_forwardEngineers are designing a system by which a falling mass m imparts kinetic energy to a rotating uniform drum to which it is attached by thin, very light wire wrapped around the rim of the drum (the figure (Figure 1)). There is no appreciable friction in the axle of the drum, and everything starts from rest. This system is being tested on earth, but it is to be used on Mars, where the acceleration due to gravity is 3.71 m/s2. In the earth tests, when m is set to 13.0 kg and allowed to fall through 5.00 m, it gives 300.0 J of kinetic energy to the drum. If the system is operated on Mars, through what distance would the 13.0-kg mass have to fall to give the same amount of kinetic energy to the drum? How fast would the 13.0-kg mass be moving on Mars just as the drum gained 300.0 J of kinetic energy?arrow_forward
- A hollow cylinder of mass M1 and radius R1 rolls without slipping on the inside surface of another hollow cylinder of mass M2 and radius R2. Assume R1<<RZ. Both axes are horizontal, and the larger cylinder is free to rotate about its axis What is the angular velocity or frequency of small oscillationsarrow_forwardA uniform bar has a length of 1m, and a mass of 5kg. If a 10 kg mass is attached to one end of the bar (at x=0), and a 30 kg mass is attached to the other end (at x=1m). The center of mass is closest to which point? x=0m x=0.3 m x=0.33 m x=0.5m x=0.67 m x=0.70 m x=1.00 marrow_forwardA compound pendulum pivoted at O consists of a hollow-disk of radius R= 40 + 2xds cm with a hole of radius 20 cm and a thin rod (1.2 kg, total length = 80 cm) attached on the top. Given the mass density of the hollow disk is 4 kg/m. 60 cm 20 cm 30 cm 40 cm R = 40 + 2xds cm (a) Find the rotational inertia I of the compound pendulum at an axis passing through the plane of paper and the pivot O. (b) Find the distance hem of the center of mass of the compound pendulum from pivot O. (c) Find the angular frequency e. (d) Find the period T.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON