
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
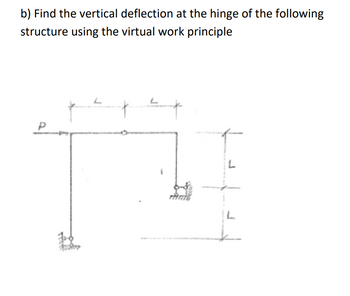
Transcribed Image Text:b) Find the vertical deflection at the hinge of the following
structure using the virtual work principle
L
L
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Solve for the the deflection at Midspan. Consider EI to be constant and begin x from A.arrow_forwardCompute the vertical and horizontal component of the deflection at C of the frame in the following figure using the method of virtual force. The direction of uniformly distributed loading is "→". Take E=200GPa, I=240(106)mm4.arrow_forwardProblem 3 Conjugate Beam Method: For the given beam below, answer the questions. El = constant: P M=Pa B a a (a) Draw the conjugate beam (clearly show the supports of the conjugate beam and mark the important values). (b) Determine the slope angle at point B, 0B, of the real beam using the conjugate beam method. Determine the deflection at point B, Ag, of the real beam using the conjugate beam method.arrow_forward
- Using the virtual work method determine slope of the beam at "A". Beam is subjected to a uniformly Distributed Load “W" and a concentrated moment "WL^2" at “A" (Express the results in terms of W, L, and EI) w ikIft=constant)arrow_forwardsketch the deflected structure of this frame (just shape no exact values for how much deflection). This is linear analysis so only looking at the displacement of the nodes. Note that D is a hinge support, E is fixed and C is a rollerarrow_forwardFor the simply supported beam shown, find the slope at A and the maximum deflection. Using moment area method. Neglect the weight of the beam. The moment of inertia of segments AB and CD of the beam is I, and the moment of inetia of segment BC is 2I. L= 4ft, P= 4 kips, E= 30x 10^6 psi, I= 16 in^4arrow_forward
- J.) For the rigid frame shown, calculate the horizontal deflection at point C. Members have the same moment of inertia of 1440 x 10 cm² and E is constant at 210 GPa. 120 kN/m B 120 kN/m A 4m P in KN 3m 5m P=229KN Solve using unit load methodarrow_forwardFind the maximum angle of rotation for the shaft subjected to linearly %3D distributed torque. Tx) = kx,GJ constant. T(x)arrow_forwardRod AB is made of steel (E = 29x106 psi), and rod BC is made of aluminum (E = 10.4x106 psi). If force Q = 10 kips, R =5 kips and P = 5 kips, find the deflections of points B and D. %3D 24 in 10 in- 10 in A B C R D 1 in diameter 3 in diameterarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning