
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
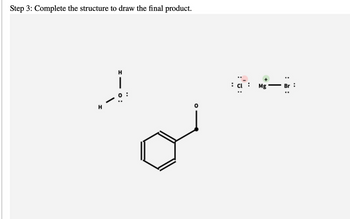
Transcribed Image Text:Step 3: Complete the structure to draw the final product.
H
Mg
Br
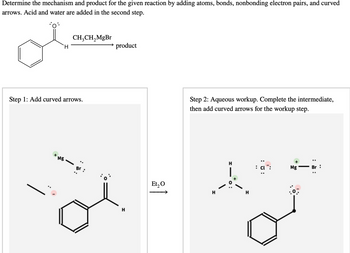
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the mechanism and product for the given reaction by adding atoms, bonds, nonbonding electron pairs, and curved
arrows. Acid and water are added in the second step.
CH₂CH₂MgBr
2
Step 1: Add curved arrows.
* MB
Br
→ product
Et₂ O
Step 2: Aqueous workup. Complete the intermediate,
then add curved arrows for the workup step.
H
: CLT:
Mg
Br
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How many steps in the mechanism of this reaction?arrow_forwardThe following reaction Reactants⟶Product has a positive ΔG value. Select all the true statements from the list below Group of answer choices The reaction is exergonic The reaction in endergonic The reaction is favorable The reaction is unfavorable The free energy associated with the product is lower than that of the reactants The free energy associated with the product is higher than that of the reactantsarrow_forwardWhat is the NAME of the Mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward
- You determine the bimolecular rate constant k for a set of SN2 reactions. Based on your understanding of how the nucleophile effects the rate constant for an SN2 reaction, drag and drop the nucleophiles into the correct rows in the table below. Alkyl halide Nucleophile k / L mol-1 s-1 CI 0.011 -CI 0.045 0.074 0.095 -NH2 -NH2 >-NH2 -NH2 -NH2arrow_forward8. Compound (A) rearranges to compound (B) spontaneously. a) Draw the mechanism using curved arrows, that describes how this rearrangement can occur. (Hint: two shifts are required to obtain the product). H Br H₂C Br b) What makes the formation of the previous product spontaneous (ie. why is the product more stable than the reactant)?arrow_forwardHO .OH cat. H2SO4 H₂O cat. H2SO4 Complete both mechanisms above. BRIEFLY explain how the different reaction conditions (in the presence of acid) result in different products being formed. How does equilibrium play a role?arrow_forward
- Draw all of the steps of the mechanism for this reaction. You do not need to show curved arrows for the step involving Mg metal. os Br OCH₂ Mg Et₂0 "MgBr "OCH3arrow_forwardDraw a detailed arrow pushing mechanism for the following reaction. In the rate-determining step unimolecular (SN1) or bimolecular (SN2)arrow_forwardIn an SN2 mechanism, how does it work, what are all of the steps, transition state and all final products?arrow_forward
- Please answer this organic chemistry question: show all three steps and radical mechanism for hydrobromic acid in peroxide reacting with 3-methylene-2-ene. Are there multiple products? Background information just in case needed for the intial question above ? but if not needed just ignore this background information: which of the following compounds will react the quickest? A) Fluorine with a tertiary radical B) chlorine with a tertiary radical C) Bromine with tertiary radical D) chlorine with a primary radical E) bromine with a primary radicalarrow_forwardDraw the mechanism arrows for both propagation steps for the radical addition of HBr to the alkene.arrow_forwardWrite mechanisms for each reactions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY