
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
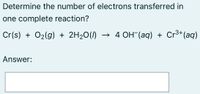
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the number of electrons transferred in
one complete reaction?
Cr(s) + O2(g) + 2H20(1)
→ 4 OH (aq) + Cr³+(aq)
Answer:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6 a b U d [Tutorial: Titration stoichiometry] This question will walk you through the steps of calculating the volume of titrant required to reach the endpoint based on the volume and concentration of analyte. Consider the standardization of NaOH by titration with C,H,O, according to the following chemical reaction: 3 NaOH(aq) + C,H,O,(aq) = Na,C,H,O,(aq) + 3 H₂O(l) Step 1: Evaluate the question. How many moles of aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) will react to completely neutralize one mole of aqueous citric acid (C,H,O,)? Which equation will be most helpful for solving this problem? Calculate the volume in mL of a 0.200 M NaOH solution needed to neutralize 345 mL of 0.033 MC,H,O, standard solution. Based on the fact that NaOH is a strong base and C,H,O, is a weak acid, how would you describe the pH of the solution at the endpoint, where moles of base = 3 times the moles of acid?arrow_forwardWhich of the following reactions is a combination reaction? Mg (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → MgSO4 (aq) + Cu (s) Na2SO4 (aq) + MgCl2 (aq) → MgSO4 (aq) + 2 NaCl (aq) 2 H2O (g) → 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) Na2CO3 (aq) + MgCl2 (aq) → MgCO3 (s) + 2 NaCl (aq) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2 H2O (g)arrow_forwardIn the following redox reaction, what are the reducing agent, and the oxidizing agent, respectively? Cl2 (aq) + 2 Fe2+ (aq) → 2 Cl‾ (aq) + 2 Fe3+ (aq)arrow_forward
- -COH (acid) &H (aldehyde) Ar-H (aromatic) (C=C-H, vinylic OH (alcohol or phenol) X-C-H (X= halogen or oxygen) Ar-C-H (benzylic) CH 10.0 (C-C-C-H, allylic H on saturated C, base position 9.0 8.0 44 7.0 4.3 30 20 10 0 6.0 In this ¹H NMR spectrum the blue floating peaks are enlargements of the peaks to their right. 4.2 ppm Hz 5.0 1 4.0 10-13 9-10 3.0 6-8.5 4.6-5.7) 1-5 3-4.5 2-2.7 2-2.7 1.6-1.9) .8-1.6 l 1.75 1.70 1.65 2.0 1.0 0.0 Which compound is most likely to have given rise to this spectrum?arrow_forwardIn the following chemical reaction, which species is the reducing agent? 2 10, (aq) + 12 H (aq) + 10 Ag(s) + 10 CI (aq)→ 10 ABCI(s) + 1,(s) + 6H,O(1) O Ag O 105 O It is not a redox reaction.arrow_forwardFor each chemical reaction listed in the table below, decide whether the highlighted atom is being oxidized or reduced. reaction 2 Cro¯(aq) +2 H₂O+ (aq) → Cr₂O²˜¯(aq)+3 H₂O(1) 2 H2(g)+O2(g) → 2 H₂O(g) NH3(aq)+2 O2(g) → HNO3(aq)+H2O(l) N2(g)+3 H₂(g) → 2 NH3(g) highlighted atom is being... oxidized reduced neither oxidized nor reducedarrow_forward
- What is the net ionic equation for the reaction between CoCl2 and LIOH? O Co2+(aq) + 2OH (aq) → Co(OH)2(s) O Co3+(aq) + 30H (aq)→ Co(OH)3(s) O Lit(aq) + Cl(aq) → LICI(s)arrow_forwardn the following reaction, when the equation is correctly balanced, what is the correct coefficient for sodium chloride? Pb(NO 3) 2( aq) + NaCl( aq) → PbCl 2 ( s) + NaNO 3( aq) 1 2 3 4 5arrow_forwardEQUATION CLASSIFICATIONS: combustion, synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement Mass in Chemical Reactions Types of Chemical Reactions: REDOX Analysis Assign Oxidation States To All Elements: 00 MgO (s) Mg(s) + O₂(g) Cuo + H₂ (g) 0.0 Cu (s) + H₂O (1) 00 00 Fe₂O3 (s) + 3 CO (g) → 3 CO₂ (g) + 2 Fe (s) 000 AgNO3(aq) + Li (s) ➜ LINO3(aq) + Ag (s) Classify The Equation Identify The OXIDIZED Element HALF REACTION: HALF REACTION: HALF REACTION: HALF REACTION: Identify The REDUCED Element HALF REACTION: HALF REACTION: HALF REACTION: HALF REACTION: half-reactions oxidation and reduction reactions that, taken together, account for all electron movement Oxidation Reduction C Overall Identify The OXIDIZING Agent Pb Pb +20 Cu Identify The REDUCING Agentarrow_forward
- 5. Identify each of the following reactions as either synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion, or neutralization 2Li(s) + H₂O(1)→ Li₂O(s) + H2(g) SO2(g) + H₂O → H₂SO3(aq) 02|| AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na₂CO3(aq) + H₂CO3(aq) 2H₂O C3H8(g) + 502(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H₂O(1) Mg(OH)2(aq) → MgO(s) + H₂O(1)arrow_forward5. Copper reacts with nitric acid according to the reaction 3 Cu (s) + 8 HNO3 (aq) > 3 Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 NO + 4 H20 m If a piece of copper weighing 3.0454 g was dissolved in a sufficient amount of nitric acid and the resulting solution was diluted to 50.0 mL with deionized water. What is the molarity of the resulting Cu(NO3)2 solution? 6. What is the concentration of a KMNO4 solution if it required 22.35 ml to react with O.5170 g of oxalic acid? 5 H2C204 (aq) + 2 KMNO4 (aq) + 3 H2SO4 (aq) → 10 CO2 ()+2 MNSO4 (ag) + KSO& (ac) +8 H;O marrow_forwardIdentify the driving force for the chemical reaction: Pb(NO3)2(ag) + 2N2OH (ag) → Pb(OH)2(s) + 2NaNO3 3(aq) O Formation of a precipitate. O Formation of a water neutralization of an acid and base reduction and oxidation. O There is no driving force.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY