
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
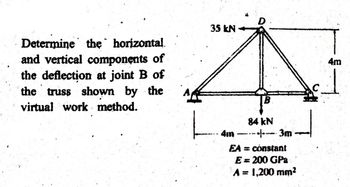
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the horizontal.
and vertical components of
the deflection at joint B of
the truss shown by the
virtual work method.
35 kN
L
4m
D
84 kN
3m
EA = constant
E = 200 GPa
A= 1,200 mm²
4m
1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a simply supported beam, deflection is always zero at supports and maximum at .midspan True O False Oarrow_forwardNEED ASAP PLEASEarrow_forwardDetermine the slope and deflection at point B of the beam shown using the AreaMoment Method. The cross-sectional area of BC is twice the cross-sectional area ofAB. Use E = 200 GPa and I = 600 x 106 mm4arrow_forward
- Solve using Virtual Work Method refer to the truss shown below. The A and B are hinge support.arrow_forwardProb 02: Use method of virtual work and determine the horizontal deflection at C. Assume the members are pin connected at their points. AE is constant 800 Ibs 8 ft 800 Ibs D B 8 ft E -8 ftarrow_forwardUsing either Virtual Method or Castigliano Theorem, compute the slope and deflection at point B of the steel beam. Use E = 200 GPa & I = 60 x 106 mm4. Support C is fixed-supported and A is free-end.arrow_forward
- For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the deflection at point C, (b) the slope at end A.arrow_forwardDetermine static indeterminacy of beamarrow_forwardDetermine the deflection (mm) at midspan of the given beam below. Use virtual work or Castigliano's Theorem. I =46(10^6) mm^4 E = 200 Gpaarrow_forward
- Determine the horizontal and vertical components of deflection at joint B using the work methodvirtual. EA constant. E = 200GPa , A = 1200 mm². Please type answer note write by hend.arrow_forwardDetermine the smallest cross-sectional area A required for the members of the truss shown, so that the horizontal deflection at joint D does not exceed 10 mm. Use Castigliano's Second Theorem for the solution.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning